A landlord primarily focuses on property ownership and tenant relations, ensuring rent collection and lease compliance. An asset manager takes a broader approach, optimizing property value through financial analysis, market positioning, and long-term investment strategies. While landlords handle day-to-day operations, asset managers drive strategic decisions to maximize returns.
Table of Comparison
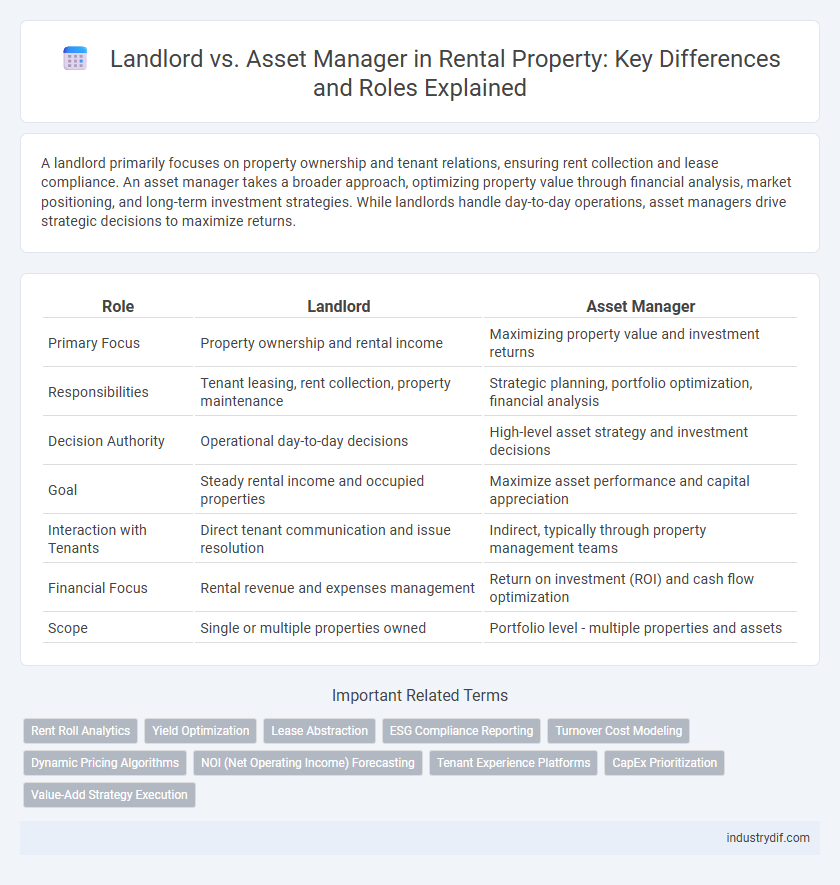
| Role | Landlord | Asset Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Property ownership and rental income | Maximizing property value and investment returns |
| Responsibilities | Tenant leasing, rent collection, property maintenance | Strategic planning, portfolio optimization, financial analysis |
| Decision Authority | Operational day-to-day decisions | High-level asset strategy and investment decisions |
| Goal | Steady rental income and occupied properties | Maximize asset performance and capital appreciation |
| Interaction with Tenants | Direct tenant communication and issue resolution | Indirect, typically through property management teams |
| Financial Focus | Rental revenue and expenses management | Return on investment (ROI) and cash flow optimization |
| Scope | Single or multiple properties owned | Portfolio level - multiple properties and assets |
Definition: Landlord vs Asset Manager
A landlord is an individual or entity that owns rental property and leases it directly to tenants, managing day-to-day operations such as rent collection and maintenance. An asset manager oversees a portfolio of real estate investments, focusing on maximizing property value and return on investment through strategic planning, financial analysis, and market positioning. While landlords handle property-level tasks, asset managers take a broader approach by aligning property performance with overall financial goals.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Landlords primarily focus on property ownership, tenant relations, lease agreements, and rent collection, ensuring the physical asset is maintained and occupancy rates are maximized. Asset managers oversee the financial performance of the property portfolio, including budgeting, investment analysis, and strategic planning to enhance property value and return on investment. Both roles require collaboration but differ as landlords handle day-to-day operations while asset managers drive long-term asset growth and profitability.
Qualifications and Skill Sets
Landlords typically require strong negotiation skills, legal knowledge of tenant rights, and basic property maintenance understanding to effectively manage rental agreements and tenant relations. Asset managers possess advanced financial acumen, investment analysis capabilities, and strategic planning expertise to optimize property value and maximize returns. While landlords focus on operational management and tenant satisfaction, asset managers emphasize portfolio performance and long-term asset growth.
Authority and Decision-Making Power
Landlords hold direct authority over property leasing decisions, tenant selection, and rent setting, ensuring compliance with legal requirements and maximizing rental income. Asset managers exercise strategic decision-making power by overseeing portfolio performance, optimizing property value, and coordinating with property managers for maintenance and operational efficiency. The distinction lies in landlords managing individual assets on a transactional level, while asset managers focus on long-term investment strategy and financial returns.
Day-to-Day Operations
Landlords primarily handle tenant relations, lease agreements, and property maintenance to ensure consistent rental income. Asset managers focus on strategic decisions such as budgeting, financial performance analysis, and long-term property value enhancement. Day-to-day operations involve landlords managing repairs, rent collection, and vacancy control, while asset managers oversee portfolio optimization and capital improvement planning.
