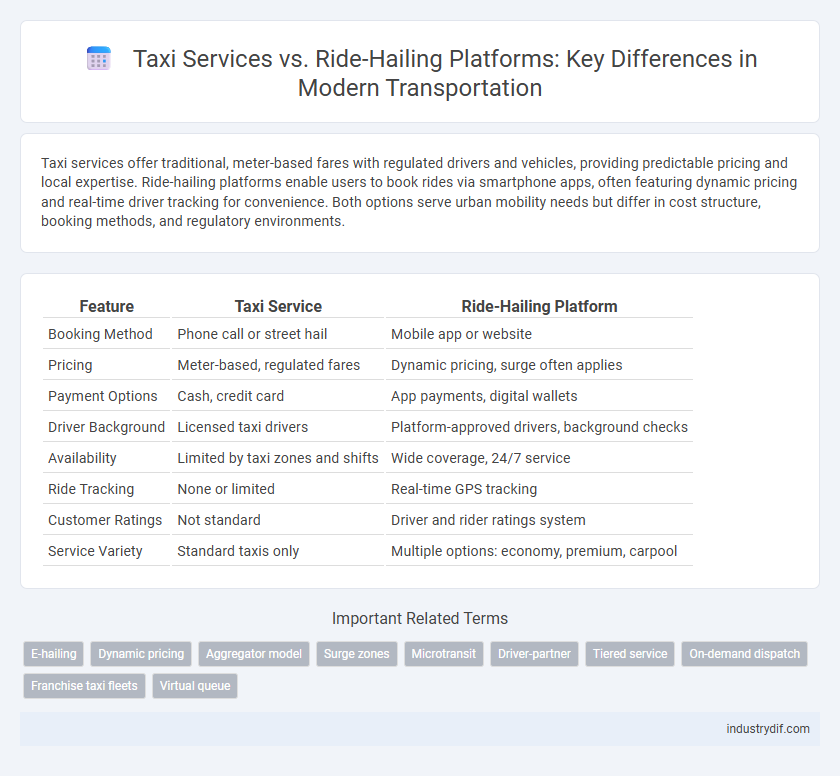
Taxi services offer traditional, meter-based fares with regulated drivers and vehicles, providing predictable pricing and local expertise. Ride-hailing platforms enable users to book rides via smartphone apps, often featuring dynamic pricing and real-time driver tracking for convenience. Both options serve urban mobility needs but differ in cost structure, booking methods, and regulatory environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Taxi Service | Ride-Hailing Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Booking Method | Phone call or street hail | Mobile app or website |
| Pricing | Meter-based, regulated fares | Dynamic pricing, surge often applies |
| Payment Options | Cash, credit card | App payments, digital wallets |
| Driver Background | Licensed taxi drivers | Platform-approved drivers, background checks |
| Availability | Limited by taxi zones and shifts | Wide coverage, 24/7 service |
| Ride Tracking | None or limited | Real-time GPS tracking |
| Customer Ratings | Not standard | Driver and rider ratings system |
| Service Variety | Standard taxis only | Multiple options: economy, premium, carpool |
Overview of Taxi Services and Ride-Hailing Platforms
Taxi services operate with licensed drivers and vehicles subject to strict regulatory oversight, ensuring standardized fares and safety protocols. Ride-hailing platforms leverage mobile technology for on-demand booking, dynamic pricing, and real-time tracking, providing greater convenience and flexibility. Both models serve urban mobility needs but differ in regulatory frameworks, pricing structures, and user experience.
Key Differences in Business Models
Taxi services operate on a traditional business model relying on licensed drivers who either lease vehicles or own them, with fares regulated by local authorities. Ride-hailing platforms leverage technology to connect passengers with freelance drivers through mobile apps, utilizing dynamic pricing based on demand and supply. The shift from regulated fare structures to flexible pricing models marks a fundamental difference in revenue generation and operational scalability between the two.
Service Accessibility and Coverage
Taxi services typically offer extensive coverage in urban areas with designated stands and easy street hailing, yet their service accessibility can be limited by availability during peak hours and in less populated zones. Ride-hailing platforms leverage mobile apps to provide on-demand access to a wider geographical range, including suburban and underserved regions, often enhancing user convenience with real-time tracking and cashless payments. The scalability and technology integration of ride-hailing apps generally result in higher service accessibility and broader coverage compared to traditional taxi services.
Pricing Structure and Fare Transparency
Taxi services typically use meter-based pricing regulated by local authorities, ensuring transparent fares based on distance and time. Ride-hailing platforms often implement dynamic pricing with surge multipliers that fluctuate according to demand, leading to less predictable costs. Passengers benefit from upfront fare estimates on ride-hailing apps, whereas taxi fares may vary due to traffic conditions and route changes.
Booking Process and User Convenience
Taxi services typically require users to book rides via phone calls or street hailing, which can be less efficient and time-consuming compared to ride-hailing platforms that offer seamless app-based booking with real-time tracking and fare estimates. Ride-hailing platforms enhance user convenience by providing cashless payments, driver reviews, and scheduled rides, streamlining the entire transportation experience. The integration of GPS technology in ride-hailing apps reduces wait times and improves route optimization, making them more user-friendly than traditional taxi services.
