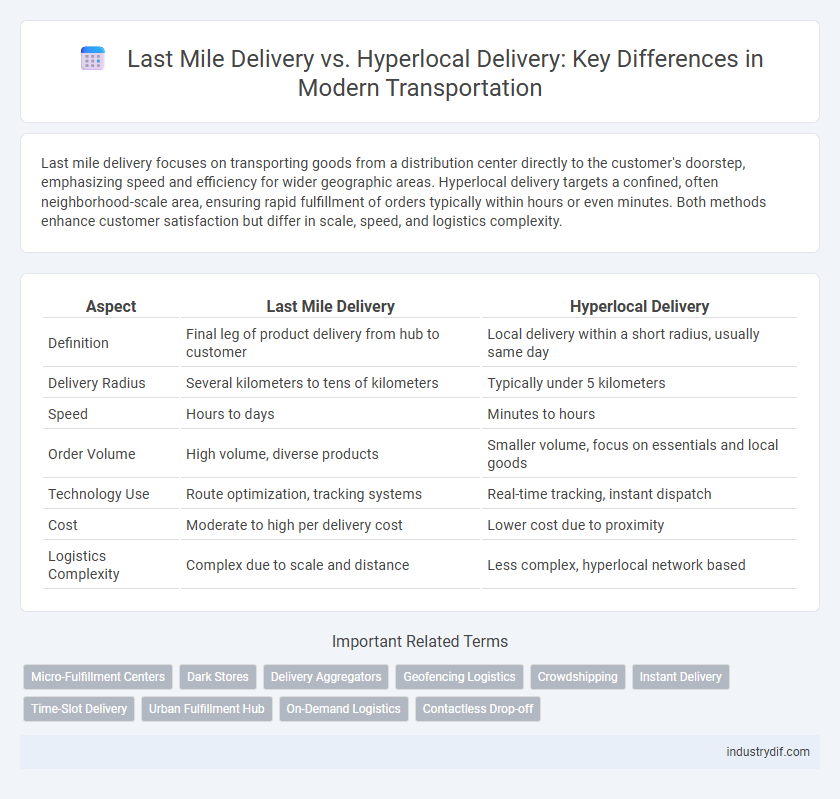
Last mile delivery focuses on transporting goods from a distribution center directly to the customer's doorstep, emphasizing speed and efficiency for wider geographic areas. Hyperlocal delivery targets a confined, often neighborhood-scale area, ensuring rapid fulfillment of orders typically within hours or even minutes. Both methods enhance customer satisfaction but differ in scale, speed, and logistics complexity.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Last Mile Delivery | Hyperlocal Delivery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Final leg of product delivery from hub to customer | Local delivery within a short radius, usually same day |
| Delivery Radius | Several kilometers to tens of kilometers | Typically under 5 kilometers |
| Speed | Hours to days | Minutes to hours |
| Order Volume | High volume, diverse products | Smaller volume, focus on essentials and local goods |
| Technology Use | Route optimization, tracking systems | Real-time tracking, instant dispatch |
| Cost | Moderate to high per delivery cost | Lower cost due to proximity |
| Logistics Complexity | Complex due to scale and distance | Less complex, hyperlocal network based |
Defining Last Mile Delivery and Hyperlocal Delivery
Last mile delivery refers to the final step of the shipping process where goods are transported from a distribution center or warehouse directly to the consumer's doorstep, typically covering longer distances and involving complex logistics. Hyperlocal delivery focuses on an ultra-localized area, often within a few kilometers, enabling rapid fulfillment of orders from nearby stores or fulfillment hubs, primarily for perishable or high-demand items. Both delivery models are crucial in supply chain optimization, with last mile delivery emphasizing broader reach and hyperlocal delivery prioritizing speed and proximity.
Key Differences Between Last Mile and Hyperlocal Models
Last mile delivery refers to the final step of the supply chain where goods are transported from a distribution center to the customer's doorstep, emphasizing speed and efficiency over longer distances. Hyperlocal delivery operates within a much smaller geographic area, often within a few kilometers, focusing on rapid service, often under an hour, for immediate customer needs. The key differences lie in delivery radius, speed, and inventory proximity, with last mile catering to broader urban or suburban zones and hyperlocal targeting dense, localized demand hotspots.
Technology Innovations Powering Last Mile and Hyperlocal Delivery
Technology innovations powering last mile and hyperlocal delivery include real-time GPS tracking, AI-driven route optimization, and autonomous delivery vehicles, which enhance speed and efficiency. IoT-enabled smart lockers and drones streamline parcel drop-offs, reducing human contact and delivery time. Advanced data analytics and machine learning enable predictive demand forecasting, minimizing delays and operational costs in urban logistics.
Logistics Challenges in Last Mile vs Hyperlocal Delivery
Last mile delivery faces significant logistics challenges such as complex route optimization, high delivery costs, and managing diverse customer time preferences in urban and suburban areas. Hyperlocal delivery demands ultra-fast fulfillment, real-time inventory accuracy, and seamless coordination between micro-fulfillment centers and local couriers to meet immediate customer needs. Both models require advanced technology solutions like AI-powered route planning and dynamic order management to overcome operational inefficiencies.
Cost Implications: Last Mile Delivery vs Hyperlocal Delivery
Last mile delivery often incurs higher transportation and fuel costs due to longer distances between distribution points and customers, resulting in increased operational expenses. Hyperlocal delivery leverages proximity by sourcing products from nearby stores or warehouses, significantly reducing travel time and transportation costs. Cost efficiency in hyperlocal delivery is enhanced through optimized route planning and reduced vehicle usage, making it a more economical solution for dense urban areas.
