Internet of Things (IoT) refers to interconnected devices that collect and exchange data to perform specific tasks, while Ambient Intelligence (AmI) involves environments embedded with intelligent systems that adapt to users' needs seamlessly. IoT emphasizes device connectivity and data communication, whereas AmI focuses on creating context-aware, responsive surroundings that enhance user experience. Both technologies drive smart environments but differ in their approach to interaction and intelligence deployment.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Internet of Things (IoT) | Ambient Intelligence (AmI) |
|---|---|---|
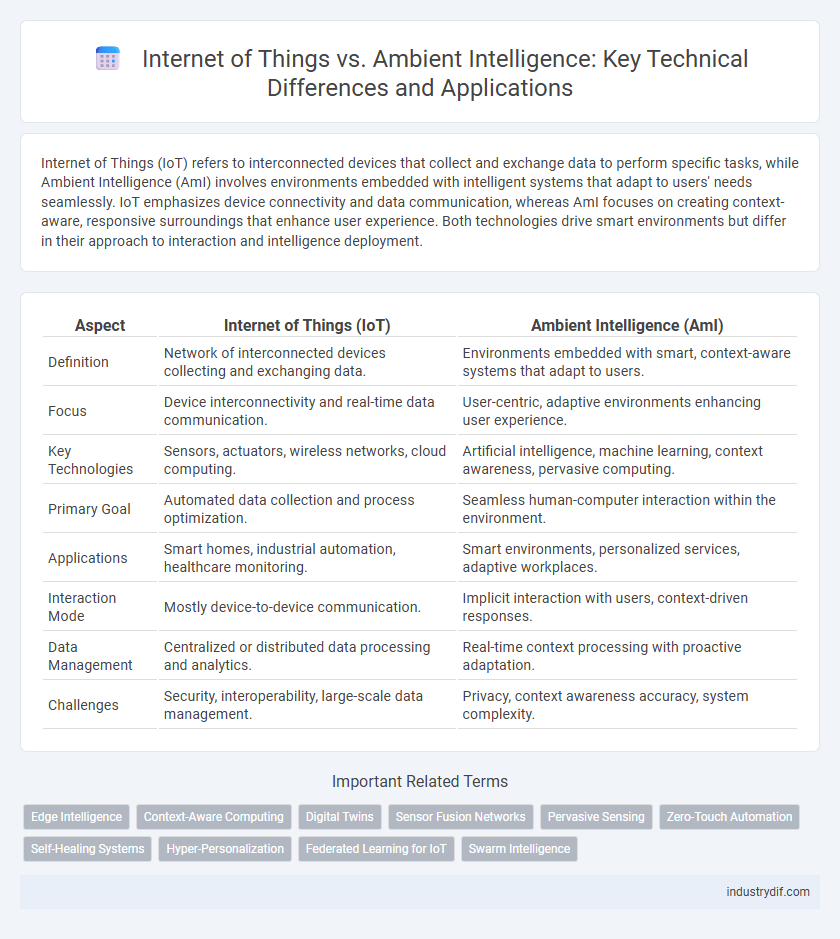
| Definition | Network of interconnected devices collecting and exchanging data. | Environments embedded with smart, context-aware systems that adapt to users. |
| Focus | Device interconnectivity and real-time data communication. | User-centric, adaptive environments enhancing user experience. |
| Key Technologies | Sensors, actuators, wireless networks, cloud computing. | Artificial intelligence, machine learning, context awareness, pervasive computing. |
| Primary Goal | Automated data collection and process optimization. | Seamless human-computer interaction within the environment. |
| Applications | Smart homes, industrial automation, healthcare monitoring. | Smart environments, personalized services, adaptive workplaces. |
| Interaction Mode | Mostly device-to-device communication. | Implicit interaction with users, context-driven responses. |
| Data Management | Centralized or distributed data processing and analytics. | Real-time context processing with proactive adaptation. |
| Challenges | Security, interoperability, large-scale data management. | Privacy, context awareness accuracy, system complexity. |
Defining Internet of Things (IoT) and Ambient Intelligence (AmI)
Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity to collect and exchange data, enabling real-time monitoring and automation across various industries. Ambient Intelligence (AmI) encompasses environments equipped with responsive and adaptive technologies that proactively support human activities by interpreting context and user behavior. While IoT focuses on device connectivity and data transmission, AmI integrates IoT data with AI-driven context awareness to create intuitive, user-centric environments.
