Warehousing and dark stores serve distinct roles in transportation logistics, with warehousing primarily focused on the storage and long-term inventory management of goods. Dark stores operate as localized fulfillment centers designed for rapid order picking and delivery, often supporting e-commerce and same-day shipping. Efficient transportation strategies must balance the volume storage capacity of warehouses with the speed and proximity advantages offered by dark stores.
Table of Comparison
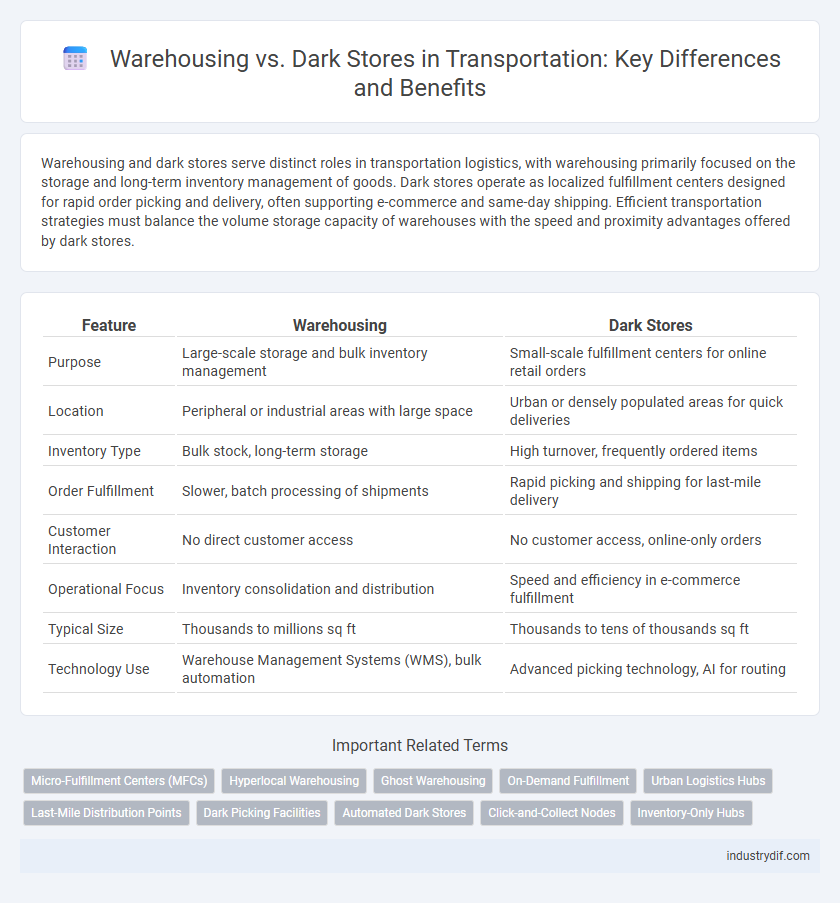
| Feature | Warehousing | Dark Stores |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Large-scale storage and bulk inventory management | Small-scale fulfillment centers for online retail orders |
| Location | Peripheral or industrial areas with large space | Urban or densely populated areas for quick deliveries |
| Inventory Type | Bulk stock, long-term storage | High turnover, frequently ordered items |
| Order Fulfillment | Slower, batch processing of shipments | Rapid picking and shipping for last-mile delivery |
| Customer Interaction | No direct customer access | No customer access, online-only orders |
| Operational Focus | Inventory consolidation and distribution | Speed and efficiency in e-commerce fulfillment |
| Typical Size | Thousands to millions sq ft | Thousands to tens of thousands sq ft |
| Technology Use | Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), bulk automation | Advanced picking technology, AI for routing |
Understanding Warehousing and Dark Stores: Key Definitions
Warehousing refers to the storage of goods in large facilities designed to hold inventory for extended periods, facilitating supply chain management and distribution. Dark stores are specialized retail outlets or fulfillment centers that serve exclusively online orders, optimizing last-mile delivery speed and inventory accessibility. Both play critical roles in modern transportation logistics by streamlining inventory management and enhancing delivery efficiency.
