SKU rationalization focuses on reducing the number of stock keeping units to eliminate underperforming products and improve inventory efficiency. Assortment optimization strategically selects the right mix of products to meet customer demand and maximize sales across channels. Both approaches enhance retail profitability but target different aspects of product management and customer satisfaction.
Table of Comparison
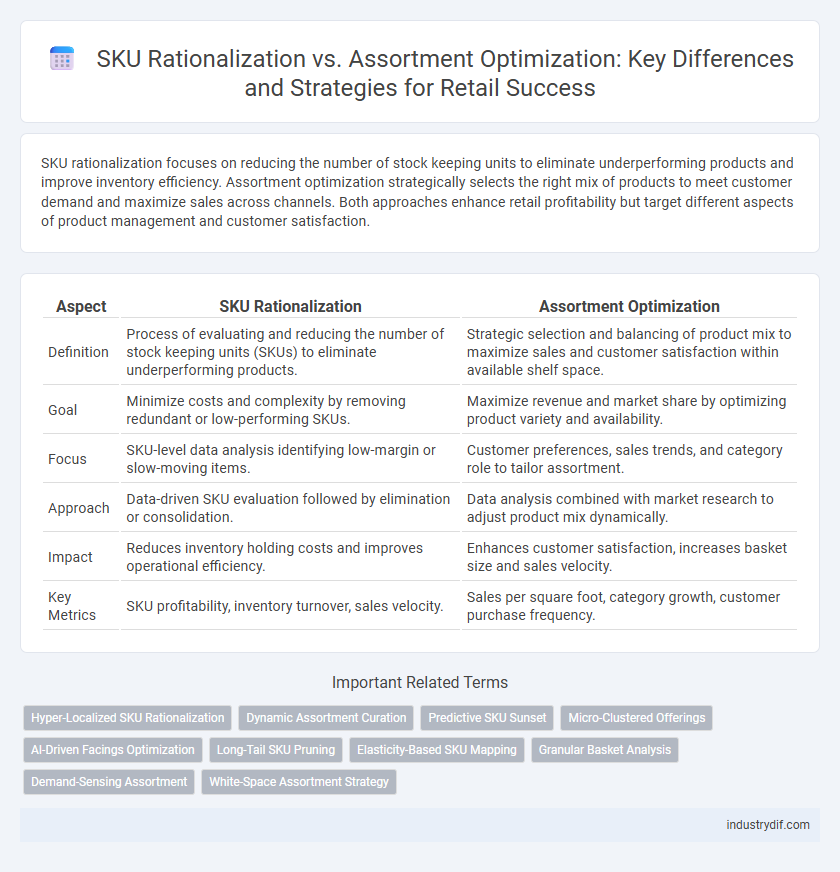
| Aspect | SKU Rationalization | Assortment Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of evaluating and reducing the number of stock keeping units (SKUs) to eliminate underperforming products. | Strategic selection and balancing of product mix to maximize sales and customer satisfaction within available shelf space. |
| Goal | Minimize costs and complexity by removing redundant or low-performing SKUs. | Maximize revenue and market share by optimizing product variety and availability. |
| Focus | SKU-level data analysis identifying low-margin or slow-moving items. | Customer preferences, sales trends, and category role to tailor assortment. |
| Approach | Data-driven SKU evaluation followed by elimination or consolidation. | Data analysis combined with market research to adjust product mix dynamically. |
| Impact | Reduces inventory holding costs and improves operational efficiency. | Enhances customer satisfaction, increases basket size and sales velocity. |
| Key Metrics | SKU profitability, inventory turnover, sales velocity. | Sales per square foot, category growth, customer purchase frequency. |
Understanding SKU Rationalization in Retail
SKU rationalization in retail involves analyzing and reducing the number of stock-keeping units (SKUs) to eliminate underperforming or redundant products, thereby improving inventory turnover and reducing carrying costs. This process leverages sales data, profit margins, and customer demand patterns to identify SKUs that contribute least to overall profitability. By streamlining the product range, retailers can enhance operational efficiency, optimize shelf space, and improve supply chain management.
Defining Assortment Optimization
Assortment optimization in retail involves strategically selecting the right mix of products to maximize sales, profitability, and customer satisfaction across various store formats and customer segments. This process uses data analytics to analyze consumer demand, inventory levels, and market trends, ensuring an optimal balance between variety and inventory costs. Unlike SKU rationalization, which focuses on reducing redundant or low-performing items, assortment optimization aims to enhance overall product relevance and availability to improve retail performance.
Key Differences Between SKU Rationalization and Assortment Optimization
SKU rationalization focuses on reducing the number of stock keeping units to eliminate underperforming products and improve inventory efficiency, while assortment optimization aims to select the best mix of products to maximize sales and meet customer preferences. SKU rationalization primarily targets cost reduction and inventory turnover, whereas assortment optimization emphasizes market demand analysis and consumer behavior insights. Both strategies rely on data analytics but serve distinct objectives within retail inventory management.
Importance of SKU Rationalization for Inventory Management
SKU Rationalization is crucial for effective inventory management as it reduces excess stock and minimizes carrying costs by eliminating underperforming or redundant items. This process enhances demand forecasting accuracy and improves stock turnover rates, leading to better shelf space utilization and increased profitability. Unlike Assortment Optimization, which focuses on selecting the best mix of products to meet customer preferences, SKU Rationalization directly streamlines inventory to prevent overstock and stockouts.
Assortment Optimization Strategies for Retailers
Assortment optimization strategies for retailers involve analyzing sales data, customer preferences, and market trends to curate the most relevant and profitable product mix. Techniques include clustering similar SKUs, leveraging predictive analytics, and balancing breadth versus depth to enhance inventory turnover and customer satisfaction. Effective assortment optimization drives increased revenue by aligning product offerings with consumer demand while minimizing excess stock and markdowns.