Core Technologies Behind IoT and AmI
Core technologies behind IoT encompass wireless sensor networks, cloud computing, and big data analytics, enabling seamless device connectivity and real-time data processing. Ambient Intelligence integrates ubiquitous computing, context-awareness, and machine learning to create adaptive environments that respond intelligently to user needs. Both IoT and AmI leverage advancements in artificial intelligence and edge computing to enhance system autonomy and interoperability.
Key Differences: IoT vs Ambient Intelligence
Internet of Things (IoT) involves interconnected devices collecting and exchanging data to enable automation and remote control, while Ambient Intelligence (AmI) emphasizes context-aware systems that adapt proactively to users' needs in real-time environments. IoT primarily focuses on connectivity and data integration from physical objects, whereas AmI integrates sensing, reasoning, and learning technologies to create intelligent environments tailored to human behavior. Key differences also lie in IoT's device-centric approach versus AmI's user-centric, seamless interaction within smart spaces.
Connectivity and Communication Protocols
Internet of Things (IoT) relies heavily on diverse connectivity options such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and LTE to enable device communication, while Ambient Intelligence (AmI) integrates these protocols with context-aware systems to facilitate seamless, adaptive interaction. IoT emphasizes robust, scalable network architectures to connect heterogeneous devices, whereas AmI focuses on intelligent, real-time data exchange optimized through protocols like MQTT and CoAP for efficient ambient environment responsiveness. Both paradigms leverage IPv6 for extensive addressability, but AmI prioritizes low-latency, secure communication tailored to user-centric context awareness.
Data Processing: Edge, Cloud, and Context-Awareness
IoT systems process data primarily at the edge to enable real-time analytics and reduce latency, while cloud computing offers scalability and deep learning architectures for complex data processing. Ambient Intelligence extends IoT by integrating context-awareness, leveraging sensor fusion and machine learning to adapt system responses dynamically based on environmental and user behavior data. Combining edge computing with cloud resources enhances data throughput and responsiveness, enabling sophisticated ambient intelligence applications that require seamless interaction between devices and context-aware services.
Real-World Applications of IoT and AmI
Internet of Things (IoT) enables seamless connectivity and data exchange among physical devices, revolutionizing smart home systems, industrial automation, and healthcare monitoring. Ambient Intelligence (AmI) extends IoT by integrating context-aware, adaptive environments that anticipate user needs, enhancing personalized experiences in intelligent buildings and urban planning. Real-world applications of IoT and AmI demonstrate improvements in energy efficiency, security, and responsive service delivery across various sectors.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Internet of Things (IoT) devices generate vast amounts of data, making encryption protocols and secure authentication mechanisms critical to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Ambient Intelligence (AmI) environments require context-aware security strategies that adapt to user behavior and environmental changes to maintain privacy while enabling seamless interaction. Both IoT and AmI face challenges in ensuring data integrity, preventing surveillance exploitation, and managing user consent in dynamic, interconnected systems.
Integration Challenges in IoT and AmI Systems
Integration challenges in Internet of Things (IoT) and Ambient Intelligence (AmI) systems include heterogeneous device interoperability, seamless data exchange, and real-time context-aware processing. Ensuring secure communication protocols and managing large-scale, dynamic networks complicate the effective convergence of IoT sensors and AmI environments. Scalability and standardization remain critical barriers, impacting the efficient deployment and maintenance of integrated intelligent systems.
Future Trends in IoT and Ambient Intelligence
Future trends in Internet of Things emphasize edge computing alongside AI integration to enhance real-time data processing and device autonomy. Ambient Intelligence advancements focus on context-aware systems that leverage machine learning and sensor fusion for seamless human-environment interaction. Both domains anticipate growing interoperability standards and heightened cybersecurity measures to support expansive smart ecosystems.
