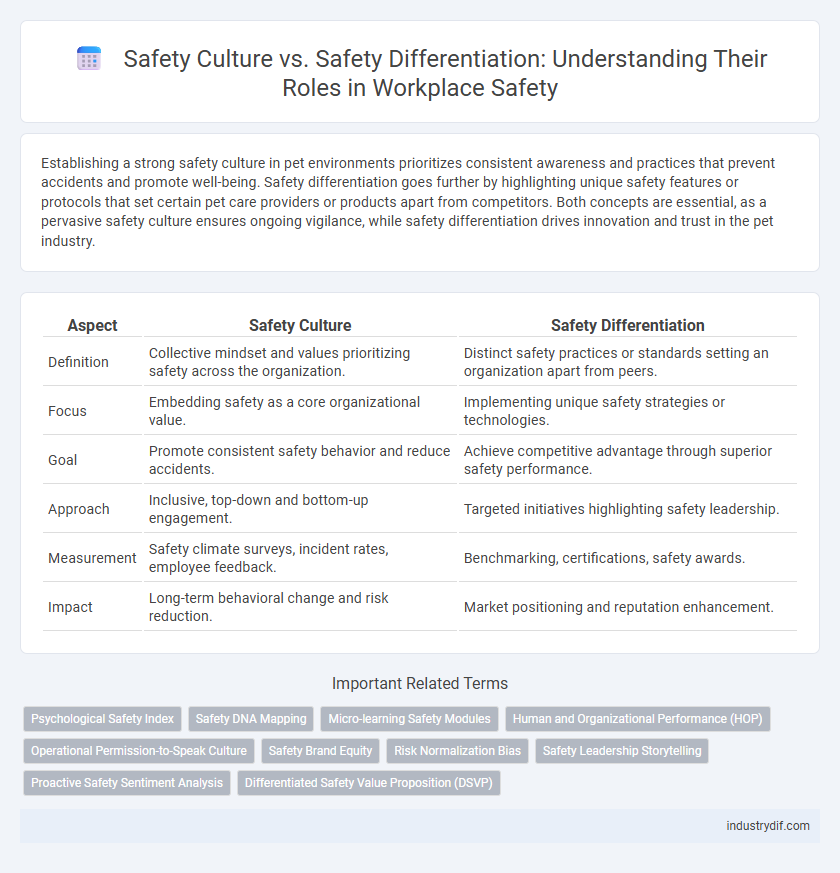
Establishing a strong safety culture in pet environments prioritizes consistent awareness and practices that prevent accidents and promote well-being. Safety differentiation goes further by highlighting unique safety features or protocols that set certain pet care providers or products apart from competitors. Both concepts are essential, as a pervasive safety culture ensures ongoing vigilance, while safety differentiation drives innovation and trust in the pet industry.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Safety Culture | Safety Differentiation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collective mindset and values prioritizing safety across the organization. | Distinct safety practices or standards setting an organization apart from peers. |
| Focus | Embedding safety as a core organizational value. | Implementing unique safety strategies or technologies. |
| Goal | Promote consistent safety behavior and reduce accidents. | Achieve competitive advantage through superior safety performance. |
| Approach | Inclusive, top-down and bottom-up engagement. | Targeted initiatives highlighting safety leadership. |
| Measurement | Safety climate surveys, incident rates, employee feedback. | Benchmarking, certifications, safety awards. |
| Impact | Long-term behavioral change and risk reduction. | Market positioning and reputation enhancement. |
Understanding Safety Culture in the Workplace
Safety culture in the workplace encompasses shared beliefs, values, and practices that prioritize employee well-being and hazard prevention. Developing a strong safety culture requires consistent leadership commitment, open communication, and employee engagement to foster proactive risk management. In contrast, safety differentiation refers to distinct safety practices or standards that set organizations apart, but without a cohesive culture, these measures may lack effectiveness and sustainability.
Defining Safety Differentiation: Key Concepts
Safety differentiation involves identifying and implementing distinct safety practices that set an organization apart in risk management and accident prevention. Key concepts include proactive hazard recognition, continuous employee engagement, and tailored safety training programs that address specific workplace challenges. This approach enhances overall safety culture by fostering a commitment to excellence and accountability at every organizational level.
Core Principles of a Positive Safety Culture
A positive safety culture prioritizes shared values, open communication, and continuous learning to reduce workplace hazards. Core principles include employee engagement, transparent reporting of incidents, and leadership commitment to safety practices. Emphasizing these elements fosters trust and accountability, creating an environment where safety is integral to every operational decision.
Factors Influencing Safety Differentiation Strategies
Safety differentiation strategies are influenced by organizational commitment to hazard recognition, employee engagement levels, and management's responsiveness to incident feedback. Variations in resource allocation, training quality, and communication clarity significantly impact the effectiveness of these strategies. The integration of advanced safety technologies and continuous improvement practices further enhances distinct safety performance outcomes.
Comparing Safety Culture and Safety Differentiation
Safety culture emphasizes shared values, beliefs, and practices promoting consistent safety behavior across all organizational levels, fostering proactive hazard identification and risk management. Safety differentiation distinguishes the varying safety performance and commitment among individuals or teams, highlighting disparities in adherence to protocols and engagement with safety initiatives. Comparing both, safety culture provides a collective framework for safety excellence, while safety differentiation identifies specific areas or groups requiring targeted interventions to enhance overall organizational safety.
