Supply chain management relies on centralized systems to coordinate the flow of goods, often facing challenges with transparency and efficiency. Blockchain logistics introduces a decentralized ledger that enhances traceability, reduces fraud, and accelerates transaction verification across the supply chain. Integrating blockchain into transportation streamlines operations, improves data accuracy, and fosters trust among stakeholders throughout the delivery process.
Table of Comparison
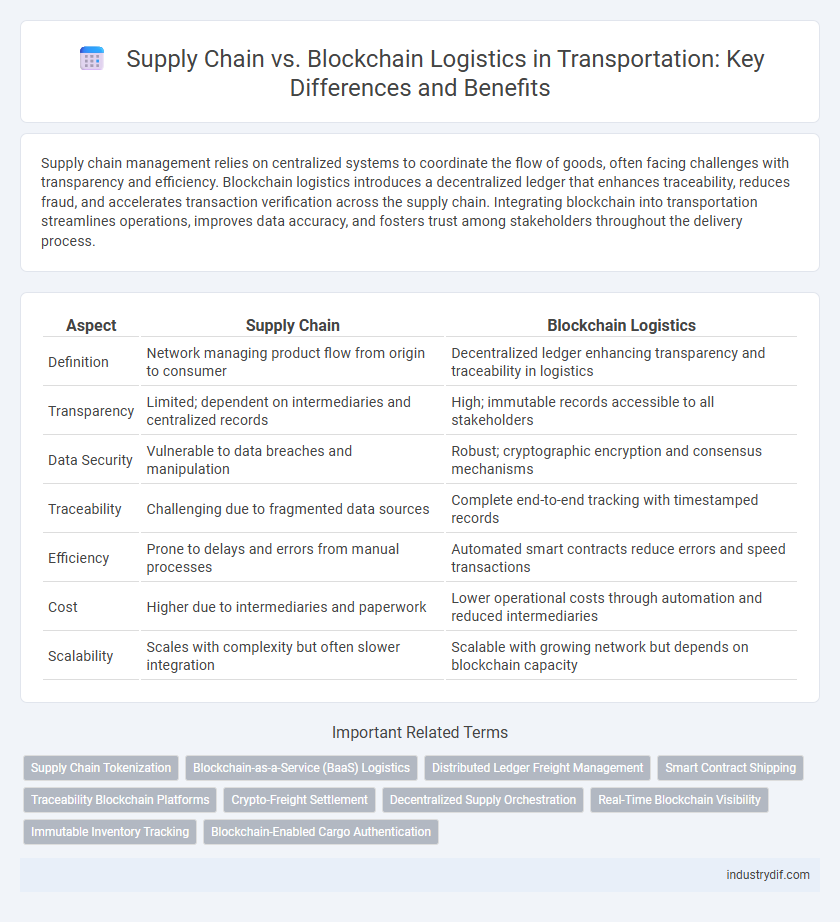
| Aspect | Supply Chain | Blockchain Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network managing product flow from origin to consumer | Decentralized ledger enhancing transparency and traceability in logistics |
| Transparency | Limited; dependent on intermediaries and centralized records | High; immutable records accessible to all stakeholders |
| Data Security | Vulnerable to data breaches and manipulation | Robust; cryptographic encryption and consensus mechanisms |
| Traceability | Challenging due to fragmented data sources | Complete end-to-end tracking with timestamped records |
| Efficiency | Prone to delays and errors from manual processes | Automated smart contracts reduce errors and speed transactions |
| Cost | Higher due to intermediaries and paperwork | Lower operational costs through automation and reduced intermediaries |
| Scalability | Scales with complexity but often slower integration | Scalable with growing network but depends on blockchain capacity |
Understanding Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management (SCM) involves coordinating the flow of goods, information, and resources from suppliers to end consumers, ensuring timely delivery and cost efficiency. Blockchain logistics enhances SCM by providing transparent, immutable records of each transaction and shipment, improving traceability and reducing fraud. Integrating blockchain technology into supply chain processes increases accountability and streamlines operations through decentralized data sharing.
Introduction to Blockchain in Logistics
Blockchain in logistics revolutionizes supply chain management by enabling transparent, immutable tracking of goods from origin to destination. This technology enhances data security, reduces fraud, and improves real-time visibility across all logistics stakeholders. Implementation of blockchain accelerates efficient coordination, lowers operational costs, and strengthens trust in supply chain networks.
Key Differences: Supply Chain vs Blockchain Logistics
Supply chain logistics involve traditional processes of managing the flow of goods, information, and resources from suppliers to consumers through centralized systems. Blockchain logistics leverage decentralized, immutable ledgers to enhance transparency, security, and real-time tracking across all supply chain stakeholders. Key differences include centralized data control in supply chains versus distributed data verification in blockchain, which reduces fraud, errors, and delays.
The Role of Transparency and Traceability
Supply chain management benefits from blockchain logistics by enhancing transparency and traceability, enabling real-time tracking of goods and reducing the risk of fraud or errors. Blockchain's decentralized ledger ensures data integrity and shared access across stakeholders, improving accountability and operational efficiency in transportation networks. Enhanced traceability aids in compliance with regulatory standards and supports faster resolution of shipment disputes.
