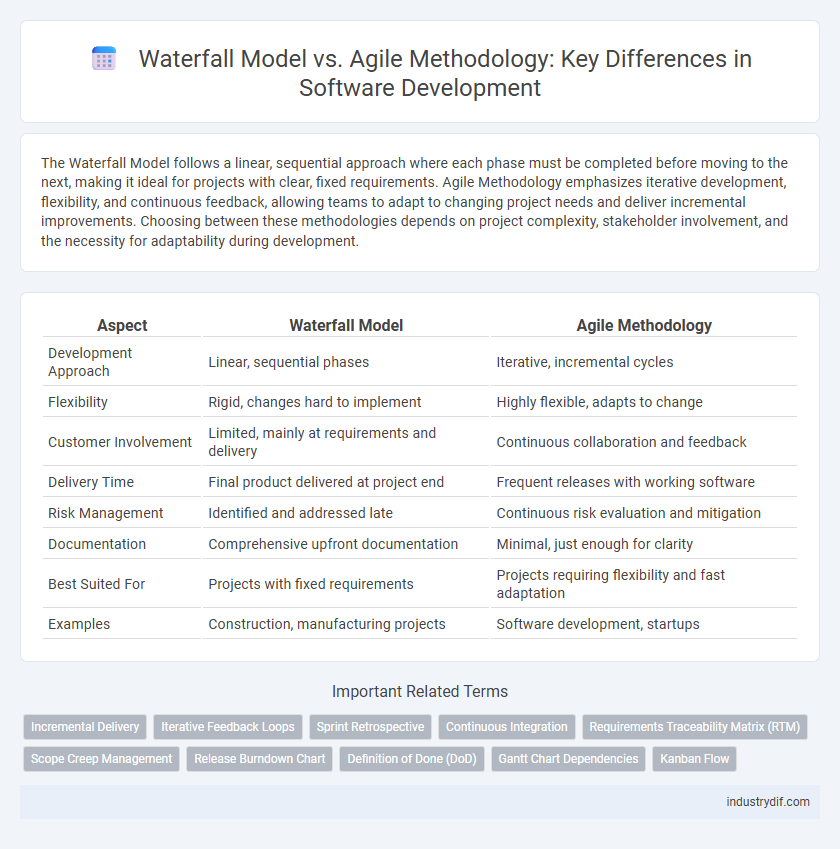
The Waterfall Model follows a linear, sequential approach where each phase must be completed before moving to the next, making it ideal for projects with clear, fixed requirements. Agile Methodology emphasizes iterative development, flexibility, and continuous feedback, allowing teams to adapt to changing project needs and deliver incremental improvements. Choosing between these methodologies depends on project complexity, stakeholder involvement, and the necessity for adaptability during development.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Waterfall Model | Agile Methodology |
|---|---|---|
| Development Approach | Linear, sequential phases | Iterative, incremental cycles |
| Flexibility | Rigid, changes hard to implement | Highly flexible, adapts to change |
| Customer Involvement | Limited, mainly at requirements and delivery | Continuous collaboration and feedback |
| Delivery Time | Final product delivered at project end | Frequent releases with working software |
| Risk Management | Identified and addressed late | Continuous risk evaluation and mitigation |
| Documentation | Comprehensive upfront documentation | Minimal, just enough for clarity |
| Best Suited For | Projects with fixed requirements | Projects requiring flexibility and fast adaptation |
| Examples | Construction, manufacturing projects | Software development, startups |
Introduction to Software Development Methodologies
Waterfall Model follows a sequential design process where each phase, including requirements gathering, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance, is completed before the next begins, making it well-suited for projects with clearly defined requirements. Agile Methodology emphasizes iterative development, continuous feedback, and flexibility, allowing teams to adapt to changing requirements through sprints and regular stakeholder collaboration. Both methodologies play a critical role in software development, with Waterfall offering structure for predictable projects and Agile providing adaptability for dynamic environments.
Overview of the Waterfall Model
The Waterfall Model is a linear and sequential software development process characterized by distinct phases such as requirement analysis, system design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance. Each phase must be completed before the next begins, making it highly structured and easy to manage for projects with well-defined requirements. This model is best suited for projects where changes are minimal and predictable, offering clear documentation and progress tracking throughout the development lifecycle.
Key Principles of Agile Methodology
Agile methodology emphasizes iterative development, continuous feedback, and adaptive planning, promoting flexibility and collaboration among cross-functional teams. It prioritizes customer involvement and delivers working software in small, incremental releases to ensure constant value and rapid response to change. Embracing principles such as transparency, frequent communication, and empowered team members enables Agile to effectively manage evolving project requirements compared to the linear, sequential approach of the Waterfall model.
Waterfall Model: Phases and Workflow
The Waterfall Model follows a linear and sequential approach, consisting of distinct phases such as Requirements, Design, Implementation, Testing, Deployment, and Maintenance. Each phase must be completed before moving to the next, ensuring a structured workflow with clear milestones and documentation. This model is highly effective for projects with well-defined requirements and minimal expected changes during the development process.
Agile Methodology: Frameworks and Practices
Agile Methodology encompasses frameworks such as Scrum, Kanban, and Extreme Programming (XP), each promoting iterative development, continuous feedback, and adaptive planning. Key practices include daily stand-ups, sprint reviews, and cross-functional team collaboration to enhance flexibility and responsiveness to change. Agile's emphasis on incremental delivery and customer involvement drives improved product quality and faster time-to-market compared to traditional Waterfall approaches.
