Public opinion polling gathers direct responses from people through structured questions, providing quantifiable data on public views about pets. Sentiment analysis examines social media posts and online content to gauge emotions and attitudes toward pets in an unstructured, real-time manner. Combining both methods offers a comprehensive understanding of public sentiment and preferences regarding pet-related issues.
Table of Comparison
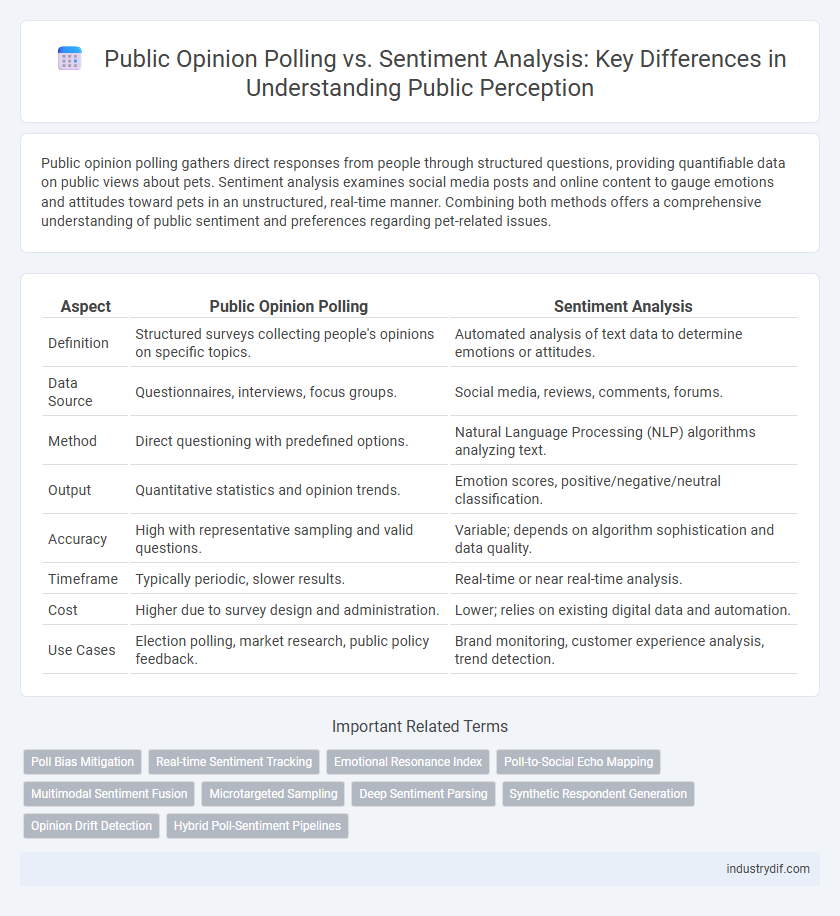
| Aspect | Public Opinion Polling | Sentiment Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured surveys collecting people's opinions on specific topics. | Automated analysis of text data to determine emotions or attitudes. |
| Data Source | Questionnaires, interviews, focus groups. | Social media, reviews, comments, forums. |
| Method | Direct questioning with predefined options. | Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms analyzing text. |
| Output | Quantitative statistics and opinion trends. | Emotion scores, positive/negative/neutral classification. |
| Accuracy | High with representative sampling and valid questions. | Variable; depends on algorithm sophistication and data quality. |
| Timeframe | Typically periodic, slower results. | Real-time or near real-time analysis. |
| Cost | Higher due to survey design and administration. | Lower; relies on existing digital data and automation. |
| Use Cases | Election polling, market research, public policy feedback. | Brand monitoring, customer experience analysis, trend detection. |
Introduction to Public Opinion Polling and Sentiment Analysis
Public opinion polling systematically collects data from a representative sample to quantify attitudes, beliefs, and preferences within a population using structured questionnaires. Sentiment analysis employs natural language processing and machine learning algorithms to interpret and categorize emotions expressed in textual data from social media, reviews, or other digital content. Both methods offer valuable insights but differ in data sources, methodologies, and types of insights they provide for understanding public attitudes.
