Logistics involves the planning and management of the flow of goods from origin to consumer, ensuring timely delivery and efficient supply chain operations. Dark stores serve as localized fulfillment centers tailored for online orders, optimizing last-mile delivery by reducing transit times and improving inventory accuracy. Both logistics and dark stores are integral to modern retail, with logistics emphasizing movement and coordination, while dark stores focus on rapid order processing and proximity to customers.
Table of Comparison
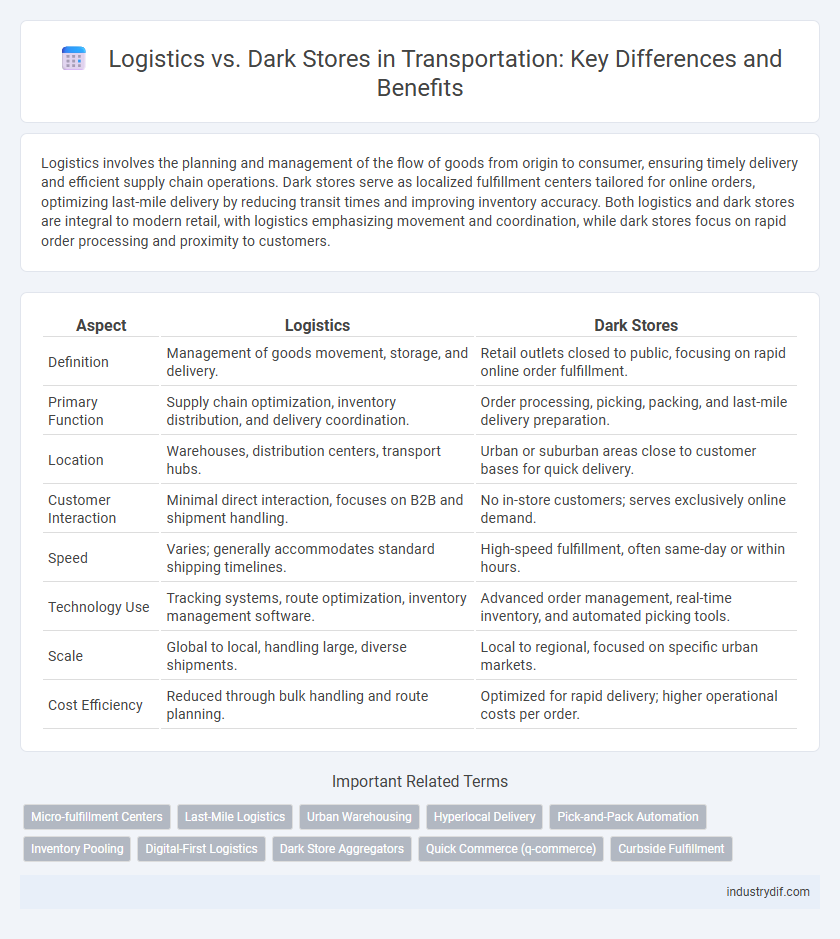
| Aspect | Logistics | Dark Stores |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Management of goods movement, storage, and delivery. | Retail outlets closed to public, focusing on rapid online order fulfillment. |
| Primary Function | Supply chain optimization, inventory distribution, and delivery coordination. | Order processing, picking, packing, and last-mile delivery preparation. |
| Location | Warehouses, distribution centers, transport hubs. | Urban or suburban areas close to customer bases for quick delivery. |
| Customer Interaction | Minimal direct interaction, focuses on B2B and shipment handling. | No in-store customers; serves exclusively online demand. |
| Speed | Varies; generally accommodates standard shipping timelines. | High-speed fulfillment, often same-day or within hours. |
| Technology Use | Tracking systems, route optimization, inventory management software. | Advanced order management, real-time inventory, and automated picking tools. |
| Scale | Global to local, handling large, diverse shipments. | Local to regional, focused on specific urban markets. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduced through bulk handling and route planning. | Optimized for rapid delivery; higher operational costs per order. |
Overview of Logistics in Modern Transportation
Logistics in modern transportation involves the strategic planning, implementation, and management of efficient movement and storage of goods from origin to consumption. Key components include fleet management, route optimization, real-time tracking, and inventory control, which collectively enhance supply chain visibility and reduce delivery times. Advanced technologies such as AI, IoT, and automation play a crucial role in optimizing logistics operations, ensuring faster fulfillment and cost efficiency compared to traditional models like dark stores.
