APIs provide a set of predefined endpoints for data access, while GraphQL allows clients to request exactly the data they need through a single query. GraphQL reduces over-fetching and under-fetching by enabling more efficient data retrieval, improving performance in complex applications. Conventional APIs often require multiple requests to different endpoints, which can increase latency and complicate client-server communication.
Table of Comparison
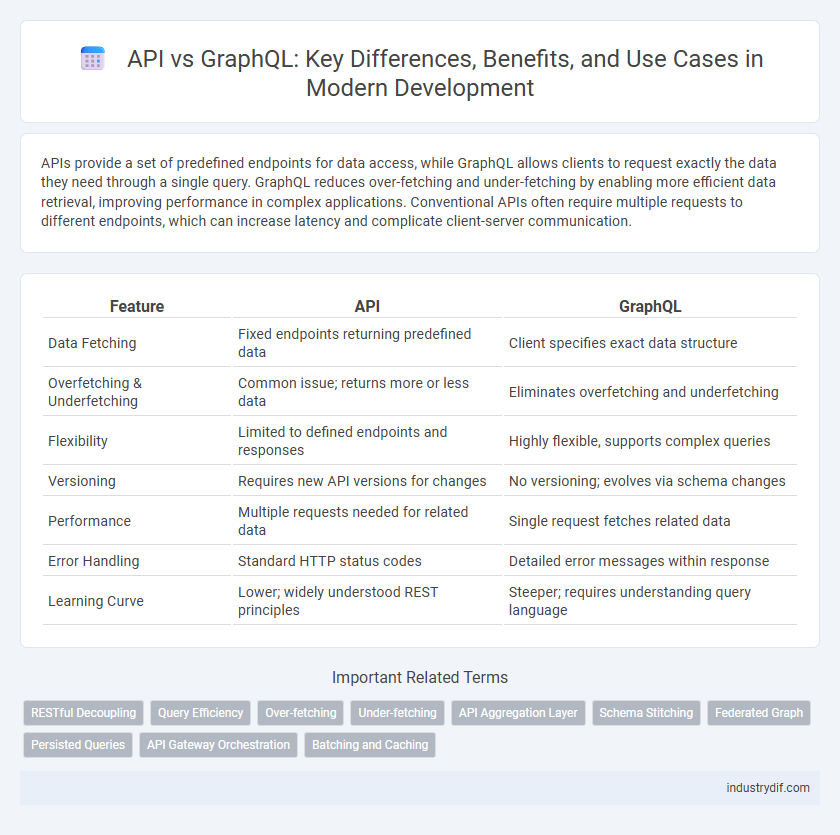
| Feature | API | GraphQL |
|---|---|---|
| Data Fetching | Fixed endpoints returning predefined data | Client specifies exact data structure |
| Overfetching & Underfetching | Common issue; returns more or less data | Eliminates overfetching and underfetching |
| Flexibility | Limited to defined endpoints and responses | Highly flexible, supports complex queries |
| Versioning | Requires new API versions for changes | No versioning; evolves via schema changes |
| Performance | Multiple requests needed for related data | Single request fetches related data |
| Error Handling | Standard HTTP status codes | Detailed error messages within response |
| Learning Curve | Lower; widely understood REST principles | Steeper; requires understanding query language |
Introduction to APIs and GraphQL
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) serve as standardized protocols that enable different software applications to communicate and exchange data efficiently. GraphQL is a query language for APIs that allows clients to request precisely the data they need, reducing over-fetching and improving performance. Unlike traditional REST APIs that expose multiple endpoints, GraphQL consolidates data fetching into a single endpoint with flexible queries.
Core Concepts: RESTful APIs vs. GraphQL
RESTful APIs operate using fixed endpoints and HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE to manage resources, enforcing a strict request-response pattern that fetches entire data objects. GraphQL centralizes data retrieval through a single endpoint, allowing clients to request exactly the data fields they need via flexible queries, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching issues. The core difference lies in REST's reliance on multiple predefined endpoints versus GraphQL's schema-driven query language offering precise, client-specific data retrieval.
Data Fetching Strategies
REST APIs rely on fixed endpoints retrieving predefined data, often leading to over-fetching or under-fetching issues. GraphQL enables precise data querying by allowing clients to specify exactly which fields they need, optimizing bandwidth and reducing latency. This selective data fetching improves performance and flexibility in applications demanding efficient and tailored data retrieval.
Schema Design and Type Systems
GraphQL uses a strongly typed schema that defines types, queries, and mutations in a single, unified system, enabling precise validation and introspection of API capabilities. Traditional REST APIs typically lack a formal type system, relying on endpoint conventions and documentation that can lead to inconsistencies and less predictable data structures. GraphQL's integrated type system facilitates efficient client-driven data querying by allowing schema evolution without breaking existing clients.
Performance and Efficiency
GraphQL enhances performance by allowing clients to request precisely the data they need, minimizing over-fetching compared to traditional REST APIs that often return fixed data structures. This targeted querying reduces network bandwidth and speeds up response times, significantly improving efficiency for mobile and low-bandwidth environments. Furthermore, GraphQL's single endpoint consolidates multiple resource requests into one, decreasing the number of HTTP calls and server load compared to REST's multiple endpoints structure.