Impact on Industry and Digital Transformation
The Internet of Things (IoT) enables seamless connectivity of devices, driving efficiency and predictive maintenance in industries by collecting real-time data for optimized operations. Ambient Intelligence (AmI) enhances this by integrating context-aware environments that adapt intelligently to human presence and behavior, fostering more intuitive and automated industrial processes. Together, IoT and AmI accelerate digital transformation through smarter resource management, improved decision-making, and enhanced user experience in manufacturing and supply chain sectors.
Related Important Terms
Edge Intelligence
Edge Intelligence enhances Internet of Things (IoT) by enabling real-time data processing and decision-making directly at the device level, reducing latency and bandwidth usage compared to traditional cloud-centric Ambient Intelligence systems. Integrating machine learning algorithms on edge devices transforms ambient environments into proactive and adaptive spaces, driving smarter, context-aware applications.
Context-Aware Computing
Internet of Things (IoT) enables devices to connect and communicate, while Ambient Intelligence (AmI) leverages context-aware computing to create responsive environments by interpreting sensor data and user interactions. Context-aware computing within AmI dynamically adapts system behavior based on real-time context such as location, user activity, and environmental conditions, enhancing personalized automation beyond traditional IoT connectivity.
Digital Twins
Digital Twins play a pivotal role in both Internet of Things (IoT) and Ambient Intelligence by creating real-time digital replicas of physical systems, enabling advanced monitoring, simulation, and predictive maintenance. While IoT focuses on data collection through interconnected devices, Ambient Intelligence leverages this data to provide context-aware, adaptive environments that improve user experiences.
Sensor Fusion Networks
Sensor fusion networks in the Internet of Things consolidate data from multiple sensors to enhance environmental awareness, enabling real-time monitoring and precise decision-making. Ambient intelligence leverages these integrated sensor systems to create adaptive environments that respond dynamically to human presence and contextual changes.
Pervasive Sensing
Pervasive sensing in the Internet of Things (IoT) involves interconnected devices collecting and transmitting data across networks, while Ambient Intelligence (AmI) integrates pervasive sensing with context-aware systems to adapt environments seamlessly. IoT emphasizes data acquisition through sensors, whereas AmI enhances this data with intelligent processing to enable proactive and intuitive user interactions.
Zero-Touch Automation
Internet of Things (IoT) enables interconnected devices to collect and exchange data, while Ambient Intelligence integrates IoT with contextual awareness and adaptive systems for seamless Zero-Touch Automation. Zero-Touch Automation leverages machine learning and AI-driven analytics to autonomously manage and optimize smart environments without human intervention.
Self-Healing Systems
Self-healing systems in Internet of Things (IoT) leverage distributed sensors and real-time data analytics to autonomously detect and repair faults, minimizing downtime and enhancing network resilience. Ambient Intelligence (AmI) extends this concept by integrating context-aware, adaptive environments that proactively optimize system functionality and user experience through seamless interaction between smart devices and their surroundings.
Hyper-Personalization
Internet of Things (IoT) enables hyper-personalization through real-time data collection from interconnected devices, creating tailored user experiences based on precise behavioral patterns. Ambient Intelligence enhances this by integrating context-aware systems that adapt dynamically to users' needs, delivering seamless and intuitive hyper-personalized interactions within smart environments.
Federated Learning for IoT
Federated Learning enhances privacy and efficiency in Internet of Things (IoT) networks by enabling decentralized model training across distributed edge devices without sharing raw data. In Ambient Intelligence systems, Federated Learning supports context-aware environments by aggregating insights from IoT sensors while preserving user data confidentiality and reducing communication overhead.
Swarm Intelligence
Swarm intelligence enhances Ambient Intelligence by enabling decentralized, self-organizing IoT devices to collaboratively adapt and respond to dynamic environments without centralized control. This collective behavior optimizes resource allocation, improves system resilience, and accelerates decision-making in complex Internet of Things deployments.
Internet of Things vs Ambient Intelligence Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com