A lease agreement establishes a long-term, legally binding contract between a tenant and landlord, outlining specific terms such as rent amount, duration, and responsibilities. A coliving license offers more flexible, short-term occupancy rights suited for community living spaces, often without the full protections or obligations of a traditional lease. Understanding the differences helps renters choose the arrangement that best fits their lifestyle and legal needs.
Table of Comparison
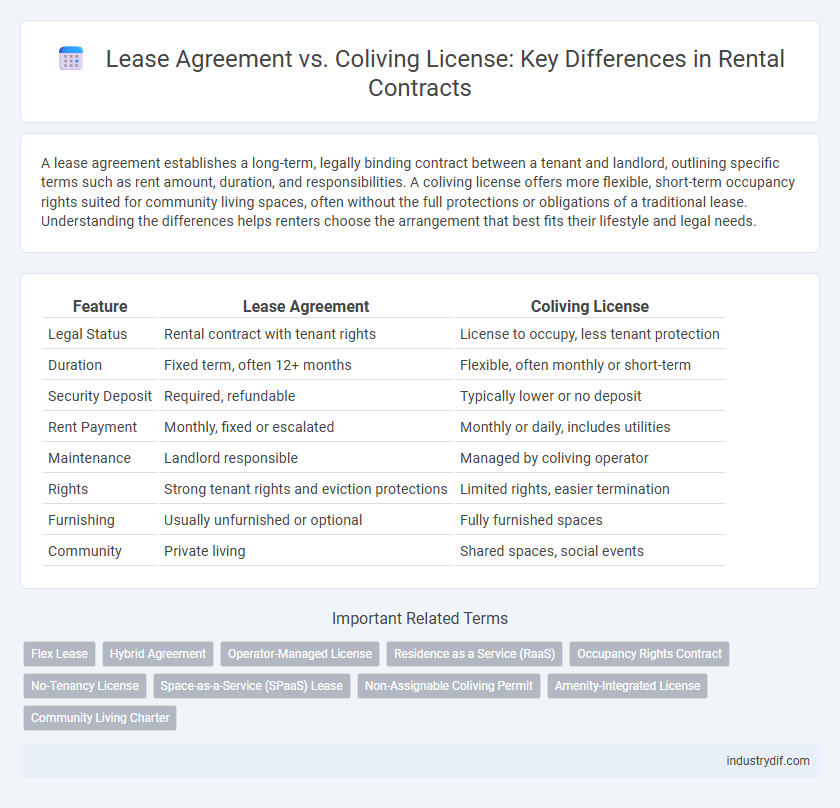
| Feature | Lease Agreement | Coliving License |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Status | Rental contract with tenant rights | License to occupy, less tenant protection |
| Duration | Fixed term, often 12+ months | Flexible, often monthly or short-term |
| Security Deposit | Required, refundable | Typically lower or no deposit |
| Rent Payment | Monthly, fixed or escalated | Monthly or daily, includes utilities |
| Maintenance | Landlord responsible | Managed by coliving operator |
| Rights | Strong tenant rights and eviction protections | Limited rights, easier termination |
| Furnishing | Usually unfurnished or optional | Fully furnished spaces |
| Community | Private living | Shared spaces, social events |
Definition of Lease Agreement and Coliving License
A Lease Agreement is a legally binding contract between a landlord and tenant granting exclusive possession of a property for a specified period, typically involving fixed terms, rent obligations, and maintenance responsibilities. A Coliving License, by contrast, offers a flexible, non-exclusive right to occupy a shared living space with communal amenities, emphasizing community living and often includes shorter terms with more lenient rules. Understanding the distinction enhances tenant rights awareness and informs decisions regarding property rental arrangements.
Key Differences Between Lease Agreements and Coliving Licenses
Lease agreements typically provide tenants with exclusive possession of a defined residential unit for a fixed term, offering more control and stability under landlord-tenant laws. In contrast, coliving licenses grant occupants a non-exclusive right to shared living spaces with more flexible terms and fewer tenant protections, often classified as licenses rather than leases. Key differences include the nature of possession, legal rights, duration, and the degree of privacy and responsibility for maintenance.
Legal Rights and Responsibilities
A lease agreement grants tenants exclusive possession of a rental property for a fixed term, providing strong legal rights such as protection from eviction and control over subleasing, whereas a coliving license offers more flexible, short-term occupancy with communal living arrangements but limited legal protections. Lease agreements impose clear responsibilities on landlords and tenants, including maintenance obligations and rent payments, while coliving licenses typically involve shared responsibilities among residents and less stringent landlord duties. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for renters to navigate their legal rights and responsibilities effectively in rental and coliving scenarios.
Duration and Termination Flexibility
Lease agreements typically involve fixed durations ranging from six months to a year, providing renters with a stable and legally binding commitment. In contrast, coliving licenses offer greater termination flexibility, often operating on a month-to-month basis that allows tenants to end their stay with minimal notice. This flexibility in coliving arrangements caters to short-term residents and those seeking adaptable living solutions without long-term obligations.
Rent Structure and Payment Terms
A Lease Agreement typically involves a fixed rent amount paid monthly with a standard security deposit, enforcing long-term tenant obligations and defined payment schedules. In contrast, a Coliving License offers flexible payment terms often including utilities and amenities within a single fee, suited for short-term stays with variable billing cycles. Rent structures in Lease Agreements prioritize stability and legal protections, whereas Coliving Licenses emphasize convenience and adaptability for shared living environments.
