Supply chain efficiency is crucial for retail businesses aiming to meet customer demand swiftly and reduce operational costs. Dark stores serve as specialized fulfillment centers that streamline last-mile delivery by acting as localized inventory hubs, enhancing order accuracy and speed. Integrating dark stores into the supply chain optimizes inventory management and supports omnichannel retail strategies.
Table of Comparison
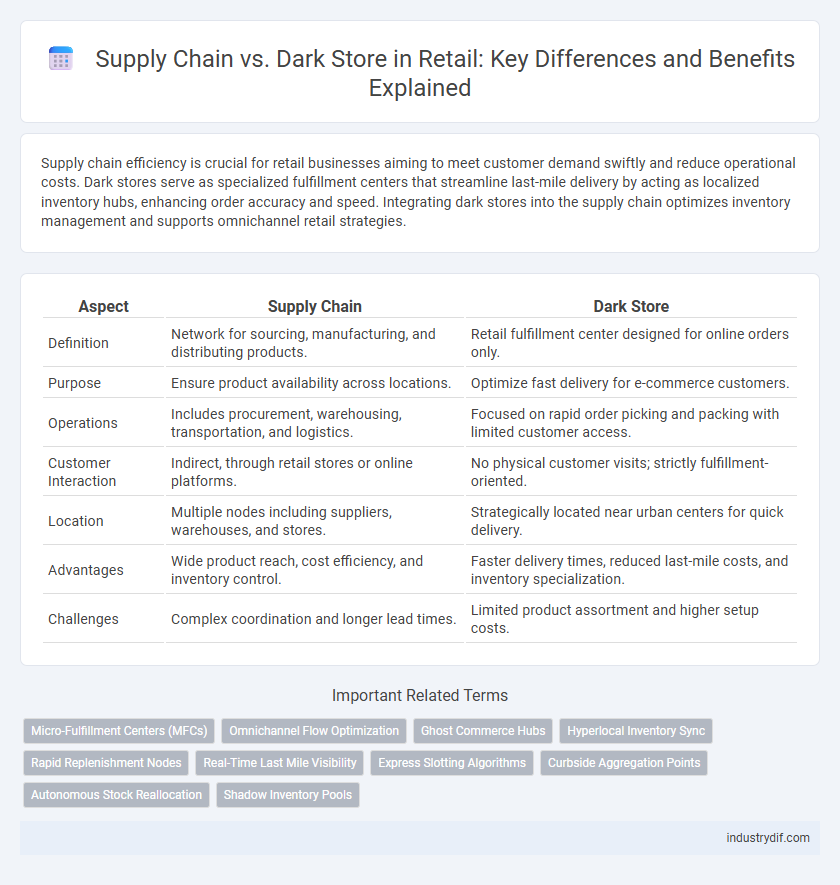
| Aspect | Supply Chain | Dark Store |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network for sourcing, manufacturing, and distributing products. | Retail fulfillment center designed for online orders only. |
| Purpose | Ensure product availability across locations. | Optimize fast delivery for e-commerce customers. |
| Operations | Includes procurement, warehousing, transportation, and logistics. | Focused on rapid order picking and packing with limited customer access. |
| Customer Interaction | Indirect, through retail stores or online platforms. | No physical customer visits; strictly fulfillment-oriented. |
| Location | Multiple nodes including suppliers, warehouses, and stores. | Strategically located near urban centers for quick delivery. |
| Advantages | Wide product reach, cost efficiency, and inventory control. | Faster delivery times, reduced last-mile costs, and inventory specialization. |
| Challenges | Complex coordination and longer lead times. | Limited product assortment and higher setup costs. |
Defining Supply Chain in Retail
Supply chain in retail encompasses the entire process of sourcing, producing, and delivering products from manufacturers to consumers, integrating suppliers, warehouses, transportation, and inventory management. Efficient supply chain management reduces costs, enhances product availability, and improves customer satisfaction by ensuring timely and accurate order fulfillment. Key components include demand forecasting, procurement, logistics, and distribution, all critical for maintaining competitive advantage in retail markets.
Understanding Dark Store Concepts
Dark stores operate as localized distribution centers designed exclusively for online order fulfillment, streamlining inventory management and accelerating delivery times. Unlike traditional retail supply chains focused on in-store customer experiences, dark stores optimize product accessibility and processing efficiency in densely populated urban areas. These concepts revolutionize retail logistics by reducing last-mile delivery challenges and enabling retailers to adapt swiftly to e-commerce demand fluctuations.
Key Differences: Supply Chain vs Dark Store
Supply chain in retail involves the end-to-end process of sourcing, manufacturing, and distributing products to physical stores or customers, emphasizing logistics, inventory management, and supplier coordination. Dark stores operate as fulfillment centers without customer-facing retail spaces, designed specifically for online order processing and rapid delivery, optimizing inventory for e-commerce demand. Key differences include supply chain's broad operational scope versus dark stores' specialized function in last-mile delivery and order fulfillment.
Impact on Inventory Management
Supply chain efficiency directly influences inventory accuracy and turnover rates, minimizing stockouts and overstocks in retail operations. Dark stores optimize last-mile delivery by serving as dedicated fulfillment centers, enabling faster order processing and better real-time inventory visibility. Combining supply chain coordination with dark store utilization enhances inventory management by synchronizing stock levels across multiple channels and reducing fulfillment delays.