Security Considerations
APIs using REST often rely on traditional authentication methods like OAuth 2.0 and API keys, whereas GraphQL introduces complexities due to its flexible query structure, requiring granular authorization and query depth analysis to prevent data over-fetching and injection attacks. Implementing rate limiting and persisted queries in GraphQL enhances security by restricting query complexity and preventing denial-of-service attacks. Both APIs and GraphQL benefit from SSL/TLS encryption and robust validation mechanisms to safeguard data integrity and confidentiality.
Versioning and Flexibility
GraphQL offers superior flexibility over traditional APIs by allowing clients to specify exactly what data they need, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching issues common in RESTful APIs. Unlike REST APIs that rely on versioning (e.g., v1, v2 endpoints) to manage changes, GraphQL evolves through schema introspection and deprecation mechanisms, enabling incremental updates without breaking existing queries. This approach minimizes the need for multiple versions and supports rapid iteration while maintaining backward compatibility.
Tooling and Ecosystem Support
GraphQL offers robust tooling and a growing ecosystem with tools like Apollo Studio, GraphiQL, and Relay, which provide real-time query validation, performance monitoring, and client-side caching. REST APIs benefit from mature, widely adopted tools such as Postman, Swagger, and Insomnia, supporting comprehensive API testing, documentation, and versioning. The choice between REST and GraphQL tooling depends on project complexity, with GraphQL excelling in flexible data fetching and REST dominating in simplicity and widespread integration support.
Common Use Cases and Industry Adoption
REST APIs are widely adopted in e-commerce, mobile applications, and cloud services due to their simplicity and stateless architecture, enabling standardized data retrieval and CRUD operations. GraphQL is increasingly used in social media platforms, complex SaaS applications, and real-time data environments for its efficiency in fetching precise data and reducing over-fetching or under-fetching issues. Industry leaders like Facebook, GitHub, and Shopify have championed GraphQL for its flexibility, while enterprises continue to rely on REST for its maturity and broad tool support.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Project
Selecting the right approach between RESTful APIs and GraphQL depends on the project's data requirements and flexibility needs. REST APIs offer simplicity and standardized endpoints, making them suitable for straightforward CRUD operations and caching. GraphQL provides efficient data querying and reduces over-fetching by allowing clients to request only the necessary fields, ideal for complex applications requiring dynamic and nested data retrieval.
Related Important Terms
RESTful Decoupling
RESTful APIs enable decoupling by providing standardized endpoints that separate client and server development, allowing independent evolution of each component. GraphQL enhances this decoupling by enabling clients to request precisely the data needed through flexible queries, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching issues common in traditional RESTful architectures.
Query Efficiency
GraphQL optimizes query efficiency by allowing clients to request only the specific data fields they need in a single request, reducing the amount of unnecessary data transferred compared to traditional REST APIs. REST APIs often require multiple endpoints and over-fetching or under-fetching of data, leading to increased latency and bandwidth usage.
Over-fetching
Traditional REST APIs often cause over-fetching by delivering excessive data in responses, leading to inefficient bandwidth use and slower performance. GraphQL addresses over-fetching by enabling clients to request precisely the needed fields, optimizing data retrieval and reducing unnecessary payloads.
Under-fetching
Under-fetching occurs in traditional REST APIs when clients receive insufficient data, requiring multiple requests to access related resources; GraphQL mitigates this by allowing clients to specify precisely the data they need in a single query, reducing network overhead and improving performance. This precise data fetching enhances efficiency, especially in complex applications with interconnected datasets.
API Aggregation Layer
An API Aggregation Layer consolidates multiple API endpoints, reducing client-server interactions and improving data retrieval efficiency compared to traditional REST APIs. GraphQL inherently functions as an aggregation layer by allowing clients to request precise data structures through a single query, minimizing over-fetching and under-fetching issues.
Schema Stitching
Schema stitching in GraphQL enables the integration of multiple GraphQL schemas into a single unified API, improving data fetching efficiency and reducing client-side complexity compared to traditional REST APIs. This technique allows developers to combine disparate data sources seamlessly, optimizing performance and maintainability in complex distributed systems.
Federated Graph
Federated Graph architecture enables multiple GraphQL services to be composed into a single data graph, improving scalability and maintainability compared to traditional REST APIs that require multiple endpoints. By unifying data sources within a federated schema, it streamlines queries and reduces over-fetching, enhancing client efficiency and developer productivity.
Persisted Queries
Persisted Queries in GraphQL enhance performance and security by pre-registering queries on the server, reducing payload size and preventing query injection attacks compared to traditional REST APIs. This optimization streamlines network communication and ensures consistent query execution, making GraphQL more efficient for complex data fetching scenarios.
API Gateway Orchestration
API Gateway orchestration streamlines communication by managing multiple REST APIs, whereas GraphQL consolidates data queries into a single endpoint, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching of data. Leveraging API Gateway with REST enhances security, rate limiting, and caching, while GraphQL excels in dynamic querying and real-time data fetching within complex microservices architectures.
Batching and Caching
GraphQL optimizes data fetching by enabling query batching, consolidating multiple requests into a single query to reduce HTTP overhead, while REST APIs typically handle batching through custom endpoints or rely on client-side aggregation. Advanced caching mechanisms in GraphQL utilize query-specific cache keys and partial data updates, whereas REST APIs often cache entire resources based on URL patterns, impacting granularity and cache efficiency.
API vs GraphQL Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com