Public governance prioritizes transparency, accountability, and citizen participation, ensuring decisions reflect community needs and ethical standards. Algorithmic governance relies on automated systems and data-driven processes to enhance efficiency and consistency but may lack human judgment and adaptability. Balancing these approaches involves integrating algorithmic tools with public oversight to achieve equitable and effective governance outcomes.
Table of Comparison
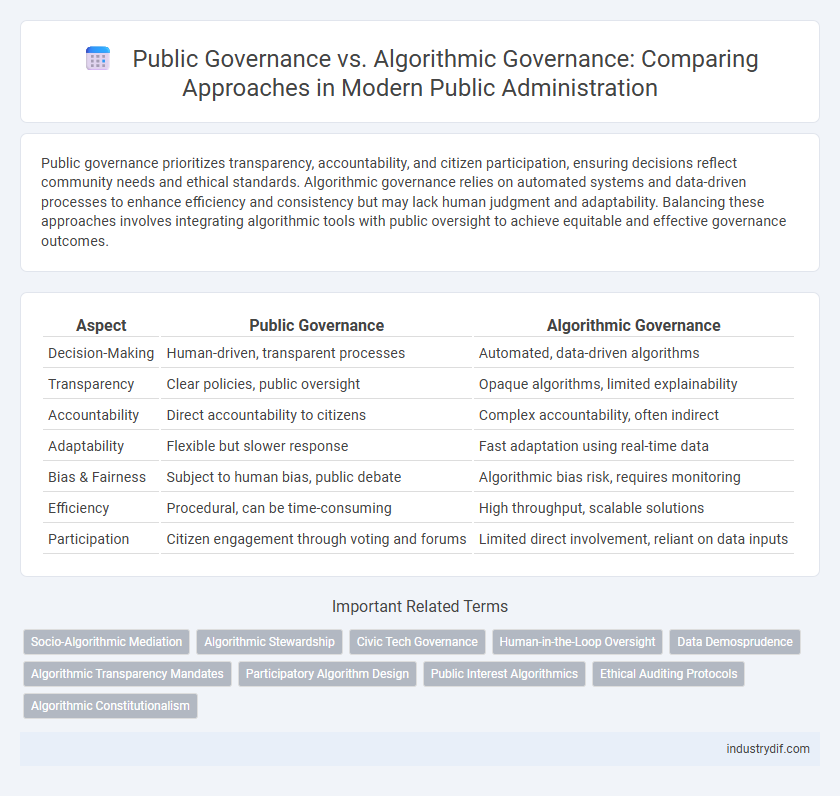
| Aspect | Public Governance | Algorithmic Governance |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making | Human-driven, transparent processes | Automated, data-driven algorithms |
| Transparency | Clear policies, public oversight | Opaque algorithms, limited explainability |
| Accountability | Direct accountability to citizens | Complex accountability, often indirect |
| Adaptability | Flexible but slower response | Fast adaptation using real-time data |
| Bias & Fairness | Subject to human bias, public debate | Algorithmic bias risk, requires monitoring |
| Efficiency | Procedural, can be time-consuming | High throughput, scalable solutions |
| Participation | Citizen engagement through voting and forums | Limited direct involvement, reliant on data inputs |
Introduction to Public and Algorithmic Governance
Public governance involves decision-making processes led by governmental institutions prioritizing transparency, accountability, and citizen participation to manage public resources and policies effectively. Algorithmic governance integrates data-driven algorithms and artificial intelligence to enhance efficiency, predict outcomes, and automate regulatory functions within public administration. Comparing both frameworks emphasizes the balance between human judgment in public governance and computational precision in algorithmic systems to improve governance quality.
Defining Public Governance in the Digital Age
Public governance in the digital age centers on transparent decision-making, inclusive citizen participation, and accountability through digital platforms and data-driven policies. It integrates technology to enhance service delivery, promote open government data, and enable real-time feedback mechanisms. The emphasis lies in balancing innovation with ethical considerations, ensuring digital tools empower democratic processes rather than undermining them.
What Is Algorithmic Governance?
Algorithmic governance refers to the use of automated algorithms and artificial intelligence systems to guide decision-making processes in public administration. These algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to optimize efficiency, predict outcomes, and enforce policies with minimal human intervention. The adoption of algorithmic governance raises critical questions about transparency, accountability, and the ethical implications of delegating authority to computational models.
Key Differences Between Public and Algorithmic Governance
Public governance relies on human decision-making processes involving elected officials, policy experts, and citizen participation, emphasizing transparency and accountability through established legal frameworks. Algorithmic governance uses data-driven algorithms and automated systems to make decisions or enforce policies, prioritizing efficiency and scalability but raising concerns about bias, lack of transparency, and reduced human oversight. Key differences include decision-making modes, with public governance being deliberative and inclusive, while algorithmic governance is adaptive and data-centric, impacting accountability mechanisms and the potential for systemic bias.
Benefits of Public Governance Systems
Public governance systems ensure transparency by involving citizens directly in decision-making processes, which enhances accountability and trust in government institutions. These systems promote inclusiveness by accommodating diverse societal interests and safeguarding minority rights through democratic mechanisms. Moreover, public governance fosters social cohesion and legitimacy, leading to more stable and sustainable policy outcomes compared to algorithmic governance models.