Financial Management and Reporting
Landlords focus on collecting rent and managing property expenses, ensuring timely payments and maintaining cash flow for their rental assets. Asset managers concentrate on maximizing property value through detailed financial reporting, budgeting, and investment strategies, providing comprehensive analyses to optimize long-term returns. Effective financial management and transparent reporting are critical roles that distinguish landlords from asset managers in rental property oversight.
Tenant Relations and Communication
Landlords directly handle tenant relations by addressing lease agreements, rent collection, and maintenance requests to ensure tenant satisfaction and timely occupancy. Asset managers oversee tenant communication strategically, focusing on long-term value optimization by coordinating with property management teams to enhance tenant retention and property performance. Effective collaboration between landlords and asset managers ensures streamlined communication, improved tenant experience, and maximized rental income.
Risk Management Strategies
Landlords prioritize direct property oversight and tenant relationship management to mitigate risks such as vacancy and property damage. Asset managers implement comprehensive risk management strategies including portfolio diversification, financial analysis, and market trend monitoring to optimize returns and minimize exposure. Both roles coordinate insurance policies and legal compliance to protect real estate investments from financial loss.
Performance Metrics and Evaluation
Performance metrics for landlords primarily include tenant retention rates, rent collection efficiency, and property maintenance costs, which directly impact net operating income. Asset managers focus on broader financial indicators such as return on investment (ROI), cash flow analysis, and market value appreciation to evaluate overall portfolio performance. Comparing these roles, landlords aim to optimize day-to-day operations, while asset managers emphasize strategic growth and long-term asset value.
Choosing Between Landlord and Asset Manager
Choosing between a landlord and an asset manager depends on control preferences and expertise requirements in rental property management. Landlords maintain direct control over leasing decisions and tenant interactions, while asset managers provide professional oversight, optimizing property performance and financial returns. Evaluating factors like property portfolio size, market knowledge, and hands-on involvement guides the decision for effective rental asset management.
Related Important Terms
Rent Roll Analytics
Landlords focus on maximizing rental income and tenant retention through rent roll analytics by tracking lease expirations, payment histories, and vacancy rates. Asset managers leverage rent roll data to optimize portfolio performance, identify revenue growth opportunities, and assess property financial health for strategic decision-making.
Yield Optimization
Landlords primarily aim to maximize rental income from their properties while asset managers focus on strategic yield optimization through portfolio diversification, market analysis, and proactive property management. Effective yield optimization involves balancing rental rates, occupancy levels, and maintenance costs to enhance overall return on investment.
Lease Abstraction
Lease abstraction enables landlords to efficiently summarize critical lease terms, facilitating quick decision-making and risk management across property portfolios. Asset managers leverage lease abstraction to analyze financial performance, monitor compliance, and optimize rental income, ensuring alignment with investment goals.
ESG Compliance Reporting
Landlords are primarily responsible for ensuring ESG compliance reporting by implementing sustainable property management practices and meeting regulatory standards, whereas asset managers focus on integrating ESG criteria into investment decisions and portfolio performance evaluations. Effective collaboration between landlords and asset managers enhances transparency, drives environmental impact reduction, and supports long-term value creation in rental properties.
Turnover Cost Modeling
Landlords focus on minimizing turnover costs by optimizing lease durations and tenant retention strategies, directly impacting net operating income. Asset managers employ advanced turnover cost modeling to forecast vacancy periods, repair expenses, and capital improvements, enhancing portfolio value and investment returns.
Dynamic Pricing Algorithms
Dynamic pricing algorithms empower landlords to adjust rental rates in real-time based on market demand, competitor pricing, and seasonal trends, maximizing revenue and occupancy rates. Asset managers utilize these algorithms to optimize portfolio performance by balancing short-term income with long-term asset value appreciation.
NOI (Net Operating Income) Forecasting
Landlords primarily concentrate on maximizing property occupancy and rental income, while asset managers utilize NOI forecasting to optimize overall investment performance by analyzing expenses, rental growth, and market trends. Accurate NOI forecasting enables asset managers to make strategic decisions that enhance property value and ensure sustainable cash flow.
Tenant Experience Platforms
Tenant Experience Platforms enhance communication, streamline maintenance requests, and offer personalized services, significantly improving tenant satisfaction compared to traditional landlord management. Asset managers leverage these platforms for data-driven insights, optimizing property performance and tenant retention strategies.
CapEx Prioritization
Landlords typically prioritize CapEx (Capital Expenditures) based on immediate property needs and tenant retention to maximize rental income and property value. Asset Managers employ a strategic, long-term approach to CapEx prioritization, balancing renovation costs with potential returns and market trends to optimize overall portfolio profitability.
Value-Add Strategy Execution
Landlords primarily focus on property ownership and tenant relationships, while asset managers execute value-add strategies by optimizing operational efficiencies, capital improvements, and financial performance to maximize return on investment. Effective value-add strategy execution involves detailed market analysis, targeted renovations, and proactive portfolio management to increase asset value and rental income.
Landlord vs Asset Manager Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com