Customization and Space Sharing Policies
Lease agreements typically offer tenants more customization options for personalizing their rental space, allowing modifications within agreed terms. In contrast, coliving licenses emphasize shared space policies, promoting community living with predefined rules on private and communal areas to optimize flexibility and social interaction. Understanding these distinctions helps renters choose arrangements aligned with their preferences for privacy and shared living.
Maintenance and Repair Obligations
Lease agreements typically place maintenance and repair obligations on the landlord, ensuring that essential repairs and upkeep are handled promptly to maintain the property's habitability. In contrast, coliving licenses often require tenants to share responsibility for minor maintenance and upkeep, fostering a communal approach to property care. Clear delineation of these obligations is crucial to avoid disputes and ensure smooth property management.
Subletting and Guest Restrictions
Lease agreements typically prohibit subletting without landlord consent, often including strict guest restrictions to maintain property security and compliance with housing regulations. Coliving licenses offer more flexible terms, frequently allowing subletting among community members and accommodating short-term guests, fostering a social and shared living environment. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for tenants to navigate legal responsibilities and maintain harmonious cohabitation.
Security Deposits and Financial Implications
Lease agreements typically require a security deposit that landlords hold to cover damages or unpaid rent, offering tenants stronger legal protections and clearer financial obligations. Coliving licenses often involve lower or no traditional security deposits, shifting financial responsibility towards monthly communal fees or service charges, which can impact tenants' upfront and ongoing costs differently. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for renters evaluating security deposits' role and overall financial commitments in leasing versus coliving arrangements.
Choosing the Right Option: Lease Agreement or Coliving License
Choosing between a lease agreement and a coliving license depends on the duration, flexibility, and legal protections required. Lease agreements generally offer long-term security and defined tenant rights, ideal for traditional renters seeking stability. Coliving licenses provide greater flexibility and shorter terms, suited for individuals prioritizing communal living and ease of entry or exit within coliving spaces.
Related Important Terms
Flex Lease
Flex Lease offers a hybrid solution that combines the formal structure of a lease agreement with the flexibility of a coliving license, catering to tenants seeking short-term commitments and communal living benefits. Unlike traditional lease agreements, Flex Lease agreements provide customizable rental terms and shared amenities, optimizing convenience and adaptability in modern urban housing markets.
Hybrid Agreement
A Hybrid Agreement combines elements of a traditional Lease Agreement and a Coliving License, offering tenants flexibility with longer-term security and access to shared amenities. This arrangement is ideal for renters seeking both personalized living spaces and community engagement without the rigid terms of conventional leases.
Operator-Managed License
An Operator-Managed License in co-living settings offers flexible, short-term occupancy agreements, differing from traditional lease agreements that require longer commitments and tenant-landlord relationships. This license prioritizes operator control over property management, facilitating streamlined access and community amenities without the legal complexities of standard leases.
Residence as a Service (RaaS)
Lease agreements offer long-term, legally binding rental contracts granting tenants exclusive rights and obligations for residential properties, while coliving licenses provide flexible, short-term access to shared living spaces under a Residence as a Service (RaaS) model. RaaS emphasizes convenience, community, and all-inclusive services, catering to modern urban dwellers seeking adaptability over traditional lease commitments.
Occupancy Rights Contract
A Lease Agreement grants tenants exclusive occupancy rights with legally binding terms outlining duration, rent, and responsibilities, providing tenants with tenant protection laws. In contrast, a Coliving License offers a flexible occupancy rights contract typically on a short-term basis, without exclusive possession, emphasizing communal living arrangements and shared amenities.
No-Tenancy License
A Lease Agreement grants tenants exclusive possession of a property, creating a landlord-tenant relationship with statutory protections, while a Coliving License, often categorized as a No-Tenancy License, provides occupants with limited rights and non-exclusive access, avoiding traditional tenancy laws. This No-Tenancy License model is popular in coliving spaces to offer flexibility and simplify management by treating residents as licensees rather than tenants.
Space-as-a-Service (SPaaS) Lease
Space-as-a-Service (SPaaS) leases provide greater flexibility compared to traditional lease agreements by allowing tenants to access fully furnished, communal living spaces with integrated services under a coliving license model. Unlike standard long-term leases, SPaaS emphasizes a subscription-based approach that includes utilities, maintenance, and community amenities, catering to the growing demand for adaptable urban housing solutions.
Non-Assignable Coliving Permit
A Lease Agreement typically grants tenants exclusive possession of a property for a fixed term and is often assignable, allowing lease transfer under certain conditions, whereas a Non-Assignable Coliving License offers residents transient, non-exclusive rights without the ability to transfer or sublet their permit. This non-assignable coliving permit restricts licensees from assigning their occupancy rights, maintaining landlord control and flexibility in shared living environments.
Amenity-Integrated License
A Lease Agreement grants tenants exclusive possession of a rental unit, while a Coliving License, particularly an Amenity-Integrated License, offers access to private living spaces combined with shared communal amenities such as kitchens, lounges, and coworking areas. This hybrid arrangement enhances community interaction and flexibility, catering to modern renters seeking both privacy and social engagement in amenity-rich environments.
Community Living Charter
Lease agreements establish traditional tenancy rights and long-term property occupation, while coliving licenses emphasize flexible terms and shared community spaces under a Community Living Charter that outlines resident responsibilities, communal etiquette, and maintenance of common areas. This charter fosters a cooperative living environment by promoting mutual respect, conflict resolution mechanisms, and collective decision-making among tenants.
Lease Agreement vs Coliving License Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com