Logistics involves managing the entire supply chain, including transportation, warehousing, and inventory control, to efficiently move goods from suppliers to customers. Micro-fulfillment centers, often located close to urban areas, enable faster order processing and delivery by using automation and streamlined storage solutions. This localized approach complements traditional logistics by reducing last-mile delivery times and improving customer satisfaction.
Table of Comparison
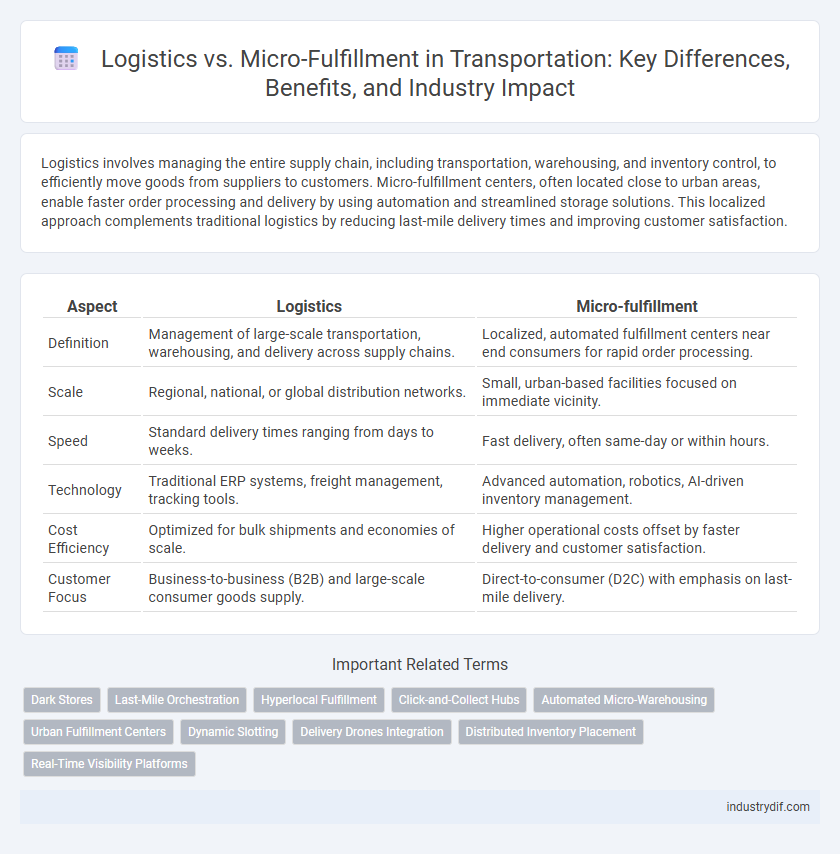
| Aspect | Logistics | Micro-fulfillment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Management of large-scale transportation, warehousing, and delivery across supply chains. | Localized, automated fulfillment centers near end consumers for rapid order processing. |
| Scale | Regional, national, or global distribution networks. | Small, urban-based facilities focused on immediate vicinity. |
| Speed | Standard delivery times ranging from days to weeks. | Fast delivery, often same-day or within hours. |
| Technology | Traditional ERP systems, freight management, tracking tools. | Advanced automation, robotics, AI-driven inventory management. |
| Cost Efficiency | Optimized for bulk shipments and economies of scale. | Higher operational costs offset by faster delivery and customer satisfaction. |
| Customer Focus | Business-to-business (B2B) and large-scale consumer goods supply. | Direct-to-consumer (D2C) with emphasis on last-mile delivery. |
Introduction to Logistics and Micro-fulfillment
Logistics involves the comprehensive management of the transportation and storage of goods across supply chains to ensure efficiency and timely delivery. Micro-fulfillment centers are compact, automated warehouses located close to the end customer, designed to accelerate order processing and last-mile delivery. While logistics covers broad supply chain coordination, micro-fulfillment focuses on speed and local inventory management to meet growing e-commerce demands.
Defining Key Concepts: Logistics vs Micro-fulfillment
Logistics encompasses the broad management of transportation, warehousing, and inventory control to optimize supply chain efficiency across long distances. Micro-fulfillment specifically targets ultra-fast order processing and delivery within small, urban warehouses or retail spaces, enhancing last-mile distribution. Understanding these distinctions highlights logistics' macro-scale scope versus micro-fulfillment's focus on rapid, localized order fulfillment in transportation networks.
Core Components of Traditional Logistics
Core components of traditional logistics include transportation management, warehousing, inventory control, and order fulfillment processes. Transportation management optimizes routes and carrier selection to ensure timely delivery, while warehousing focuses on storage, handling, and distribution efficiency. Inventory control maintains stock accuracy and availability, supporting seamless order fulfillment and reducing lead times in supply chain operations.
The Rise of Micro-fulfillment Centers
Micro-fulfillment centers are rapidly transforming logistics by enabling faster order processing through localized, automated storage and retrieval systems within urban areas. This shift reduces last-mile delivery times and lowers transportation costs by minimizing the distance between inventory and consumers. As e-commerce demand surges, micro-fulfillment centers complement traditional warehouses by enhancing supply chain agility and supporting same-day or next-day delivery expectations.
Technology Integration in Logistics and Micro-fulfillment
Technology integration in logistics enhances supply chain efficiency through advanced tracking systems, AI-powered route optimization, and real-time data analytics, enabling faster delivery and inventory management. Micro-fulfillment leverages automation, robotics, and IoT sensors within urban warehouses to accelerate order processing and minimize last-mile delivery times. Both sectors prioritize seamless software integration and innovative technologies to improve accuracy, reduce costs, and meet growing e-commerce demands.