What Are Dark Stores?
Dark stores are retail distribution centers that operate exclusively for online order fulfillment, enabling faster delivery by serving as local hubs for picking and packing products. Unlike traditional retail stores, dark stores are not open to the public and are strategically located to optimize last-mile logistics and reduce transit times. These facilities play a crucial role in e-commerce supply chains by improving inventory management and enhancing delivery efficiency.
Key Differences Between Logistics and Dark Stores
Logistics involves the management of the entire supply chain, encompassing transportation, warehousing, and inventory control to ensure timely delivery of goods. Dark stores are specialized fulfillment centers designed exclusively for online order processing, often optimized for rapid picking and dispatch within urban areas. The key difference lies in logistics' broad operational scope versus dark stores' targeted focus on e-commerce order fulfillment and last-mile delivery efficiency.
How Dark Stores Are Revolutionizing Last-Mile Delivery
Dark stores are revolutionizing last-mile delivery by operating as dedicated fulfillment centers strategically located in urban areas, enabling faster order processing and reduced delivery times. These facilities optimize inventory management with real-time data integration, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of order fulfillment compared to traditional logistics hubs. Leveraging advanced technology and localized stock, dark stores support same-day and even one-hour delivery services, meeting the rising consumer demand for immediate product availability.
The Role of Technology in Logistics and Dark Stores
Advanced technology powers the efficiency of both logistics and dark stores by integrating real-time data analytics, automated inventory management systems, and AI-driven route optimization. Logistics operations leverage GPS tracking, IoT sensors, and warehouse robotics to streamline supply chain visibility and reduce delivery times. Dark stores utilize sophisticated software platforms for order processing and demand forecasting, enabling rapid fulfillment and minimizing stockouts in urban environments.
Inventory Management: Logistics vs Dark Stores
Logistics centers optimize inventory management by decentralizing stock across multiple distribution hubs, enabling faster order fulfillment and reduced transportation costs. Dark stores centralize inventory within urban locations, streamlining last-mile delivery and improving product availability for immediate consumer demand. Efficient inventory tracking systems in both models are critical for minimizing stockouts and excess inventory, directly impacting supply chain responsiveness and customer satisfaction.
Impact on Supply Chain Efficiency
Logistics optimization enhances supply chain efficiency through streamlined inventory management, real-time tracking, and faster last-mile delivery, reducing operational costs and improving customer satisfaction. Dark stores, serving as localized fulfillment centers, minimize delivery times by strategically positioning inventory near demand hotspots, thus accelerating order processing and reducing transportation complexities. Integrating dark stores within advanced logistics frameworks supports agile distribution networks, enabling responsive supply chains adaptable to fluctuating market demands.
Cost Implications: Choosing Logistics or Dark Stores
Logistics centers demand high investment in transportation and warehousing infrastructure, with operational costs driven by fuel, labor, and inventory management, impacting overall supply chain efficiency. Dark stores reduce last-mile delivery expenses by positioning inventory closer to urban customers but incur higher costs in real estate and technology for real-time inventory tracking. Evaluating trade-offs between centralized logistics cost benefits and localized dark store expenses is essential for optimizing transportation budgets in e-commerce fulfillment.
Challenges Faced by Logistics and Dark Store Operations
Logistics faces challenges such as route optimization, last-mile delivery efficiency, and inventory management complexities across diverse geographic locations. Dark stores encounter operational hurdles including high real-time order accuracy demands, rapid fulfillment speed, and maintaining stock availability without direct consumer interaction. Both models grapple with technology integration and adapting to fluctuating consumer demand patterns in the transportation ecosystem.
