Single-family homes offer privacy, personalized space, and long-term investment stability, making them ideal for families seeking independence. Co-living spaces provide affordable, community-focused living with shared amenities, appealing to young professionals and those prioritizing social interaction. Choosing between the two depends on lifestyle preferences, budget constraints, and the desire for either solitude or communal engagement.
Table of Comparison
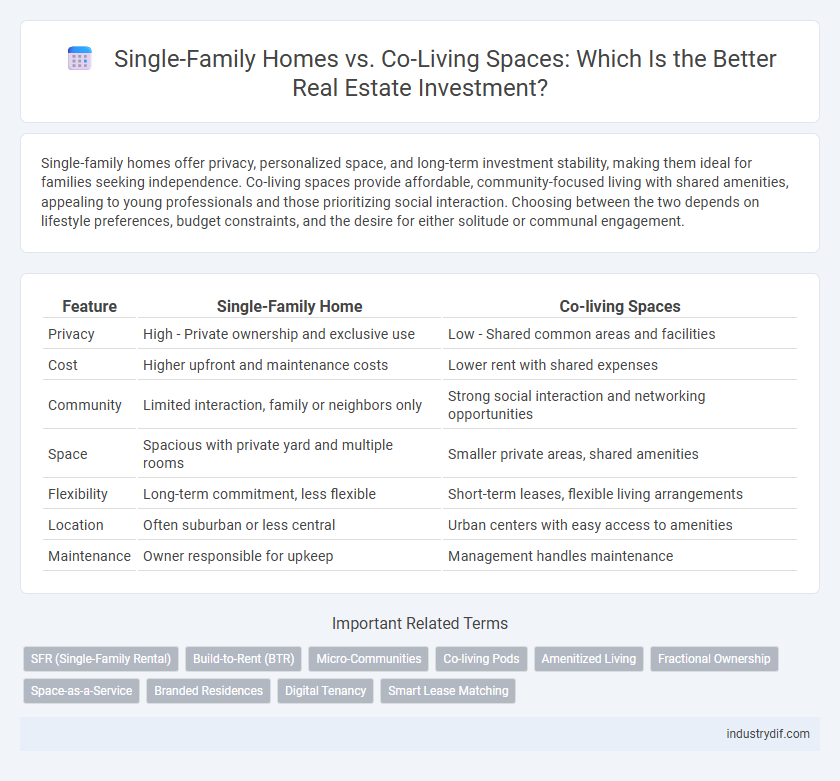
| Feature | Single-Family Home | Co-living Spaces |
|---|---|---|
| Privacy | High - Private ownership and exclusive use | Low - Shared common areas and facilities |
| Cost | Higher upfront and maintenance costs | Lower rent with shared expenses |
| Community | Limited interaction, family or neighbors only | Strong social interaction and networking opportunities |
| Space | Spacious with private yard and multiple rooms | Smaller private areas, shared amenities |
| Flexibility | Long-term commitment, less flexible | Short-term leases, flexible living arrangements |
| Location | Often suburban or less central | Urban centers with easy access to amenities |
| Maintenance | Owner responsible for upkeep | Management handles maintenance |
Overview of Single-Family Homes and Co-living Spaces
Single-family homes provide private living spaces with full ownership of the property, often featuring yards and multiple bedrooms ideal for families seeking long-term stability. Co-living spaces emphasize shared amenities and common areas, offering a community-focused housing option with flexible lease terms typically attractive to young professionals and remote workers. Both housing types differ significantly in privacy, cost structure, and social interaction, influencing buyer and renter preferences in urban real estate markets.
Key Differences Between Single-Family Homes and Co-living
Single-family homes offer exclusive ownership and privacy with private yards and personalized living spaces, while co-living spaces emphasize shared common areas and community living, reducing individual costs through shared amenities. Single-family properties typically require higher upfront investment and maintenance responsibilities, whereas co-living spaces provide flexible lease terms and a turnkey lifestyle ideal for young professionals or transient residents. The choice between these housing types depends on budget, lifestyle preferences, and long-term investment goals in the real estate market.
Market Trends: Demand for Single-Family vs Co-living
Market trends indicate a shift as demand for single-family homes remains strong due to preferences for privacy and larger living spaces, particularly among families and remote workers. Co-living spaces gain traction in urban areas, driven by young professionals seeking affordability, community, and flexible leasing options. Real estate developers respond by diversifying portfolios to accommodate both market segments, balancing traditional homeownership appeal with innovative shared living solutions.
Investment Potential: Profitability and ROI
Single-family homes typically offer stable appreciation and consistent rental income, making them a reliable choice for long-term investment with moderate risk. Co-living spaces provide higher cash flow potential through multiple tenants sharing one property, but require active management and carry greater market volatility. Evaluating local demand, property management costs, and occupancy rates is crucial to determine the profitability and ROI of each option.
Tenant Demographics and Lifestyle Preferences
Single-family homes typically attract families and long-term tenants seeking privacy, stability, and space for children and pets, favoring suburban or residential neighborhoods. Co-living spaces appeal primarily to young professionals, students, and digital nomads who prioritize affordability, community interaction, and flexible lease terms in urban environments. Understanding these tenant demographics and lifestyle preferences helps real estate investors and developers tailor properties to meet evolving market demands.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Ongoing Expenses
Single-family homes generally require higher upfront costs including down payments, closing fees, and maintenance expenses, whereas co-living spaces offer lower initial investments with shared utilities and amenities reducing monthly costs. Ongoing expenses for single-family homes encompass property taxes, insurance, and potential renovation costs, while co-living arrangements distribute rent and utilities among residents, leading to predictable and often more affordable monthly payments. Evaluating cost efficiency demands considering long-term financial commitments, individual lifestyle preferences, and potential appreciation or depreciation of property value.
