Public libraries and community makerspaces both serve as vital hubs for learning and creativity, but they differ in their primary offerings; libraries provide extensive access to books, digital resources, and quiet study areas, fostering literacy and research skills. In contrast, community makerspaces focus on hands-on experiences with tools, technology, and collaborative projects, nurturing innovation and practical skill development. Each space supports public engagement and knowledge sharing, catering to diverse interests and educational needs within the community.
Table of Comparison
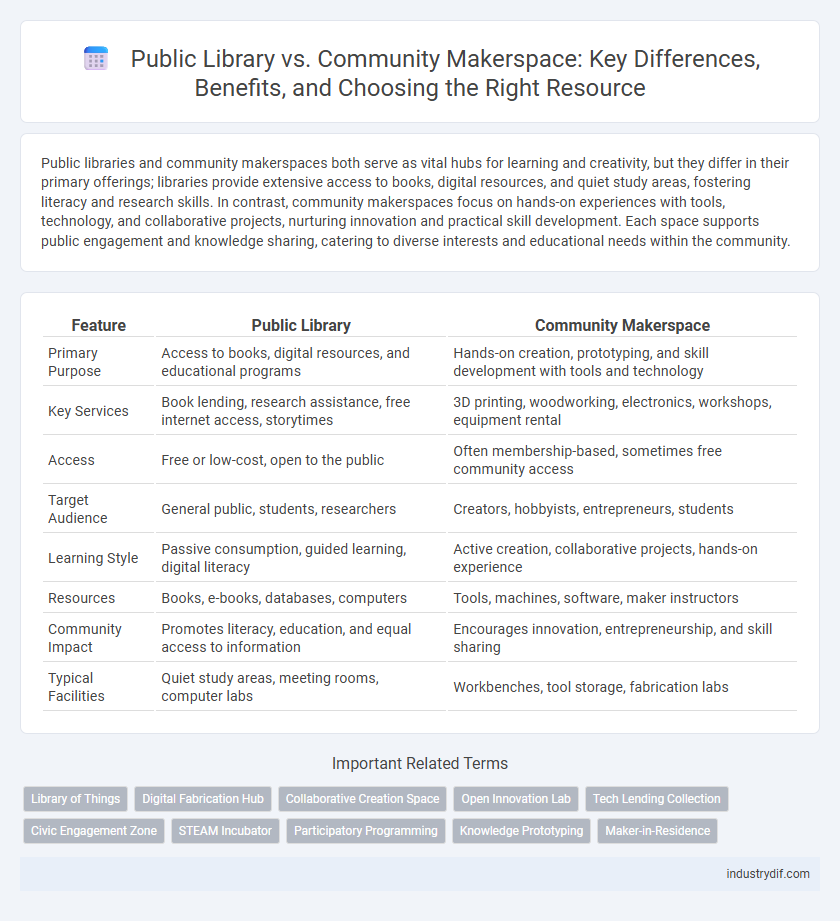
| Feature | Public Library | Community Makerspace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Access to books, digital resources, and educational programs | Hands-on creation, prototyping, and skill development with tools and technology |
| Key Services | Book lending, research assistance, free internet access, storytimes | 3D printing, woodworking, electronics, workshops, equipment rental |
| Access | Free or low-cost, open to the public | Often membership-based, sometimes free community access |
| Target Audience | General public, students, researchers | Creators, hobbyists, entrepreneurs, students |
| Learning Style | Passive consumption, guided learning, digital literacy | Active creation, collaborative projects, hands-on experience |
| Resources | Books, e-books, databases, computers | Tools, machines, software, maker instructors |
| Community Impact | Promotes literacy, education, and equal access to information | Encourages innovation, entrepreneurship, and skill sharing |
| Typical Facilities | Quiet study areas, meeting rooms, computer labs | Workbenches, tool storage, fabrication labs |
Defining Public Libraries and Community Makerspaces
Public libraries are government-funded institutions that provide free access to a vast collection of books, digital media, and educational resources aimed at fostering literacy and lifelong learning. Community makerspaces are collaborative workspaces equipped with tools such as 3D printers, laser cutters, and electronics, designed to support creativity, innovation, and hands-on learning. Both spaces serve the public but differ in their primary focus, with libraries emphasizing information access and makerspaces promoting practical skills and technology development.
Historical Evolution of Public Libraries
Public libraries have evolved from ancient repositories of knowledge to modern centers of digital access and community engagement, reflecting societal shifts in information needs. The historical evolution of public libraries highlights their role in democratizing information, initially serving elite scholars before expanding to support literacy and lifelong learning for all citizens. This progression contrasts with community makerspaces, which emerged more recently to emphasize hands-on creativity, technology, and collaborative innovation within local neighborhoods.
The Rise of Community Makerspaces
Community makerspaces have rapidly gained popularity as dynamic hubs for innovation, creativity, and hands-on learning, providing resources like 3D printers, laser cutters, and electronics kits that traditional public libraries may lack. These spaces foster collaboration among diverse groups, including artists, engineers, and entrepreneurs, driving local economic development and STEM education. The rise of community makerspaces complements public libraries by expanding access to cutting-edge technology and skill-building opportunities, transforming how communities engage with knowledge and creativity.
Core Services: Books vs. Hands-On Creation
Public libraries primarily provide access to books, digital resources, and informational materials supporting literacy and education. Community makerspaces emphasize hands-on creation, offering tools, technology, and collaborative spaces for innovation in areas like 3D printing, woodworking, and electronics. Both serve educational purposes but cater to different user needs: knowledge consumption versus practical skill development.