Future Trends in Logistics and Dark Store Integration
Future trends in logistics emphasize the seamless integration of dark stores as micro-fulfillment hubs to enhance last-mile delivery efficiency and speed. Advanced technologies such as AI-driven inventory management, autonomous vehicles, and real-time data analytics optimize stock allocation and route planning within dark store networks. This convergence supports urban logistics by reducing delivery times and operational costs, meeting the growing demand for rapid e-commerce fulfillment.
Related Important Terms
Micro-fulfillment Centers
Micro-fulfillment centers operate as compact, automated warehouses located near urban areas, enabling faster last-mile delivery compared to traditional logistics hubs and dark stores that primarily serve as inventory holding points. These centers optimize transportation by reducing delivery distances, enhancing supply chain efficiency, and supporting real-time order fulfillment in high-demand urban environments.
Last-Mile Logistics
Last-mile logistics plays a crucial role in the efficiency of dark stores, which are strategically located fulfillment centers designed to expedite urban deliveries by minimizing transit time. Optimizing route planning and real-time inventory management in last-mile logistics enhances the speed and accuracy of orders from dark stores, reducing delivery costs and improving customer satisfaction.
Urban Warehousing
Urban warehousing leverages logistics strategies to optimize the storage and rapid distribution of goods within city centers, enhancing last-mile delivery efficiency. Dark stores function as localized fulfillment hubs without customer access, enabling faster order processing and reducing transportation times in urban logistics networks.
Hyperlocal Delivery
Hyperlocal delivery leverages dark stores as strategically located micro-fulfillment centers to streamline logistics, reducing delivery times and improving efficiency in urban areas. Unlike traditional logistics hubs, dark stores are optimized for rapid order processing and last-mile delivery, meeting the growing demand for instant gratification in e-commerce.
Pick-and-Pack Automation
Pick-and-pack automation in logistics enhances order accuracy and speed through advanced robotics and AI-driven sorting systems, reducing labor costs and processing times in distribution centers. Dark stores employ similar automation but prioritize last-mile delivery efficiency by optimizing inventory layouts for rapid, small-batch order fulfillment tailored to e-commerce demand.
Inventory Pooling
Logistics systems optimize inventory pooling by centralizing stock in distribution centers to enable faster delivery and reduce transportation costs. Dark stores function as micro-fulfillment hubs, leveraging localized inventory pools to enhance last-mile efficiency and meet high demand in urban areas.
Digital-First Logistics
Digital-first logistics leverages advanced technology and real-time data analytics to optimize inventory management and last-mile delivery, contrasting with traditional dark stores that function as static urban fulfillment centers. Emphasizing seamless integration of e-commerce platforms and automated warehouses, digital-first logistics enhances speed, accuracy, and scalability in supply chain operations.
Dark Store Aggregators
Dark store aggregators streamline last-mile delivery by consolidating inventory from multiple dark stores to optimize order fulfillment and reduce delivery times. These platforms leverage real-time data analytics and localized distribution networks to enhance efficiency in urban logistics and meet rising consumer demand for rapid e-commerce delivery.
Quick Commerce (q-commerce)
Logistics in quick commerce (q-commerce) focuses on optimizing last-mile delivery through centralized warehouses and efficient inventory distribution, while dark stores act as localized fulfillment centers designed to expedite order processing and reduce delivery times. Integrating dark stores with advanced logistics networks enhances real-time inventory management, enabling faster delivery speeds crucial for meeting consumer expectations in the rapidly growing q-commerce sector.
Curbside Fulfillment
Curbside fulfillment leverages dark stores to optimize last-mile delivery by streamlining inventory management and reducing delivery times through dedicated urban micro-fulfillment centers. This approach contrasts with traditional logistics hubs by prioritizing proximity to customers and enabling rapid order processing for same-day or instant curbside pickup.
Logistics vs Dark Stores Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com