Picnic areas provide designated spaces for pet owners to relax and enjoy meals outdoors while keeping pets safely contained and entertained. Foraging zones stimulate pets' natural instincts by encouraging exploration and mental engagement through scent trails and hidden treats. Balancing picnic areas with foraging zones enhances recreational experiences, catering to both social interaction and cognitive enrichment for pets.
Table of Comparison
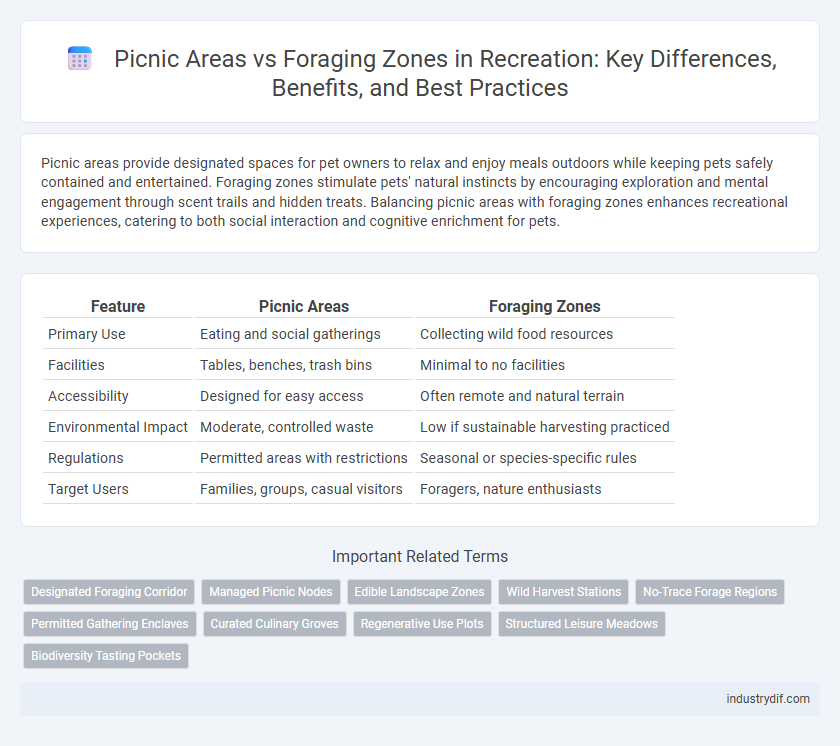
| Feature | Picnic Areas | Foraging Zones |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Eating and social gatherings | Collecting wild food resources |
| Facilities | Tables, benches, trash bins | Minimal to no facilities |
| Accessibility | Designed for easy access | Often remote and natural terrain |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate, controlled waste | Low if sustainable harvesting practiced |
| Regulations | Permitted areas with restrictions | Seasonal or species-specific rules |
| Target Users | Families, groups, casual visitors | Foragers, nature enthusiasts |
Defining Picnic Areas in Recreational Settings
Picnic areas in recreational settings are designated outdoor spaces equipped with tables, benches, and sometimes grills, designed to facilitate outdoor dining and social gatherings. These areas often feature amenities such as waste receptacles and shade structures to enhance visitor comfort and maintain cleanliness. Unlike foraging zones, picnic areas are specifically maintained to support leisurely meals and family-friendly recreation rather than food gathering or harvesting from natural vegetation.
Foraging Zones: Characteristics and Purpose
Foraging zones are designated outdoor areas where individuals can gather wild edible plants, mushrooms, berries, and herbs, promoting sustainable interaction with natural ecosystems. These zones prioritize biodiversity conservation and environmental education while encouraging responsible harvesting practices in line with local regulations. Often located in forests, parks, or meadows, foraging zones serve as living classrooms that enhance ecological awareness and support healthy recreational activities connected to nature.
Accessibility and Infrastructure Comparison
Picnic areas typically offer accessible infrastructure such as paved paths, designated seating, and trash receptacles, catering to a wide range of visitors including families and individuals with mobility challenges. In contrast, foraging zones often have minimal infrastructure, emphasizing natural terrains that may limit accessibility but provide a more immersive, hands-on recreational experience. The ease of access and presence of facilities in picnic areas support convenience and comfort, whereas foraging zones prioritize interaction with the environment, often requiring more physical effort and knowledge of the local flora.
Environmental Impact: Managed vs. Wild Spaces
Picnic areas, typically managed and maintained, minimize environmental impact by providing designated spaces that control waste and reduce habitat disruption. Foraging zones, being wild and natural, support biodiversity but face risks of overharvesting and ecosystem imbalance if not regulated. Effective recreation planning balances preservation in foraging zones with sustainable use in picnic areas to protect native flora and fauna.
Safety Considerations for Users
Picnic areas are designed with safety in mind, offering clean, maintained spaces equipped with facilities to prevent accidents and exposure to harmful wildlife or plants. Foraging zones require heightened vigilance due to the risk of misidentifying edible plants, potential exposure to pesticides, and the presence of hazardous terrain or animals. Users should adhere to posted guidelines, carry appropriate safety gear, and familiarize themselves with local flora to minimize health risks in foraging environments.