Benefits of Promoting a Strong Safety Culture
Promoting a strong safety culture significantly reduces workplace accidents by fostering employee awareness and proactive risk management. Organizations with robust safety cultures experience improved compliance with regulations and enhanced operational efficiency. Investing in safety culture cultivates trust and accountability, leading to sustained organizational resilience and reduced costs associated with incidents.
Challenges in Implementing Safety Differentiation
Implementing safety differentiation faces challenges such as resistance from employees accustomed to uniform safety policies, difficulties in accurately assessing individual risk levels, and potential perceptions of unfairness that can undermine trust. Variability in job roles and environments complicates the establishment of clear criteria, making consistent application of differentiated safety measures problematic. Overcoming these obstacles requires transparent communication, robust data analysis, and ongoing training to ensure safety differentiation enhances rather than detracts from overall safety culture.
Integrating Safety Culture with Differentiation Approaches
Integrating safety culture with differentiation approaches enhances organizational resilience by embedding shared values and behaviors that prioritize risk prevention alongside tailored safety strategies specific to operational contexts. This fusion drives continuous improvement through employee engagement, transparent communication, and adaptive safety practices aligned with unique industry demands. Organizations that successfully combine these elements experience reduced incidents, increased compliance, and a proactive safety mindset that supports both standardization and innovation.
Measuring the Impact: Safety Culture vs. Differentiation Metrics
Measuring the impact of safety culture involves assessing employee attitudes, behaviors, and adherence to safety protocols through surveys and observational data, while safety differentiation metrics focus on quantifiable outcomes such as incident rates, near-miss reports, and compliance statistics. Safety culture metrics provide insights into the underlying psychological and social factors that influence workplace safety, whereas differentiation metrics highlight tangible performance differences across departments or teams. Combining both approaches offers a comprehensive evaluation, enabling organizations to identify gaps and target improvements for stronger overall safety performance.
Future Trends in Workplace Safety Culture and Differentiation
Future trends in workplace safety culture emphasize the integration of advanced technologies like AI and IoT to proactively identify hazards and tailor safety protocols. Safety differentiation will increasingly rely on data analytics and employee engagement metrics to customize training and foster accountability. Organizations adopting these innovations demonstrate measurable reductions in incidents and cultivate resilient, adaptive safety environments.
Related Important Terms
Psychological Safety Index
A robust Safety Culture fosters employee trust and open communication, directly enhancing the Psychological Safety Index by encouraging risk reporting and learning from errors. In contrast, Safety Differentiation emphasizes performance and compliance metrics, which may suppress psychological safety by creating fear of punishment for mistakes.
Safety DNA Mapping
Safety DNA Mapping identifies intrinsic behaviors and attitudes that shape an organization's safety culture, enabling targeted interventions that enhance overall safety performance. Distinguishing safety culture from safety differentiation involves recognizing that while culture reflects shared values and norms, differentiation leverages unique safety competencies to achieve competitive advantages.
Micro-learning Safety Modules
Micro-learning safety modules enhance safety culture by delivering concise, targeted training that reinforces consistent safety behaviors across all organizational levels. Differentiating safety approaches through personalized micro-learning content addresses diverse risk profiles, promoting adaptive and proactive safety practices.
Human and Organizational Performance (HOP)
Safety Culture emphasizes shared values and behaviors promoting proactive risk management, while Safety Differentiation highlights individual accountability and performance metrics within Human and Organizational Performance (HOP) frameworks to optimize workplace safety outcomes. Integrating HOP principles enhances both collective cultural commitment and precise differentiation of safety responsibilities, leading to sustained hazard reduction and operational excellence.
Operational Permission-to-Speak Culture
Operational permission-to-speak culture fosters an inclusive safety environment where every employee feels empowered to voice concerns without fear of retaliation, directly enhancing hazard identification and risk mitigation. Unlike traditional safety differentiation, which categorizes roles and responsibilities, this culture promotes proactive communication across all levels, driving continuous safety improvements and operational excellence.
Safety Brand Equity
Safety brand equity significantly influences organizational trust and employee commitment by embedding safety culture into every operational aspect, creating a reliable and recognizable identity. Unlike safety differentiation, which emphasizes competitive safety features, safety brand equity fosters long-term loyalty through consistent demonstration of safety values and practices.
Risk Normalization Bias
Risk normalization bias within safety culture often leads employees to underestimate hazards as routine, compromising proactive risk management and increasing incident likelihood. Safety differentiation combats this bias by recognizing and addressing varying risk perceptions and behaviors, fostering individualized safety interventions to maintain high awareness and prevent complacency.
Safety Leadership Storytelling
Safety leadership storytelling ingrains a robust safety culture by sharing real-life experiences that highlight the importance of safe practices and accountability. This approach transcends safety differentiation by emotionally connecting teams to safety values, driving consistent behavior change and proactive risk management.
Proactive Safety Sentiment Analysis
Proactive safety sentiment analysis enhances safety culture by systematically monitoring employee attitudes and behaviors toward risk, enabling early identification of safety concerns before incidents occur. This data-driven approach surpasses traditional safety differentiation by fostering continuous engagement and promoting a collective commitment to organizational safety goals.
Differentiated Safety Value Proposition (DSVP)
Differentiated Safety Value Proposition (DSVP) emphasizes unique safety practices tailored to specific organizational risks, enhancing overall safety performance beyond standard Safety Culture norms. By integrating customized safety solutions and measurable outcomes, DSVP drives competitive advantage through targeted risk mitigation and employee engagement.
Safety Culture vs Safety Differentiation Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com