Order Fulfillment Strategies Compared
Supply chain management in retail centers on optimizing the flow of goods from suppliers to customers, emphasizing inventory control, distribution efficiency, and cost reduction to ensure timely order fulfillment. Dark stores function as localized fulfillment hubs designed exclusively for online orders, leveraging streamlined inventory and rapid picking processes to enhance last-mile delivery speed. Compared to traditional supply chain models, dark stores prioritize quick order processing and proximity to customers, significantly improving same-day delivery rates and reducing fulfillment complexity.
Technological Integration in Both Models
Technological integration in retail supply chains enhances inventory accuracy, demand forecasting, and real-time tracking through advanced ERP systems and IoT devices. Dark stores utilize automation technologies and AI-driven order fulfillment to streamline operations and enable rapid delivery in urban environments. Both models leverage data analytics and cloud computing to optimize resource allocation and improve overall efficiency in meeting consumer demand.
Advantages of Traditional Supply Chains
Traditional supply chains in retail offer advantages such as established supplier relationships, enabling consistent inventory management and reliable product availability. These supply chains benefit from integrated logistics networks that support faster replenishment cycles compared to dark stores. The physical presence of warehouses and distribution centers enhances transparency and quality control throughout the supply chain process.
Benefits of Adopting Dark Stores
Dark stores enhance supply chain efficiency by streamlining last-mile delivery and reducing order fulfillment time. They enable retailers to optimize inventory management through centralized stock allocation, minimizing out-of-stock situations and excess warehousing costs. Implementing dark stores increases order accuracy and improves customer satisfaction by accelerating delivery speed and maintaining product availability.
Challenges Faced by Retailers
Retailers face significant challenges in managing supply chains due to demand volatility, inventory inaccuracies, and last-mile delivery complexities. Dark stores complicate these issues by requiring precise coordination between online order fulfillment and physical stock availability, often leading to increased operational costs. Integrating real-time data analytics and scalable logistics solutions is critical to overcoming these hurdles and maintaining customer satisfaction.
Future Trends in Retail Logistics
Supply chain innovations increasingly integrate dark store models to enhance last-mile delivery efficiency and reduce fulfillment times in urban areas. Advanced data analytics and AI-driven inventory management optimize stock allocation between traditional distribution centers and dark stores, minimizing delays and out-of-stock incidents. Future retail logistics will rely heavily on seamless coordination between supply chain networks and dark stores to meet growing consumer demand for rapid, contactless delivery.
Related Important Terms
Micro-Fulfillment Centers (MFCs)
Micro-Fulfillment Centers (MFCs) streamline retail supply chains by enabling faster order processing and reducing last-mile delivery costs through localized inventory storage. Unlike traditional dark stores, MFCs integrate automation and real-time inventory management to optimize stock levels and enhance fulfillment speed in urban areas.
Omnichannel Flow Optimization
Integrating dark stores into retail supply chains enhances omnichannel flow optimization by enabling faster order fulfillment and reducing last-mile delivery times through strategically localized inventory. Leveraging real-time data analytics across supply chain nodes and dark store operations ensures seamless inventory visibility and synchronized cross-channel demand management.
Ghost Commerce Hubs
Ghost commerce hubs, including dark stores, optimize retail supply chains by serving as strategic fulfillment centers that expedite last-mile delivery and reduce inventory holding costs. These hubs leverage real-time data analytics and automation to synchronize demand forecasting with efficient product allocation, enhancing overall supply chain responsiveness and customer satisfaction.
Hyperlocal Inventory Sync
Hyperlocal inventory sync enhances supply chain efficiency by integrating real-time stock data between warehouses and dark stores, enabling faster fulfillment and accurate availability for hyperlocal delivery. This synchronization reduces stockouts and overstock scenarios, optimizing inventory across retail nodes to meet immediate customer demand within specific localities.
Rapid Replenishment Nodes
Rapid replenishment nodes in retail supply chains enhance inventory turnover by enabling quick restocking through strategically located dark stores designed for efficient order fulfillment. Integrating dark stores within supply chain networks reduces lead times and improves delivery speed, leveraging localized inventory to meet rising consumer demand for faster service.
Real-Time Last Mile Visibility
Real-time last mile visibility in retail supply chains enhances the efficiency of order fulfillment by tracking inventory flow from dark stores directly to consumers, minimizing delays and improving delivery accuracy. Integrating advanced IoT sensors and AI analytics enables retailers to monitor shipments and adjust routes dynamically, optimizing customer satisfaction and operational costs.
Express Slotting Algorithms
Express slotting algorithms optimize supply chain efficiency by dynamically assigning inventory to dark stores, reducing delivery times and improving order accuracy. By leveraging real-time data and predictive analytics, these algorithms enhance inventory distribution, enabling rapid fulfillment in high-demand retail environments.
Curbside Aggregation Points
Curbside aggregation points in retail supply chains accelerate order fulfillment by consolidating goods from dark stores, enabling seamless and efficient customer pickups without entering physical stores. This integration optimizes last-mile delivery, reduces operational costs, and enhances the overall shopping experience by bridging centralized inventory management with localized consumer demand.
Autonomous Stock Reallocation
Autonomous stock reallocation leverages AI-driven analytics to dynamically shift inventory between supply chain nodes and dark stores, optimizing product availability and reducing delivery times. This technology enhances retail efficiency by enabling real-time demand response, minimizing overstock and stockouts in both traditional warehouses and dark store environments.
Shadow Inventory Pools
Shadow inventory pools in retail supply chains represent unseen stock held in dark stores, enabling rapid fulfillment without traditional warehouse delays. Leveraging these hidden inventory reserves enhances last-mile delivery efficiency and reduces out-of-stock scenarios by dynamically reallocating goods closer to point-of-sale demand.
Supply Chain vs Dark Store Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com