Driver Employment and Regulation
Taxi services typically employ drivers directly or engage them as independent contractors, adhering to stringent local licensing and safety regulations that ensure passenger protection. Ride-hailing platforms classify drivers as independent contractors, often resulting in less regulatory oversight but greater flexibility in work hours and geographic operation. Regulatory frameworks continue to evolve, with many regions imposing stricter rules on ride-hailing to address concerns around labor rights, insurance coverage, and passenger safety.
Safety Measures and Customer Trust
Taxi services maintain rigorous safety protocols such as driver background checks, vehicle inspections, and regulated fare systems, fostering long-standing customer trust. Ride-hailing platforms enhance safety with real-time GPS tracking, driver ratings, and in-app emergency features, appealing to tech-savvy users seeking transparency and accountability. Both models prioritize passenger security but differ in regulatory frameworks and technology integration, shaping user confidence and preferences in urban transportation.
Payment Methods and Transaction Security
Taxi services traditionally rely on cash payments and credit card terminals, offering a straightforward but sometimes less flexible payment experience. Ride-hailing platforms utilize integrated digital payment systems, including mobile wallets and in-app payments, enhancing convenience and transaction speed. Advanced encryption and tokenization technologies in ride-hailing apps provide higher transaction security compared to conventional taxi payment methods.
Customer Experience and Service Quality
Taxi services offer a regulated and standardized customer experience with licensed drivers and fixed fare structures, ensuring reliability and safety. Ride-hailing platforms provide enhanced convenience through app-based bookings, real-time tracking, and dynamic pricing, which often improves wait times and service customization. Both options emphasize service quality, but ride-hailing platforms leverage technology for greater transparency and user feedback integration.
Future Trends in Urban Transportation
Taxi services are increasingly integrating digital platforms to compete with ride-hailing apps, leveraging GPS technology and cashless payments to enhance user experience. Ride-hailing platforms utilize advanced data analytics and AI for dynamic pricing and optimized routing, setting new standards in urban mobility efficiency. Future trends indicate a convergence of both models with electric and autonomous vehicles, aimed at reducing congestion and emissions in smart cities.
Related Important Terms
E-hailing
E-hailing platforms leverage advanced mobile applications and GPS technology to provide real-time ride requests, dynamic pricing, and cashless payments, offering enhanced convenience compared to traditional taxi services. These digital platforms also enable greater transparency through driver ratings and route tracking, significantly improving user experience and operational efficiency in urban transportation.
Dynamic pricing
Taxi services typically use fixed or meter-based fares regulated by local authorities, ensuring price stability and predictability for passengers, while ride-hailing platforms implement dynamic pricing models that adjust rates in real-time based on demand, traffic, and availability, optimizing driver earnings and resource allocation. Dynamic pricing in ride-hailing can lead to surge pricing during peak hours or high-demand events, creating cost variability that contrasts with the generally consistent taxi fare structure.
Aggregator model
Taxi service traditionally operates through direct bookings or street hailing, whereas ride-hailing platforms utilize an aggregator model that connects passengers with multiple independent drivers via a single app interface. This aggregator model optimizes route efficiency, dynamic pricing, and real-time driver allocation, leading to enhanced service availability and customer convenience.
Surge zones
Surge zones in ride-hailing platforms dynamically increase fares based on real-time demand and supply imbalances, enabling efficient allocation of drivers and maximizing revenue during peak hours. Traditional taxi services typically lack this automated surge pricing mechanism, often resulting in fixed or negotiated rates that may not accurately reflect fluctuating market conditions.
Microtransit
Microtransit leverages ride-hailing platforms to provide flexible, on-demand shared rides within urban areas, optimizing routes and reducing wait times compared to traditional taxi services. These platforms use dynamic routing algorithms and real-time data to improve operational efficiency and lower costs, enhancing accessibility and scalability in public transportation networks.
Driver-partner
Taxi service drivers typically operate independently or for a specific company with fixed shifts, while ride-hailing platform driver-partners enjoy flexible schedules, leveraging app-based demand to maximize earnings. Driver-partners on ride-hailing platforms benefit from real-time routing algorithms and dynamic pricing models that enhance trip efficiency and income potential compared to traditional taxi drivers.
Tiered service
Taxi services offer tiered options based on vehicle type and service level, providing customers with choices from standard cabs to luxury sedans, ensuring tailored pricing and comfort. Ride-hailing platforms incorporate dynamic tiered services such as economy, premium, and shared rides, leveraging real-time demand to optimize availability and pricing flexibility for diverse customer needs.
On-demand dispatch
Taxi services offer on-demand dispatch through traditional radio or phone requests, requiring manual coordination that can lead to longer wait times. Ride-hailing platforms utilize GPS-enabled apps for instant vehicle matching and real-time tracking, significantly enhancing efficiency and reducing passenger wait times.
Franchise taxi fleets
Franchise taxi fleets offer standardized service quality, regulatory compliance, and predictable pricing, differentiating them from ride-hailing platforms that rely on independent drivers and dynamic pricing models. This structured approach enhances passenger safety and fosters trust, positioning franchise taxi services as a reliable choice within the urban transportation ecosystem.
Virtual queue
Virtual queue systems in taxi services often rely on traditional dispatch mechanisms that can lead to longer wait times and limited passenger control, whereas ride-hailing platforms use dynamic, app-based virtual queues to provide real-time updates, efficient vehicle allocation, and enhanced user convenience. These technology-driven queues optimize customer flow, reduce idle time for drivers, and improve overall service reliability in urban transportation networks.
Taxi service vs Ride-hailing platform Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com