Role of E-commerce in Shaping Delivery Models
E-commerce growth fundamentally reshapes last mile and hyperlocal delivery models by driving demand for speed, efficiency, and customer convenience. Last mile delivery focuses on transporting goods from distribution centers to consumers' doorsteps, leveraging extensive logistics networks optimized for a broad geographic scale. Hyperlocal delivery targets immediate neighborhoods with ultra-fast service enabled by localized inventory and real-time order processing, enhancing the customer experience in dense urban markets.
Customer Experience: Expectations and Fulfillment
Last mile delivery focuses on completing shipments from distribution centers directly to customers' doorsteps, emphasizing speed and convenience to meet growing expectations for faster delivery times. Hyperlocal delivery narrows the geographic radius, offering near-instant fulfillment through local stores or dark kitchens, enhancing customer satisfaction by providing fresh, immediate access to products. Both models prioritize transparency, real-time tracking, and flexible delivery options to elevate the overall customer experience and ensure timely fulfillment.
Scalability and Geographic Reach Comparison
Last mile delivery typically operates on a broader geographic scale, efficiently serving wider urban and suburban areas but facing scalability challenges due to variable traffic and infrastructure limits. Hyperlocal delivery focuses on a smaller, densely populated radius, enabling faster scalability with concentrated resources and quicker fulfillment times. The scalability of hyperlocal delivery benefits from localized demand, while last mile delivery leverages broader regional networks to maximize geographic reach.
Popular Use Cases: Industry Applications
Last mile delivery is widely utilized in e-commerce and retail sectors for delivering goods directly to consumers, ensuring timely and efficient doorstep service. Hyperlocal delivery excels in food and grocery industries, enabling quick, on-demand fulfillment within limited geographic zones. Both methods enhance customer satisfaction by optimizing delivery speed and reducing logistics costs in urban environments.
Future Trends in Last Mile and Hyperlocal Delivery
Future trends in last mile delivery emphasize increased automation through drone and autonomous vehicle integration, significantly reducing delivery times and operational costs. Hyperlocal delivery is shifting towards AI-driven demand forecasting and dynamic routing to enhance efficiency and meet rising consumer expectations for near-instantaneous service. Both models are converging on sustainability initiatives, utilizing electric vehicles and eco-friendly packaging to minimize environmental impact.
Related Important Terms
Micro-Fulfillment Centers
Micro-fulfillment centers enable hyperlocal delivery by strategically positioning inventory within densely populated urban areas to reduce delivery times and costs for last mile delivery. This approach enhances efficiency by minimizing transportation distances, supporting faster order fulfillment compared to traditional last mile logistics that often rely on centralized warehouses.
Dark Stores
Last mile delivery focuses on transporting goods from a local distribution center to the customer's doorstep, optimizing speed and convenience, while hyperlocal delivery leverages dark stores--small, strategically located fulfillment centers without storefronts--to enable ultra-fast delivery within a limited geographic area. Dark stores play a critical role in hyperlocal delivery by minimizing delivery times and inventory costs, supporting real-time order processing and efficient stock management.
Delivery Aggregators
Last mile delivery focuses on transporting goods from a distribution center to the final customer, emphasizing speed and efficiency in urban environments. Hyperlocal delivery, driven by delivery aggregators, targets ultra-short distances within localized areas, leveraging real-time demand to optimize routes and reduce delivery times significantly.
Geofencing Logistics
Last mile delivery leverages geofencing logistics to optimize route planning and ensure timely package drop-offs within a predefined boundary, reducing transit times and operational costs. Hyperlocal delivery uses geofencing to target ultra-specific neighborhoods, enabling rapid fulfillment and real-time tracking in dense urban areas for groceries and on-demand goods.
Crowdshipping
Last mile delivery focuses on transporting goods from a transportation hub to the final destination, often involving professional couriers, whereas hyperlocal delivery emphasizes rapid, short-distance shipments within a confined geographic area, frequently leveraging local vendors. Crowdshipping enhances both models by utilizing a decentralized network of everyday commuters and local drivers to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve delivery speed in last mile and hyperlocal logistics.
Instant Delivery
Last mile delivery targets the final leg of transporting goods to customers, often within hours to days, whereas hyperlocal delivery emphasizes instant delivery within a limited geographical area, typically under an hour. Instant delivery relies on sophisticated routing algorithms and real-time inventory management to fulfill consumer demand rapidly in urban settings.
Time-Slot Delivery
Last mile delivery involves transporting goods from a distribution center to the final customer, typically within a broad time slot, while hyperlocal delivery emphasizes ultra-fast, time-slot delivery often within hours, focusing on immediate local demand fulfillment. Time-slot delivery in hyperlocal logistics enhances customer satisfaction by guaranteeing narrow delivery windows, significantly reducing wait times compared to traditional last mile services.
Urban Fulfillment Hub
Urban Fulfillment Hubs streamline last mile delivery by centralizing inventory close to dense customer areas, reducing transit time and costs significantly compared to traditional hyperlocal delivery models. These hubs leverage advanced route optimization and real-time tracking to enhance delivery speed and improve customer satisfaction within metropolitan regions.
On-Demand Logistics
Last mile delivery focuses on transporting goods from a distribution center to the final customer address, prioritizing speed and efficiency in urban and suburban areas. Hyperlocal delivery operates within a much smaller geographic radius, often using on-demand logistics to fulfill orders from nearby stores or warehouses within minutes to a few hours.
Contactless Drop-off
Last mile delivery emphasizes efficient final movement of goods to the customer's doorstep, often incorporating contactless drop-off methods like secure lockers or designated drop zones to minimize physical interaction. Hyperlocal delivery operates within a confined geographic area, leveraging rapid, on-demand services that prioritize real-time tracking and seamless contactless handoffs to enhance customer convenience and safety.
Last Mile Delivery vs Hyperlocal Delivery Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com