Pros and Cons of the Waterfall Model
The Waterfall Model features a linear, sequential approach making it easy to manage and understand, especially for projects with well-defined requirements and scope. Its major drawbacks include limited flexibility to accommodate changes once the process is underway, and late-stage testing often leads to costly revisions. This methodology suits projects with fixed deliverables but can struggle with dynamic, evolving requirements common in software development.
Advantages and Challenges of Agile Methodology
Agile methodology enhances project flexibility by promoting iterative development and continuous stakeholder collaboration, allowing for faster adaptation to changing requirements. Its advantages include improved product quality through frequent testing and integration, as well as increased customer satisfaction due to regular feedback loops. Challenges involve managing scope creep, ensuring team discipline in adhering to agile principles, and the need for experienced facilitators to navigate dynamic project environments effectively.
Comparative Analysis: Waterfall vs Agile
The Waterfall Model follows a linear, sequential approach with distinct phases such as requirement gathering, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance, which emphasizes thorough documentation and upfront planning but lacks flexibility for changes during the development process. Agile Methodology promotes iterative development, collaboration, and continuous feedback through short sprints, enabling faster adaptation to evolving requirements and fostering enhanced customer engagement. Comparative analysis reveals that Waterfall suits projects with well-defined, stable requirements, while Agile excels in environments demanding rapid delivery, flexibility, and ongoing stakeholder involvement.
Suitability and Use Cases in Industry
The Waterfall Model excels in projects with well-defined requirements and linear processes such as construction and manufacturing, where stages like design, development, and testing follow a sequential flow. Agile Methodology suits dynamic environments like software development and startups, emphasizing iterative progress, collaboration, and adaptability to changing customer needs. Enterprises handling complex, evolving products often adopt Agile to improve flexibility and faster delivery cycles compared to the rigid structure of Waterfall.
Future Trends in Software Development Approaches
Future trends in software development emphasize increased adoption of Agile methodologies due to their flexibility and iterative delivery, which better accommodate rapid market changes and customer feedback. Emerging technologies like AI-driven project management tools and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines enhance Agile's efficiency compared to the linear structure of the Waterfall model. Hybrid approaches combining elements of both Waterfall and Agile are gaining traction to address complex project requirements and regulatory constraints in industries such as healthcare and finance.
Related Important Terms
Incremental Delivery
The Waterfall Model delivers software in a linear, sequential process where each phase must be completed before the next begins, resulting in a final product delivered only at the end of the project. Agile Methodology emphasizes incremental delivery by producing small, functional releases in iterative cycles, allowing continuous customer feedback and faster adaptation to change.
Iterative Feedback Loops
The Waterfall model follows a linear, sequential approach with limited opportunities for iterative feedback, often leading to delayed issue identification and reduced flexibility. Agile methodology emphasizes continuous iterative feedback loops throughout development cycles, enabling rapid adjustments, enhanced collaboration, and improved product adaptability.
Sprint Retrospective
Sprint Retrospective is a core ceremony exclusive to Agile methodology, facilitating iterative feedback and continuous team improvement after each sprint, unlike the Waterfall Model, which follows a linear, phase-based process with limited scope for reflection post-project. Agile's adaptive nature through Sprint Retrospectives enhances responsiveness to change, while Waterfall's rigid structure limits flexibility and iterative learning opportunities.
Continuous Integration
The Waterfall Model follows a linear and sequential approach with limited opportunities for continuous integration, often leading to delayed testing and feedback cycles. Agile Methodology prioritizes continuous integration by enabling frequent code commits, automated testing, and iterative delivery, resulting in faster detection of defects and improved software quality.
Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
The Waterfall Model employs a rigid Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) to ensure each requirement is systematically documented and verified throughout sequential phases, enhancing accountability but limiting flexibility. In contrast, Agile Methodology uses a dynamic RTM integrated within iterative sprints, facilitating continuous validation and adaptive changes aligned with evolving customer needs.
Scope Creep Management
The Waterfall Model offers rigid scope control by following a sequential phase structure, minimizing scope creep through comprehensive upfront planning and fixed requirements. Agile Methodology embraces iterative development, allowing scope adjustments throughout the project lifecycle, which improves adaptability but requires active backlog grooming to manage scope creep effectively.
Release Burndown Chart
The Release Burndown Chart in Agile Methodology visually tracks the completion of work over time, providing real-time data for sprint progress and project velocity, which facilitates iterative improvements and adaptive planning. In contrast, the Waterfall Model lacks a dynamic Release Burndown Chart, as its linear, sequential phases limit visibility into ongoing progress and reduce flexibility in responding to project changes.
Definition of Done (DoD)
The Definition of Done (DoD) in the Waterfall Model is a fixed, predetermined checklist finalized at the project's outset, ensuring each phase's deliverables are completed before moving forward. In contrast, Agile Methodology employs an evolving, iterative DoD that adapts with each sprint, emphasizing continuous delivery and incremental improvements aligned with stakeholder feedback.
Gantt Chart Dependencies
The Waterfall model relies heavily on Gantt chart dependencies to map out sequential phases, ensuring strict task order and clear milestone tracking. Agile methodology minimizes reliance on Gantt charts, favoring flexible, iterative workflows that adapt to changing priorities without rigid dependency constraints.
Kanban Flow
The Waterfall Model follows a linear, sequential design process with distinct phases, whereas Agile Methodology, particularly Kanban flow, emphasizes continuous delivery through a visual workflow that limits work in progress to enhance efficiency and adaptability. Kanban enables real-time project tracking and flexibility by allowing teams to prioritize tasks dynamically, contrasting with Waterfall's rigid, pre-defined project stages.
Waterfall Model vs Agile Methodology Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com