Typical Activities in Picnic Areas vs Foraging Zones
Picnic areas typically involve activities like eating meals, socializing, playing casual games, and relaxing with family or friends in designated spots equipped with tables and benches. Foraging zones are characterized by gathering wild plants, mushrooms, and edible herbs, emphasizing nature exploration and sustainable harvesting. Both areas encourage outdoor recreation but differ in activity focus--picnic areas prioritize leisure and dining, while foraging zones promote ecological knowledge and food sourcing.
Regulatory Guidelines and Permissions
Picnic areas typically have clear regulatory guidelines that require permits for large gatherings, adherence to designated fire pits, and waste disposal rules to minimize environmental impact. Foraging zones often demand specific permissions, as regulations protect native plant species and ensure sustainable harvesting practices aligned with local conservation laws. Both recreational activities must comply with regional policies to promote safety and ecological balance.
Visitor Experience and Engagement
Picnic areas offer structured spaces with tables and amenities that enhance comfort and social interaction, creating a relaxed visitor experience. Foraging zones provide immersive, educational engagement by encouraging visitors to connect with nature and explore local flora. Both settings enrich recreational outings but cater to different preferences for activity and learning.
Maintenance and Resource Management
Picnic areas require regular maintenance such as waste removal, table repairs, and landscaping to ensure cleanliness and safety for visitors. Foraging zones demand careful resource management, including monitoring plant populations and limiting harvesting to prevent ecosystem depletion. Effective stewardship balances visitor enjoyment with sustainable practices to preserve recreational and natural resources.
Future Trends in Recreational Land Use
Picnic areas will increasingly incorporate sustainable design features such as renewable materials and waste reduction systems to enhance user experience while minimizing environmental impact. Foraging zones are expected to expand within recreational land use, promoting ecological literacy and local food sourcing as part of urban green space initiatives. Integration of technology, like augmented reality guides, will support safe and informed foraging, aligning conservation efforts with recreational demands.
Related Important Terms
Designated Foraging Corridor
Designated Foraging Corridors are specialized zones within recreational areas designed to sustainably support local wildlife by allowing natural food foraging without human interference. Unlike picnic areas intended for outdoor dining and social gatherings, these corridors prioritize habitat preservation and biodiversity through strategic vegetation management and restricted human access.
Managed Picnic Nodes
Managed picnic nodes offer designated spaces equipped with amenities like tables, grills, and waste bins, ensuring a clean and organized environment for visitors. Unlike foraging zones, these areas prioritize structured recreation and environmental conservation by minimizing disturbances to local flora and fauna.
Edible Landscape Zones
Picnic areas provide designated spaces with amenities for outdoor dining, ideal for social gatherings, while foraging zones emphasize natural, edible landscape zones where visitors can harvest wild fruits, herbs, and mushrooms, promoting sustainable interaction with the environment. Edible landscape zones enhance recreation by combining leisure with education on native plant species and their uses in cultural food traditions.
Wild Harvest Stations
Wild harvest stations enhance foraging zones by providing designated areas where visitors can sustainably gather wild edibles, promoting ecological awareness and responsible recreation. Picnic areas, in contrast, prioritize comfort and convenience with amenities for dining but lack the interactive experience of harvesting from nature.
No-Trace Forage Regions
No-trace forage regions prioritize sustainable foraging practices by minimizing environmental impact and preserving natural habitats for future use. Designated picnic areas, while structured for convenience and waste management, often lack the ecological sensitivity required to support ethical foraging activities without habitat disturbance.
Permitted Gathering Enclaves
Picnic areas offer designated, permitted gathering enclaves designed for group activities with tables, benches, and waste facilities, ensuring organized, accessible recreation spaces. Foraging zones, while allowing the collection of natural resources, typically restrict large gatherings to protect habitats and sustain biodiversity, emphasizing minimal-impact outdoor experiences.
Curated Culinary Groves
Picnic areas offer designated spaces equipped with amenities for outdoor dining, while foraging zones provide natural environments for harvesting wild edibles. Curated culinary groves blend these concepts by cultivating specific plants and herbs, enhancing recreational foraging with intentional, sustainable food sources.
Regenerative Use Plots
Regenerative Use Plots in recreation balance Picnic Areas and Foraging Zones by promoting sustainable resource use and habitat restoration. These plots enhance biodiversity while providing designated spots for responsible foraging and outdoor gatherings, supporting ecological health and visitor experience.
Structured Leisure Meadows
Structured leisure meadows in picnic areas offer manicured, accessible spaces designed for relaxation and organized activities, contrasting with foraging zones that feature wild, biodiverse habitats encouraging natural exploration and edible plant gathering. These structured environments balance human recreation with ecological stewardship, enhancing visitor experiences while supporting local flora and fauna.
Biodiversity Tasting Pockets
Picnic areas provide curated environments for social dining and relaxation, while foraging zones serve as biodiversity tasting pockets where visitors engage directly with native edible plants, enhancing ecological awareness and flavors unique to local ecosystems. These biodiversity pockets promote conservation education by allowing people to experience the diverse, natural food resources that sustain local wildlife and plant populations.
Picnic Areas vs Foraging Zones Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com