Defining Public Opinion Polling: Methods and Applications
Public opinion polling involves systematic data collection through structured surveys using random sampling techniques to measure the attitudes, beliefs, and preferences of a target population. Methods include face-to-face interviews, telephone surveys, and online questionnaires, ensuring statistically significant results that guide policy decisions, marketing strategies, and electoral forecasts. Applications extend to political campaigns, market research, and social issue analysis, providing quantitative insights into public sentiment at a given moment.
What is Sentiment Analysis? Key Concepts and Techniques
Sentiment analysis is a computational technique used to identify and extract subjective information from text, enabling the classification of opinions as positive, negative, or neutral. Key concepts include natural language processing (NLP), machine learning algorithms, and lexicon-based approaches that analyze emotions, opinions, and attitudes expressed in data sources like social media, reviews, and surveys. This method provides real-time insights into public sentiment, complementing traditional public opinion polling by capturing nuanced emotional context and the intensity of opinions.
Data Sources: Surveys vs Digital Platforms
Public opinion polling primarily relies on structured surveys conducted through randomized sampling methods, ensuring statistically representative data from targeted demographics. Sentiment analysis gathers unstructured data from digital platforms such as social media, forums, and review websites, capturing real-time emotional and attitudinal trends across diverse user interactions. The contrasting data sources affect the scope, immediacy, and granularity of insights generated, with surveys offering controlled responses and digital platforms providing vast, organic expression patterns.
Accuracy and Reliability: Comparing Methodologies
Public opinion polling relies on structured surveys with carefully designed questions and representative sampling to ensure high accuracy and reliability in measuring collective attitudes. Sentiment analysis uses natural language processing algorithms to interpret emotions from unstructured data, but its accuracy can vary due to nuances in language, sarcasm, and context. While polling provides statistically validated results, sentiment analysis offers real-time insights but with potential limitations in reliability depending on the quality of data and algorithm sophistication.
Speed and Scale: Timeliness of Insights
Public opinion polling provides structured data with reliable demographic breakdowns but often requires days or weeks for collection and analysis, limiting timeliness. Sentiment analysis leverages real-time data from social media and online platforms, enabling rapid insights at massive scale but may sacrifice accuracy due to noise and bias. Combining polling's methodological rigor with sentiment analysis's speed enhances timely decision-making in dynamic environments.
Human Bias vs Machine Learning Bias
Public opinion polling often suffers from human bias due to questionnaire design, respondent selection, and interviewer influence, which can skew results and reduce accuracy. Sentiment analysis leverages machine learning algorithms to process vast amounts of textual data but faces challenges like algorithmic bias, training data limitations, and contextual misunderstanding. Understanding and mitigating both human and machine learning biases are crucial to improving the reliability and validity of opinion measurement methods.
Use Cases: When to Choose Polling vs Sentiment Analysis
Public opinion polling excels in situations requiring statistically representative data on specific questions, such as electoral preferences or policy approval ratings. Sentiment analysis is ideal for real-time monitoring of emotions and opinions across vast amounts of unstructured data from social media, reviews, or forums. Choose polling for precise quantification with controlled sampling and sentiment analysis for continuous, scalable insights into public mood and emerging trends.
Ethical Considerations and Privacy Concerns
Public opinion polling and sentiment analysis both raise significant ethical considerations and privacy concerns centered on data collection and consent. Polling relies on direct participant engagement with clear consent protocols, whereas sentiment analysis often uses large-scale data harvested from social media without explicit permission, increasing privacy risks. Ensuring transparency, data anonymization, and adherence to regulatory standards like GDPR are critical to addressing ethical challenges in both methodologies.
Future Trends in Measuring Public Opinion
Future trends in measuring public opinion will heavily integrate advanced sentiment analysis techniques powered by AI and machine learning, enabling real-time interpretation of social media data and large-scale textual content. Enhanced natural language processing models will improve the accuracy of detecting nuanced emotions and opinions beyond traditional polling methods, reducing reliance on costly, time-consuming surveys. The convergence of big data analytics with sentiment analysis tools promises more dynamic, granular insights into public attitudes, facilitating faster decision-making for policymakers and businesses.