Impact on Delivery Speed and Efficiency
Micro-fulfillment centers leverage automated technology and localized inventory to drastically reduce delivery times compared to traditional logistics hubs. By positioning goods closer to urban customers, micro-fulfillment enhances last-mile delivery efficiency, cutting transit distances and operational costs. Traditional logistics, while effective for bulk shipments, often face slower response times due to centralized warehousing and longer distribution channels.
Cost Considerations: Logistics vs Micro-fulfillment
Logistics costs encompass transportation, warehousing, and labor expenses, often increasing with longer delivery distances and larger inventory volumes. Micro-fulfillment centers reduce last-mile delivery costs by situating inventory closer to urban consumers, but they incur higher capital expenditures due to automation technology and specialized infrastructure. Companies must weigh the trade-offs between logistics scalability and micro-fulfillment's expedited delivery efficiency when estimating total cost of ownership.
Scalability and Flexibility in Modern Supply Chains
Micro-fulfillment centers offer increased scalability by enabling rapid deployment closer to customers, reducing last-mile delivery times and enhancing flexibility in inventory management. Logistics systems integrate broader network coordination, optimizing transportation routes and warehousing capacity to handle varying demand levels efficiently. Combining micro-fulfillment with traditional logistics improves responsiveness and adaptability in modern supply chains, balancing speed and cost-effectiveness.
Use Cases: When to Choose Logistics or Micro-fulfillment
Logistics excels in managing large-scale transportation networks and long-haul deliveries, making it ideal for businesses requiring distribution across extensive geographical areas. Micro-fulfillment centers focus on fast, localized order processing, perfect for urban retailers aiming to reduce last-mile delivery times and enhance customer experience. Choose logistics for broad supply chain efficiency and micro-fulfillment to optimize speed and proximity in dense city environments.
Future Trends in Transportation: Logistics and Micro-fulfillment
Future trends in transportation emphasize the integration of logistics and micro-fulfillment to enhance delivery speed and efficiency. Advanced technologies such as AI-driven route optimization, autonomous vehicles, and real-time inventory management enable seamless last-mile delivery and demand-responsive supply chains. Urban micro-fulfillment centers are increasingly pivotal for reducing delivery times and addressing consumer expectations in the evolving e-commerce landscape.
Related Important Terms
Dark Stores
Dark stores play a critical role in micro-fulfillment by serving as localized, inventory-focused hubs designed to expedite last-mile delivery and reduce fulfillment time. Unlike traditional logistics centers that manage broad distribution networks, dark stores optimize urban inventory management and order accuracy to meet rising consumer demand for rapid e-commerce delivery.
Last-Mile Orchestration
Last-mile orchestration in logistics emphasizes optimizing routes and delivery schedules across large geographic areas using centralized warehouses, while micro-fulfillment focuses on localized, automated inventory hubs near urban centers to accelerate delivery speed and reduce transportation costs. Integrating micro-fulfillment centers enhances last-mile efficiency by shortening delivery distances and enabling dynamic dispatch within dense urban environments.
Hyperlocal Fulfillment
Hyperlocal fulfillment optimizes last-mile delivery by leveraging micro-fulfillment centers strategically located within urban areas, drastically reducing transit time and enhancing delivery speed. Logistics traditionally relies on centralized warehouses, but micro-fulfillment enables real-time inventory management and scalable order processing tailored to hyperlocal demand patterns.
Click-and-Collect Hubs
Click-and-collect hubs serve as pivotal nodes in micro-fulfillment strategies by streamlining last-mile delivery and reducing shipment times compared to traditional logistics centers. These hubs leverage advanced inventory management systems and local proximity to customers, enhancing efficiency and customer satisfaction in omnichannel retail operations.
Automated Micro-Warehousing
Automated micro-warehousing in logistics enhances last-mile delivery speed by integrating compact, technology-driven storage solutions within urban areas, reducing transportation costs and transit times. This approach contrasts traditional large-scale fulfillment centers by emphasizing decentralized inventory management and real-time order processing, optimizing supply chain efficiency in dense metropolitan markets.
Urban Fulfillment Centers
Urban fulfillment centers optimize last-mile delivery efficiency by strategically locating inventory closer to consumers, reducing transit times and transportation costs compared to traditional logistics hubs that manage large-scale, regional distribution. Leveraging micro-fulfillment systems within these centers integrates automation and real-time inventory tracking, enabling rapid order processing and enhancing urban supply chain responsiveness.
Dynamic Slotting
Dynamic slotting in logistics enhances warehouse efficiency by continuously adjusting inventory locations based on demand patterns and order profiles, reducing picking time and labor costs. In micro-fulfillment centers, dynamic slotting optimizes space utilization and accelerates order processing, catering to faster delivery requirements in urban retail environments.
Delivery Drones Integration
Logistics leverages delivery drones for large-scale, long-distance transportation enhancing supply chain efficiency, while micro-fulfillment integrates drones for rapid last-mile delivery within urban environments, reducing delivery times and operational costs. Drone integration in logistics emphasizes airspace management and payload capacity, whereas micro-fulfillment focuses on precision navigation and decentralized hub connectivity.
Distributed Inventory Placement
Distributed inventory placement enhances logistics efficiency by strategically positioning stock closer to end consumers, reducing delivery times and transportation costs while improving order fulfillment rates. Micro-fulfillment centers leverage this approach by using automated, localized warehouses to enable rapid, last-mile delivery in urban areas, optimizing supply chain responsiveness.
Real-Time Visibility Platforms
Real-time visibility platforms in transportation enhance both logistics and micro-fulfillment by providing instant tracking of shipments, inventory levels, and delivery statuses, enabling faster decision-making and improved supply chain efficiency. These platforms utilize IoT sensors, GPS data, and AI analytics to optimize route planning, reduce transit times, and ensure accurate order fulfillment in micro-fulfillment centers.
Logistics vs Micro-fulfillment Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com