Brick-and-mortar stores offer customers tangible product experiences and immediate purchase gratification, while dark stores operate exclusively as fulfillment centers for online orders, optimizing inventory management and delivery speed. Retailers leverage dark stores to meet growing e-commerce demands without sacrificing the physical store experience. Combining both models enhances supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction across multiple shopping channels.
Table of Comparison
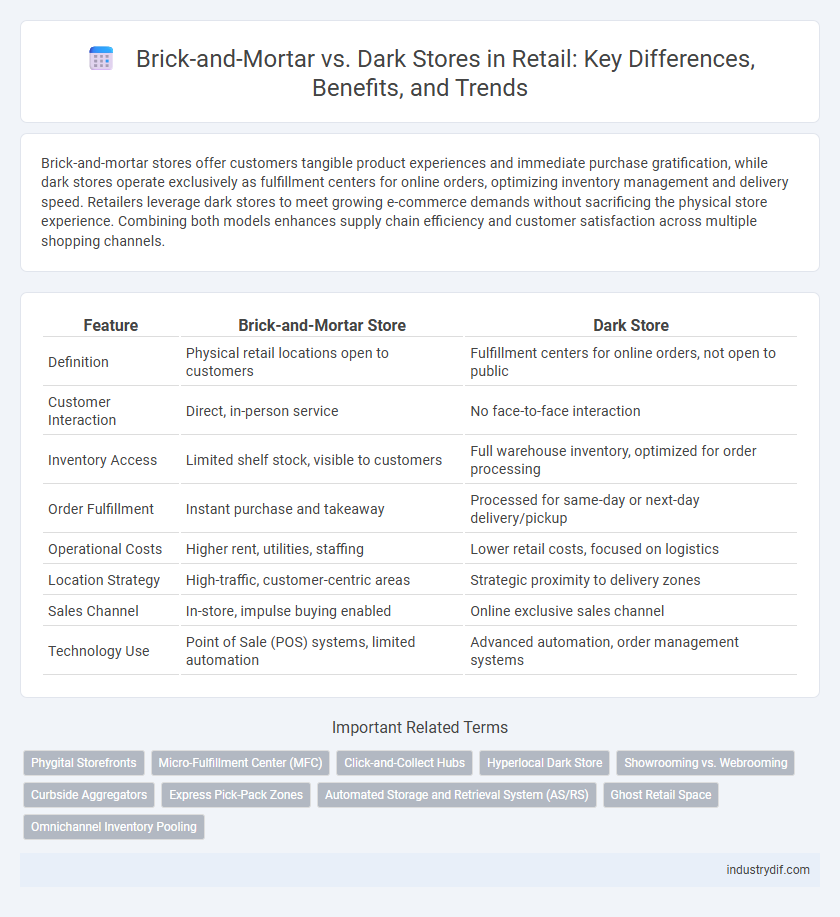
| Feature | Brick-and-Mortar Store | Dark Store |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical retail locations open to customers | Fulfillment centers for online orders, not open to public |
| Customer Interaction | Direct, in-person service | No face-to-face interaction |
| Inventory Access | Limited shelf stock, visible to customers | Full warehouse inventory, optimized for order processing |
| Order Fulfillment | Instant purchase and takeaway | Processed for same-day or next-day delivery/pickup |
| Operational Costs | Higher rent, utilities, staffing | Lower retail costs, focused on logistics |
| Location Strategy | High-traffic, customer-centric areas | Strategic proximity to delivery zones |
| Sales Channel | In-store, impulse buying enabled | Online exclusive sales channel |
| Technology Use | Point of Sale (POS) systems, limited automation | Advanced automation, order management systems |
Defining Brick-and-Mortar and Dark Stores
Brick-and-mortar stores are physical retail locations where customers can browse and purchase products in person, creating a tactile and immediate shopping experience. Dark stores function as fulfillment centers designed exclusively for online orders, optimized for rapid picking and delivery rather than in-store customer interaction. The rise of e-commerce has amplified the role of dark stores, enabling retailers to meet growing demand for quick home delivery while brick-and-mortar outlets focus on experiential shopping.