Advantages and Challenges of Algorithmic Governance
Algorithmic governance enhances decision-making efficiency by processing vast datasets to identify patterns and optimize resource allocation, leading to faster and more consistent policy implementation. Challenges include the risk of algorithmic bias, opacity in automated decisions, and ethical concerns regarding accountability and transparency. Balancing these advantages and challenges is critical for integrating algorithmic tools within public governance frameworks effectively.
Transparency and Accountability in Governance Models
Transparency in public governance ensures citizen access to decision-making processes, fostering trust and enabling informed participation. Algorithmic governance relies on coded rules but often lacks clear visibility into its mechanisms, raising concerns about opaque decision criteria. Accountability in public models is enforced through established legal frameworks and public scrutiny, while algorithmic systems struggle with assigning responsibility due to complex, often proprietary algorithms.
Public Participation vs Automated Decision-Making
Public participation fosters transparency and accountability by involving citizens directly in policy-making, ensuring diverse perspectives shape governance. Algorithmic governance leverages automated decision-making to enhance efficiency and process vast data quickly but risks reducing human oversight and marginalizing public input. Balancing participatory engagement with algorithmic efficiency is essential for equitable and responsive governance systems.
Ethical and Legal Implications
Public governance prioritizes transparency, accountability, and citizen participation to uphold democratic values, whereas algorithmic governance raises complex ethical concerns such as bias, discrimination, and lack of accountability in automated decision-making processes. Legal implications involve the need for robust frameworks addressing data privacy, algorithmic transparency, and liability to prevent misuse and protect individual rights. The intersection of ethics and law necessitates constant evaluation of how algorithms impact public trust, fairness, and justice in governance systems.
Future Trends: Integrating Public and Algorithmic Governance
Future governance models will increasingly integrate public participation with algorithmic decision-making to enhance transparency and efficiency. Hybrid systems leveraging AI analytics and citizen input can optimize policy outcomes by balancing data-driven insights with democratic accountability. Emerging technologies such as blockchain and machine learning will facilitate real-time participatory mechanisms, transforming governance into adaptive and inclusive frameworks.
Related Important Terms
Socio-Algorithmic Mediation
Socio-algorithmic mediation integrates human judgment with algorithmic processing to enhance transparency and accountability in governance, addressing biases while optimizing decision-making efficiency. This hybrid approach leverages public participation and data-driven models to balance societal values with computational accuracy, fostering more inclusive and adaptive governance frameworks.
Algorithmic Stewardship
Algorithmic stewardship prioritizes transparency, accountability, and ethical data management in automated decision-making, ensuring algorithms align with public values and societal norms. Effective algorithmic governance incorporates continuous monitoring and stakeholder engagement to mitigate biases and uphold fairness in digital public services.
Civic Tech Governance
Civic Tech Governance leverages public participation and transparency to enhance decision-making processes, contrasting with Algorithmic Governance which relies on automated systems and data-driven algorithms to enforce policies and manage resources. Emphasizing inclusivity, Civic Tech Governance integrates citizen feedback through digital platforms, promoting accountability and democratic engagement in public administration.
Human-in-the-Loop Oversight
Human-in-the-loop oversight in public governance integrates human judgment within algorithmic decision-making processes to ensure transparency, accountability, and ethical standards are maintained. This approach mitigates risks associated with automated biases and enhances the legitimacy of governance by enabling human intervention in critical algorithmic outcomes.
Data Demosprudence
Data demosprudence emphasizes the ethical and democratic management of data governance, ensuring transparency, accountability, and public participation in decision-making processes. Unlike algorithmic governance, which relies on automated systems and opaque algorithms, public governance prioritizes human oversight and inclusivity to safeguard citizens' rights and promote equitable outcomes.
Algorithmic Transparency Mandates
Algorithmic transparency mandates require organizations to disclose the data sources, decision-making processes, and potential biases embedded in AI systems to ensure accountability and fairness. These mandates enhance public trust by allowing independent audits and fostering clearer understanding of algorithmic governance compared to traditional public administration.
Participatory Algorithm Design
Participatory algorithm design enhances public trust and accountability by involving diverse stakeholders in the development and evaluation of algorithms used in governance, promoting transparency and reducing biases. Embedding public input in algorithmic decision-making processes fosters more equitable outcomes and aligns automated systems with societal values and democratic principles.
Public Interest Algorithmics
Public interest algorithmics prioritize transparency, accountability, and fairness to ensure algorithms serve societal well-being rather than private or opaque agendas. Integrating public values into algorithmic governance fosters inclusive decision-making processes, mitigating biases and enhancing trust in automated systems.
Ethical Auditing Protocols
Ethical auditing protocols in public governance emphasize transparency, accountability, and stakeholder participation to ensure decisions align with societal values and human rights. Algorithmic governance requires specialized audits integrating bias detection, data privacy assessments, and impact evaluations to address automated system risks and promote ethical AI deployment.
Algorithmic Constitutionalism
Algorithmic constitutionalism redefines governance by embedding legal principles within algorithmic frameworks to ensure transparency, accountability, and fairness in decision-making processes. This approach challenges traditional public governance by automating rights protection and regulatory enforcement through coded rules aligned with constitutional values.
Public vs Algorithmic Governance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com