Technology Access in Public Libraries and Makerspaces
Public libraries provide free, reliable access to computers, high-speed internet, and specialized software, supporting digital literacy and research for diverse populations. Community makerspaces offer hands-on technology like 3D printers, laser cutters, and electronics kits, fostering innovation and practical skills development. Both spaces bridge the digital divide by enabling underserved communities to engage with emerging technologies and collaborative learning.
Educational Roles and Lifelong Learning
Public libraries serve as essential educational hubs by providing access to vast resources, digital literacy programs, and structured learning environments that support all ages in lifelong learning. Community makerspaces complement this role by offering hands-on, experiential learning opportunities in technology, engineering, and creative arts, fostering innovation and practical skills acquisition. Together, these spaces enhance community education by balancing traditional knowledge access with collaborative, skill-based learning.
Community Engagement and Social Impact
Public libraries foster community engagement through accessible resources, educational programs, and inclusive events that encourage lifelong learning and cultural exchange. Community makerspaces drive social impact by providing hands-on opportunities for innovation, skill development, and collaboration, empowering diverse groups to create and solve local challenges. Both institutions serve as vital hubs for strengthening social cohesion, promoting digital literacy, and supporting economic growth within their communities.
Funding and Sustainability Models
Public libraries primarily rely on government funding and grants, ensuring steady financial support for ongoing operations and resource expansion. Community makerspaces often depend on a hybrid model combining membership fees, private sponsorships, and crowdfunding, which can introduce variability in funding but encourages local engagement. Sustainable growth in libraries is driven by long-term public investment, while makerspaces focus on adaptive financial strategies to maintain innovation and accessibility.
Challenges and Opportunities in Modernization
Public libraries face challenges in modernization due to limited funding and the need to integrate digital resources, while community makerspaces struggle with sustaining membership and acquiring high-tech equipment. Both spaces offer unique opportunities: libraries can expand digital literacy programs and provide access to curated knowledge, whereas makerspaces foster hands-on learning, innovation, and collaboration in STEAM fields. Embracing technology partnerships and community engagement enhances the relevance and accessibility of both institutions in the digital age.
Future Trends in Public Knowledge Spaces
Public libraries and community makerspaces are evolving into hybrid knowledge hubs that blend traditional resources with innovative technology access, fostering collaborative learning and creativity. Future trends emphasize digital literacy, 3D printing, virtual reality, and STEAM programming to support diverse community needs and enhance educational outcomes. Integration of smart technologies and data-driven services will personalize user experiences, driving engagement and expanding access to cutting-edge tools in public knowledge spaces.
Related Important Terms
Library of Things
Public libraries are increasingly integrating Library of Things programs, lending tools, technology, and equipment to promote community access and skill development. Community makerspaces emphasize hands-on creation with advanced machinery and collaborative workspaces, while libraries provide curated, low-barrier access to everyday and specialized items to support diverse learning needs.
Digital Fabrication Hub
Public libraries increasingly integrate digital fabrication hubs, offering 3D printers, laser cutters, and CNC machines for accessible community innovation and learning. Community makerspaces complement these services by providing collaborative environments and specialized workshops, fostering hands-on skill development in digital fabrication technologies.
Collaborative Creation Space
Public libraries offer collaborative creation spaces that provide access to resources such as books, digital media, and study areas, fostering knowledge sharing and quiet teamwork. Community makerspaces emphasize hands-on innovation with tools like 3D printers, woodworking equipment, and electronics, encouraging practical skill development and creative collaboration.
Open Innovation Lab
Open Innovation Labs within community makerspaces foster collaborative environments where members experiment with emerging technologies, contrasting with traditional public libraries that prioritize information access and quiet study. These labs accelerate local innovation ecosystems by providing tools like 3D printers, laser cutters, and coding workshops, supporting hands-on learning and entrepreneurship directly in the community.
Tech Lending Collection
Public libraries increasingly integrate tech lending collections, offering items like laptops, tablets, and 3D printers to bridge the digital divide and support diverse learning needs. Community makerspaces complement this by providing hands-on access to advanced tools and collaborative environments, enhancing creativity and practical skills beyond traditional library resources.
Civic Engagement Zone
Public libraries serve as traditional Civic Engagement Zones by providing access to information, educational programs, and community events that foster civic literacy and participation. Community makerspaces complement these efforts by offering hands-on workshops, collaborative projects, and technology access that empower citizens to actively contribute to local innovation and problem-solving initiatives.
STEAM Incubator
Public libraries provide access to extensive educational resources and digital tools supporting STEAM learning, while community makerspaces offer hands-on workshops and specialized equipment fostering innovation and collaboration. A STEAM incubator within these environments accelerates skill development by integrating technology, creativity, and entrepreneurship for diverse learners.
Participatory Programming
Public libraries emphasize participatory programming through diverse literacy workshops and collaborative reading groups designed to engage all age groups, fostering community learning and cultural enrichment. Community makerspaces offer hands-on participatory programming focused on creative technology, such as 3D printing and coding classes, promoting innovation and skill development among local makers and entrepreneurs.
Knowledge Prototyping
Public libraries offer extensive access to curated knowledge resources and expertise, fostering foundational learning and research, while community makerspaces provide hands-on tools and collaborative environments for rapid knowledge prototyping and experiential innovation. The synergy between public libraries' informational infrastructure and makerspaces' creative facilities accelerates iterative design and practical application of ideas within local communities.
Maker-in-Residence
A Maker-in-Residence program in public libraries fosters innovation by providing community members access to expert guidance and advanced tools, bridging educational resources and creative prototyping. Unlike traditional community makerspaces, libraries integrate these residencies with extensive digital archives and learning workshops, enhancing skill development and collaborative projects.
Public Library vs Community Makerspace Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com