Historical Evolution of Retail Formats
Brick-and-mortar stores historically dominated retail, offering physical shopping experiences since the early 20th century and evolving through innovations like department stores and shopping malls. The rise of e-commerce in the 2000s spurred the development of dark stores, specialized retail outlets not open to the public, designed to fulfill online orders efficiently. This shift reflects the changing consumer behavior favoring convenience and speed, driving retailers to integrate dark stores for omnichannel fulfillment and last-mile delivery optimization.
Key Operational Differences
Brick-and-mortar stores require extensive customer-facing staff and inventory management on-site, demanding significant floor space and visual merchandising efforts. Dark stores operate solely as fulfillment centers, optimizing layout for rapid picking and packing, reducing customer interaction needs while increasing order accuracy and speed. The operational focus shifts from in-store customer experience in brick-and-mortar to logistical efficiency and last-mile delivery optimization in dark stores.
Customer Experience Comparison
Brick-and-mortar stores offer tactile product interaction and immediate purchase gratification, enhancing sensory engagement and personal service that drives customer loyalty. Dark stores optimize online order fulfillment with faster delivery times and better inventory accuracy, improving convenience and satisfaction for digital shoppers. Customer experience in retail increasingly benefits from integrating physical presence with efficient digital fulfillment to meet evolving consumer expectations.
Inventory Management Strategies
Brick-and-mortar stores rely on real-time inventory tracking to manage in-store product availability and reduce stockouts, utilizing point-of-sale data to optimize reorder cycles. Dark stores prioritize centralized inventory control with integrated warehouse management systems (WMS) to fulfill online orders quickly, emphasizing accuracy in picking and packing processes. Both models benefit from demand forecasting algorithms and automated replenishment systems to enhance inventory turnover and minimize holding costs.
Fulfillment and Delivery Models
Brick-and-mortar stores primarily rely on in-store fulfillment models, where customers physically select and purchase products, supporting immediate pickup but often limited by store hours and stock visibility. Dark stores operate exclusively as fulfillment centers without customer access, optimizing inventory management and enabling rapid delivery or curbside pickup with streamlined order processing systems. Delivery models for dark stores leverage advanced logistics and last-mile delivery networks to ensure faster shipping times compared to traditional retail stores.
Cost Structure Analysis
Brick-and-mortar stores incur higher fixed costs due to rent, utilities, and in-store staff, while dark stores reduce overhead with smaller spaces optimized for online order fulfillment and fewer on-site employees. Inventory management in dark stores is often more efficient, lowering carrying costs and minimizing waste through streamlined stock control processes. Operational expenses favor dark stores by leveraging technology and automation, resulting in cost savings that can improve profit margins compared to traditional retail outlets.
Technological Integration in Retail
Brick-and-mortar stores are increasingly integrating advanced technologies like AI-powered inventory management, augmented reality for enhanced customer experience, and IoT sensors to optimize in-store operations. Dark stores leverage automation and real-time data analytics to streamline order fulfillment and reduce delivery times, often employing robotic systems and sophisticated warehouse management software. The convergence of these technological innovations drives efficiency, personalized service, and seamless omnichannel retail strategies.
Market Trends Influencing Store Formats
Retail market trends reveal a growing shift from traditional brick-and-mortar stores to dark stores as consumer demand for faster delivery and online shopping convenience rises. Dark stores, optimized for inventory management and last-mile logistics, are expanding rapidly in urban areas where e-commerce penetration is high. Retailers increasingly adopt hybrid models combining physical stores with dark store capabilities to enhance operational efficiency and meet evolving customer expectations.