Community Features and Social Dynamics
Single-family homes offer privacy and personalized space, fostering strong family bonds and long-term neighborhood stability. Co-living spaces emphasize shared community features such as communal kitchens, lounges, and organized social events that encourage interaction and networking among diverse residents. The social dynamics in co-living environments promote collaboration and convenience, while single-family homes prioritize individual autonomy and quieter living experiences.
Location Considerations for Each Housing Type
Single-family homes typically thrive in suburban or residential neighborhoods offering privacy, space, and family-friendly amenities, making proximity to quality schools, parks, and low-density environments crucial location considerations. Co-living spaces are often situated in urban centers or neighborhoods with robust public transportation, cultural hotspots, and employment hubs to cater to young professionals or transient residents seeking community and convenience. Evaluating local demographics, access to essential services, and neighborhood safety significantly impacts the suitability and appeal of each housing type.
Regulatory and Zoning Implications
Single-family homes are typically subject to strict zoning laws that limit property use to residential purposes, ensuring neighborhood stability and property value preservation. Co-living spaces often face complex regulatory challenges, including compliance with multi-family housing codes, fire safety standards, and occupancy limits, which vary significantly by municipality. Navigating zoning ordinances and obtaining necessary permits can be more difficult for co-living developments, impacting their scalability and integration into predominantly single-family neighborhoods.
Future Outlook: Evolving Preferences in Residential Real Estate
Single-family homes remain desirable for privacy and space, but co-living spaces are rapidly gaining traction among millennials and remote workers seeking affordability and community. Market forecasts indicate a steady rise in co-living developments, driven by urbanization and shifting lifestyle priorities. Real estate investors and developers are increasingly focusing on mixed-use projects that blend traditional housing with co-living amenities to meet evolving residential demands.
Related Important Terms
SFR (Single-Family Rental)
Single-Family Rentals (SFR) offer tenants privacy, larger living spaces, and private yards, appealing to families and long-term residents seeking stability. In contrast, co-living spaces emphasize affordability, shared amenities, and community engagement, attracting young professionals and transient renters in urban areas.
Build-to-Rent (BTR)
Build-to-Rent (BTR) developments emphasize single-family homes designed for long-term tenants seeking privacy and personalized living environments, contrasting with co-living spaces that prioritize shared amenities and community interaction. Investors favor BTR single-family homes for their appeal to families and professionals desiring stability, while co-living targets urban renters valuing affordability and social connectivity.
Micro-Communities
Single-family homes offer private, individualized living spaces ideal for families seeking stability, while co-living spaces foster dynamic micro-communities that enhance social interaction and resource sharing among professionals and urban dwellers. Micro-communities in co-living environments facilitate collaboration, affordable living, and a sense of belonging, appealing especially to millennials and remote workers in high-density cities.
Co-living Pods
Co-living pods offer a modern, affordable alternative to traditional single-family homes by maximizing space efficiency and fostering community living through shared amenities and flexible leasing options. These compact, fully furnished units appeal to urban professionals and students seeking cost-effective housing solutions without sacrificing privacy.
Amenitized Living
Single-family homes offer personalized amenity control such as private gardens, garages, and customized interiors, enhancing individual living experiences. Co-living spaces provide communal amenities like shared kitchens, coworking areas, and social lounges, fostering community engagement and cost-effective access to luxury facilities.
Fractional Ownership
Fractional ownership in single-family homes offers investors shared equity and access to vacation properties without full financial responsibility, while co-living spaces provide communal living with reduced individual costs but limited ownership rights. This model optimizes real estate investment by balancing asset control and cost-efficiency in dynamic housing markets.
Space-as-a-Service
Single-family homes offer private, customizable living spaces that cater to long-term residential needs, while co-living spaces utilize the Space-as-a-Service model to provide flexible, community-oriented environments with shared amenities and shorter lease terms. This innovative approach in real estate supports urban professionals seeking convenience, affordability, and social interaction within metropolitan areas.
Branded Residences
Branded residences in single-family homes offer exclusive design, premium amenities, and personalized services that cater to affluent buyers seeking privacy and ownership, while co-living spaces with branded residences emphasize community, flexible leases, and shared amenities tailored for urban professionals and millennials. The choice hinges on investment goals, lifestyle preferences, and the value placed on privacy versus communal living within high-end real estate markets.
Digital Tenancy
Single-family homes offer privacy and personalized control, while co-living spaces leverage digital tenancy platforms to enhance community engagement and streamline lease management. Digital tenancy solutions in co-living environments facilitate seamless communication, automated payments, and real-time maintenance tracking, optimizing tenant experience and operational efficiency.
Smart Lease Matching
Smart lease matching technology leverages advanced algorithms and data analytics to pair tenants with single-family homes or co-living spaces that best fit their preferences, lifestyle, and budget. This innovation enhances tenant satisfaction by optimizing property utilization and reducing vacancy rates in the competitive real estate market.
Single-Family Home vs Co-living Spaces Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com