Related Important Terms
Poll Bias Mitigation
Public opinion polling and sentiment analysis both face challenges of poll bias mitigation, where sampling methods and question framing in traditional polling can skew results, while sentiment analysis must address algorithmic bias and data representativeness in social media sources. Effective poll bias mitigation relies on stratified sampling techniques in public opinion polling and the integration of diverse, balanced datasets alongside advanced natural language processing models in sentiment analysis.
Real-time Sentiment Tracking
Real-time sentiment tracking leverages advanced sentiment analysis techniques to continuously monitor public opinion across social media platforms, offering instantaneous insights into public mood shifts. Unlike traditional public opinion polling, which relies on intermittent surveys and delayed results, real-time sentiment tracking provides dynamic, large-scale data that enhances decision-making with up-to-the-minute accuracy.
Emotional Resonance Index
Public opinion polling quantifies voter preferences and attitudes through structured surveys, providing statistically significant insights into collective viewpoints. Sentiment analysis evaluates emotional resonance by analyzing textual data from social media and online platforms, with the Emotional Resonance Index measuring the intensity and positivity of public emotions toward specific topics or brands.
Poll-to-Social Echo Mapping
Public opinion polling relies on structured survey data to capture individual viewpoints, while sentiment analysis processes vast social media content to gauge collective emotions; Poll-to-Social Echo Mapping bridges these methods by correlating poll results with real-time digital sentiment trends, enhancing the accuracy of public attitude measurement. This fusion enables analysts to detect shifting societal opinions more dynamically, leveraging both quantitative poll statistics and qualitative social media narratives.
Multimodal Sentiment Fusion
Multimodal sentiment fusion enhances public opinion polling by integrating textual, visual, and auditory data to capture nuanced voter emotions and attitudes, improving accuracy beyond traditional survey methods. Combining facial expressions, voice tone, and social media text enables a comprehensive analysis that reflects real-time public sentiment more effectively than isolated sentiment analysis techniques.
Microtargeted Sampling
Microtargeted sampling in public opinion polling uses demographic, behavioral, and psychographic data to select specific population segments, enhancing the accuracy of predictions for targeted groups. Sentiment analysis complements this by processing large-scale social media and textual data, providing real-time emotional insights that refine and validate microtargeted polling outcomes.
Deep Sentiment Parsing
Deep sentiment parsing leverages advanced natural language processing techniques to extract nuanced emotional and attitudinal information from textual data, offering a more granular understanding than traditional public opinion polling. By analyzing complex linguistic structures and contextual cues, deep sentiment parsing enables real-time, large-scale sentiment assessment, enhancing the accuracy and depth of public opinion insights.
Synthetic Respondent Generation
Synthetic Respondent Generation enhances public opinion polling by creating artificial respondent profiles that simulate diverse demographic and behavioral traits, enabling more comprehensive and cost-effective data collection. This method overcomes limitations of traditional sentiment analysis by providing structured, quantifiable insights from simulated responses rather than relying solely on unstructured social media or text data.
Opinion Drift Detection
Public opinion polling provides structured quantitative data through surveys, capturing explicit attitudes at specific points in time, while sentiment analysis uses natural language processing to interpret emotions and opinions from unstructured text data, enabling continuous monitoring for opinion drift detection. Combining these methods enhances the accuracy of tracking shifts in public sentiment and detecting subtle changes in opinion trends across diverse populations.
Hybrid Poll-Sentiment Pipelines
Hybrid poll-sentiment pipelines combine traditional public opinion polling data with real-time sentiment analysis from social media and online platforms, enhancing accuracy in capturing public attitudes. This integrated approach leverages quantitative survey metrics alongside qualitative sentiment cues to provide a comprehensive understanding of population trends and shifts.
public opinion polling vs sentiment analysis Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com