Future Outlook for Brick-and-Mortar and Dark Stores
Brick-and-mortar stores are evolving by integrating digital technologies and personalized experiences to enhance customer engagement and compete with the convenience of e-commerce. Dark stores, optimized for online order fulfillment, are expanding rapidly to meet the growing demand for fast delivery and contactless shopping. The future retail landscape predicts a hybrid model where physical stores serve as experience centers while dark stores focus on efficient last-mile logistics.
Related Important Terms
Phygital Storefronts
Phygital storefronts combine the tangible experience of brick-and-mortar retail with the efficiency and convenience of dark stores, enabling retailers to optimize inventory management and enhance customer engagement. This hybrid model leverages real-time data analytics and seamless online-to-offline integration to deliver personalized shopping experiences, driving higher conversion rates and improved operational agility.
Micro-Fulfillment Center (MFC)
Micro-fulfillment centers (MFCs) optimize inventory management and speed up order fulfillment by leveraging automation within compact spaces, supporting both brick-and-mortar retailers and dark stores. Integrating MFCs enhances supply chain efficiency and enables faster last-mile delivery, meeting consumer demand for convenience in retail environments.
Click-and-Collect Hubs
Click-and-collect hubs in brick-and-mortar stores offer customers immediate product access and enhance in-store foot traffic, while dark stores optimize inventory fulfillment and speed online order processing without traditional retail display constraints. Retailers balancing these models leverage dark stores for efficient logistics and click-and-collect points to improve customer convenience and reduce last-mile delivery costs.
Hyperlocal Dark Store
Hyperlocal dark stores optimize inventory for rapid order fulfillment within a defined radius, reducing last-mile delivery time compared to traditional brick-and-mortar retail outlets. These strategically located facilities leverage data analytics and local demand patterns to enhance product availability and customer satisfaction in high-density urban areas.
Showrooming vs. Webrooming
Brick-and-mortar stores serve as physical showrooms enabling customers to engage in showrooming, where they inspect products in-store before purchasing online for better deals. Conversely, dark stores optimize webrooming by facilitating online product research with quick delivery options, catering to customers who explore products digitally and complete purchases in physical locations.
Curbside Aggregators
Curbside aggregators bridge the gap between brick-and-mortar retailers and dark stores by offering rapid order fulfillment and seamless pickup options, enhancing customer convenience and operational efficiency. Leveraging physical store inventories, they optimize last-mile delivery while reducing dependency on traditional retail spaces.
Express Pick-Pack Zones
Express pick-pack zones in brick-and-mortar stores enable rapid order fulfillment by integrating customer shopping with immediate product picking, enhancing same-day delivery capabilities. Dark stores, optimized solely for online order processing, utilize these zones to streamline inventory management and minimize picking time, driving efficiency in e-commerce fulfillment.
Automated Storage and Retrieval System (AS/RS)
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS) in brick-and-mortar stores enhance inventory management by enabling rapid, accurate product handling and reducing labor costs, which improves in-store customer service. Dark stores leverage AS/RS to streamline order fulfillment, increase picking efficiency, and support same-day delivery, making them highly effective for e-commerce operations and minimizing last-mile logistics challenges.
Ghost Retail Space
Ghost retail spaces, often referred to as dark stores, function exclusively as fulfillment centers without physical customer access, optimizing inventory management and accelerating delivery times for e-commerce orders. Unlike traditional brick-and-mortar stores that prioritize in-person shopping experiences, dark stores leverage advanced logistics and localized distribution to meet the growing demand for rapid online order fulfillment.
Omnichannel Inventory Pooling
Omnichannel inventory pooling integrates stock from both brick-and-mortar stores and dark stores, enabling retailers to fulfill orders efficiently across channels while reducing inventory redundancy and improving customer satisfaction. This approach leverages physical store locations as mini-warehouses alongside dedicated dark stores, optimizing product availability and delivery speed in the competitive retail landscape.
Brick-and-Mortar vs Dark Store Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com