Benefits of Effective SKU Rationalization
Effective SKU rationalization reduces inventory carrying costs by eliminating underperforming products, thereby improving cash flow and maximizing profitability. It enhances supply chain efficiency and minimizes complexity, allowing retailers to focus on high-demand items that drive sales growth. Streamlining SKUs also improves shelf space utilization and customer satisfaction by presenting a more targeted and relevant product assortment.
Enhancing Customer Experience through Assortment Optimization
Assortment optimization strategically curates product selections to closely align with customer preferences, driving increased satisfaction and loyalty. Unlike SKU rationalization, which primarily reduces inventory complexity by eliminating underperforming items, assortment optimization balances variety and depth to meet diverse consumer demands effectively. Retailers leveraging assortment optimization see improved sales conversion rates and enhanced shopper experiences through tailored product availability.
Data-Driven Approaches to SKU Rationalization
Data-driven approaches to SKU rationalization leverage sales analytics, inventory turnover rates, and customer demand patterns to identify underperforming products and streamline the product assortment. Retailers use machine learning algorithms and predictive modeling to forecast SKU profitability, reduce excess inventory, and enhance supply chain efficiency. Integrating point-of-sale data with market trends enables more precise decision-making, ultimately improving margins and operational agility.
Measuring Success: KPIs for SKU and Assortment Optimization
Measuring success in SKU rationalization involves tracking KPIs such as inventory turnover, sales per SKU, and carrying costs to identify underperforming products and streamline inventory. Assortment optimization effectiveness is evaluated using metrics like gross margin return on investment (GMROI), customer retention rates, and conversion rates to ensure the product mix aligns with consumer demand and maximizes profitability. Combining these KPIs provides retailers with clear insights into inventory efficiency and customer satisfaction, driving data-informed decisions in merchandise planning.
Best Practices for Implementing SKU Rationalization and Assortment Optimization
Effective SKU rationalization requires detailed sales data analysis and clear criteria for product performance, enabling retailers to eliminate underperforming SKUs and reduce inventory costs. Assortment optimization benefits from leveraging customer insights and market trends to tailor product mixes that maximize sales and improve shelf space utilization. Consistent monitoring and cross-functional collaboration ensure that both strategies align with business goals, driving profitability and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Related Important Terms
Hyper-Localized SKU Rationalization
Hyper-localized SKU rationalization focuses on analyzing sales data and customer preferences at a granular geographic level to eliminate underperforming SKUs, thereby enhancing inventory efficiency and reducing carrying costs. It complements assortment optimization by tailoring product selections to specific local markets, driving higher turnover and improved customer satisfaction.
Dynamic Assortment Curation
SKU rationalization reduces excess inventory by identifying underperforming products, while assortment optimization enhances sales through dynamic assortment curation that adapts to consumer preferences and seasonal trends in real-time. Dynamic assortment curation leverages data analytics and AI to tailor product selections, maximizing revenue and improving customer satisfaction by offering relevant, timely options.
Predictive SKU Sunset
Predictive SKU Sunset leverages advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to identify underperforming SKUs that contribute to inventory inefficiencies and reduced profitability in retail operations. By integrating this approach within SKU Rationalization, retailers can streamline their product assortment, enhance inventory turnover, and optimize shelf space allocation for maximum sales impact.
Micro-Clustered Offerings
SKU Rationalization reduces inventory complexity by eliminating underperforming products, while Assortment Optimization focuses on tailoring product mixes to specific micro-clustered customer segments for maximum relevance. Micro-clustered offerings leverage detailed consumer data analytics to customize assortments that enhance sales efficiency and improve customer satisfaction in localized retail environments.
AI-Driven Facings Optimization
AI-driven facings optimization leverages machine learning algorithms to dynamically adjust product placements based on real-time sales data and consumer behavior, enhancing SKU rationalization by identifying underperforming items for removal. This approach streamlines assortment optimization by maximizing shelf space efficiency and boosting overall category profitability through predictive analytics and automated decision-making.
Long-Tail SKU Pruning
Long-tail SKU pruning reduces inventory complexity by eliminating underperforming products with low sales volume, enhancing overall profitability and operational efficiency. Assortment optimization uses data analytics to balance product variety and demand, ensuring a tailored inventory that maximizes customer satisfaction and shelf space utilization.
Elasticity-Based SKU Mapping
Elasticity-based SKU mapping enhances SKU rationalization by identifying products with overlapping demand elasticity, allowing retailers to eliminate underperforming SKUs while maintaining overall category revenue. This method optimizes assortment by focusing on price sensitivity and customer preference, ensuring a balanced inventory that maximizes sales and reduces stock redundancy.
Granular Basket Analysis
SKU rationalization streamlines inventory by identifying underperforming products through granular basket analysis that examines individual purchase patterns and product affinities. Assortment optimization leverages this detailed data to curate product selections tailored to specific customer segments, enhancing basket size and overall sales efficiency.
Demand-Sensing Assortment
SKU rationalization streamlines inventory by eliminating underperforming products, improving operational efficiency and reducing carrying costs. Demand-sensing assortment leverages real-time data analytics to dynamically adjust product offerings, enhancing customer satisfaction and driving sales through precise demand forecasting.
White-Space Assortment Strategy
SKU rationalization reduces inventory complexity by eliminating underperforming products, while assortment optimization focuses on strategically expanding offerings to capture market opportunities. White-space assortment strategy identifies gaps in current product lines, enabling retailers to introduce new SKUs that meet unmet customer needs and drive incremental sales growth.
SKU Rationalization vs Assortment Optimization Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com