Data Security in Modern Logistics
Supply chain logistics often face data security challenges due to centralized information systems vulnerable to cyberattacks and data tampering. Blockchain logistics enhances data security by providing a decentralized, immutable ledger that ensures transparency, traceability, and tamper-proof records across the entire transportation network. This technology reduces fraud, improves compliance, and strengthens trust among stakeholders in modern logistics operations.
Improving Efficiency with Blockchain Solutions
Blockchain logistics enhances supply chain efficiency by providing transparent, immutable records that streamline tracking and reduce fraud. Smart contracts automate transactions, minimizing delays and errors in inventory management. Real-time data sharing across stakeholders accelerates decision-making processes and optimizes resource allocation.
Challenges of Blockchain Implementation in Supply Chains
Blockchain implementation in supply chains faces challenges such as scalability issues, high energy consumption, and integration with existing legacy systems. Data privacy concerns and regulatory uncertainties hinder widespread adoption across diverse transportation networks. Overcoming these obstacles requires advanced consensus mechanisms and collaboration among stakeholders to enhance transparency and efficiency in logistics operations.
Real-World Use Cases: Blockchain in Logistics
Blockchain technology enhances transparency and traceability in logistics by enabling real-time tracking of shipments across supply chains, reducing fraud and errors. Major corporations like Maersk and IBM have implemented blockchain platforms such as TradeLens to streamline documentation processes and improve collaboration among stakeholders. This adoption leads to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and stronger security in global supply chain management.
Future Trends in Supply Chain and Blockchain Integration
Future trends in supply chain management emphasize the integration of blockchain technology to enhance transparency, traceability, and security of logistics operations. Blockchain's decentralized ledger system enables real-time data sharing among stakeholders, reducing fraud and improving inventory accuracy across the supply chain network. Advanced smart contracts automate transactions and compliance processes, driving efficiency and cost savings in global transportation and logistics ecosystems.
Comparing Cost and ROI: Traditional vs Blockchain Logistics
Traditional supply chain logistics incur higher operational costs due to centralized coordination, manual record-keeping, and delays from intermediaries, often resulting in reduced ROI. Blockchain logistics streamline processes with decentralized, transparent ledgers, lowering transaction costs and minimizing fraud, which enhances real-time tracking and increases ROI through improved efficiency. Companies adopting blockchain report cost reductions of up to 30% and faster return on investment compared to conventional supply chain models.
Related Important Terms
Supply Chain Tokenization
Supply chain tokenization leverages blockchain technology to create digital tokens representing assets, improving transparency, traceability, and security throughout transportation logistics. This innovative approach enables real-time tracking of shipments, reduces fraud, and streamlines documentation, enhancing efficiency in global supply chain management.
Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) Logistics
Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) logistics revolutionizes traditional supply chain management by offering decentralized, transparent, and immutable transaction records, enhancing traceability and reducing fraud. Integrating BaaS platforms streamlines inventory tracking, automates contract execution through smart contracts, and improves overall supply chain efficiency and security.
Distributed Ledger Freight Management
Distributed ledger technology enhances supply chain transparency by enabling real-time freight tracking and immutable data records across multiple stakeholders. Blockchain logistics streamlines freight management through secure, decentralized transaction validation, reducing delays and fraud in shipment processing.
Smart Contract Shipping
Smart contract shipping leverages blockchain logistics to automate contract execution, reduce fraud, and enhance transparency in supply chain operations. This technology ensures real-time tracking and secure data sharing, optimizing shipment accuracy and efficiency compared to traditional supply chain methods.
Traceability Blockchain Platforms
Traceability blockchain platforms enable end-to-end visibility in supply chain logistics by securely recording every transaction on an immutable ledger, enhancing transparency and reducing fraud. These platforms outperform traditional supply chain systems by providing real-time data sharing across stakeholders, improving product provenance and regulatory compliance.
Crypto-Freight Settlement
Supply chain management benefits from blockchain logistics through enhanced transparency, security, and efficiency, particularly in crypto-freight settlement where smart contracts automate payments and reduce fraud risk. Implementing decentralized ledgers in freight transactions ensures real-time tracking and immutable records, optimizing payment reconciliation and trust among stakeholders.
Decentralized Supply Orchestration
Decentralized supply orchestration leverages blockchain logistics to enhance transparency, traceability, and security across the entire supply chain network, eliminating single points of failure. This paradigm shift enables real-time data sharing among stakeholders, optimizing inventory management, reducing delays, and improving overall supply chain resilience.
Real-Time Blockchain Visibility
Real-time blockchain visibility enhances supply chain logistics by providing immutable, transparent tracking of goods, reducing delays and minimizing fraud. This technology enables precise asset monitoring and data sharing across stakeholders, improving efficiency and accountability in transportation networks.
Immutable Inventory Tracking
Immutable inventory tracking in blockchain logistics enhances supply chain transparency by securely recording each transaction on a tamper-proof ledger, reducing errors and fraud. Traditional supply chain methods rely on centralized databases vulnerable to manipulation, whereas blockchain ensures real-time, verifiable asset authentication and provenance.
Blockchain-Enabled Cargo Authentication
Blockchain-enabled cargo authentication enhances supply chain transparency by providing immutable, real-time records of cargo origin, handling, and transfer, reducing fraud and counterfeiting risks. This technology streamlines logistics processes through decentralized verification, ensuring secure and efficient cargo tracking across global supply networks.
Supply Chain vs Blockchain Logistics Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com