Core Functions in Warehousing vs Dark Stores
Warehousing primarily focuses on bulk storage, inventory management, and long-term stock preservation to support supply chain efficiency. Dark stores specialize in rapid order fulfillment, acting as local distribution hubs optimized for e-commerce and last-mile delivery. Core functions in warehousing include space optimization and stock control, while dark stores prioritize picking speed and real-time inventory accuracy.
Inventory Management: Warehouses vs Dark Stores
Warehouses manage large-scale inventory with systematic storage and inventory control systems designed for bulk goods, enabling efficient order fulfillment and distribution across multiple regions. Dark stores focus on rapid inventory turnover and real-time stock updates to support online order picking and last-mile delivery in urban areas, often utilizing automation for streamlined, high-frequency restocking. Efficient inventory management in both relies on advanced software, but warehouses prioritize space optimization while dark stores emphasize speed and accessibility.
Location Strategies and Their Impact
Warehousing strategies prioritize centralized locations near major transportation hubs to optimize inventory management and reduce distribution costs. Dark stores focus on proximity to urban centers, enhancing last-mile delivery speed and meeting growing e-commerce demand. Choosing between these locations significantly impacts operational efficiency, delivery times, and customer satisfaction in the transportation and supply chain network.
Order Fulfillment Efficiencies: Comparing Both Models
Warehousing centers optimize order fulfillment by storing bulk inventory and utilizing automated systems for rapid picking and packing, enhancing delivery speed and accuracy. Dark stores prioritize proximity to urban consumers, enabling faster last-mile delivery through localized inventory but often handle smaller stock volumes. Comparing both, warehouses excel in large-scale distribution efficiency, while dark stores offer superior speed in fulfilling immediate, local orders.
Technology Integration in Warehousing and Dark Stores
Technology integration in warehousing leverages advanced automation systems such as robotics, IoT sensors, and AI-driven inventory management to optimize storage and distribution efficiency. Dark stores utilize similar technologies but emphasize real-time order processing and rapid fulfillment through sophisticated software platforms and mobile robotics tailored for last-mile delivery. Both models rely heavily on data analytics and cloud computing to streamline operations, reduce errors, and enhance scalability in meeting fluctuating consumer demands.
Cost Structures Explained: Warehousing vs Dark Stores
Warehousing typically involves higher fixed costs due to large storage facilities, extensive inventory management, and longer handling times, whereas dark stores reduce expenses by operating smaller, strategically located fulfillment centers focused solely on online orders. Dark stores optimize last-mile delivery costs by improving delivery speed and minimizing stockkeeping unit (SKU) volumes, which leads to lower labor and transportation costs. The cost efficiency of dark stores is amplified in urban environments where quick order fulfillment and reduced delivery distances are critical.
Roles in Omni-Channel Retail Logistics
Warehousing in omni-channel retail logistics serves as centralized hubs for storing and distributing inventory across multiple sales channels, enabling efficient bulk handling and long-term stock management. Dark stores function as mini-fulfillment centers located closer to end consumers, optimizing last-mile delivery speed for online orders and supporting rapid click-and-collect services. Combining traditional warehousing with dark stores enhances inventory accuracy, reduces delivery times, and improves customer experience across e-commerce and brick-and-mortar platforms.
Scalability and Flexibility in Supply Chain Operations
Warehousing offers scalable storage capacity with predictable inventory management, supporting long-term supply chain expansions. Dark stores provide greater flexibility by enabling rapid order fulfillment and real-time inventory adjustments tailored for e-commerce demand fluctuations. Integrating both models enhances supply chain efficiency through balanced scalability and agile responsiveness.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Warehousing and Dark Stores
Warehousing and dark stores are evolving through automation and AI integration to meet rising e-commerce demand and rapid urbanization. Predictive analytics and IoT technology optimize inventory management and delivery speed, reducing operational costs and carbon footprint. The convergence of dark stores with hyperlocal fulfillment centers supports same-day delivery and personalized customer experiences, reshaping last-mile logistics.
Related Important Terms
Micro-Fulfillment Centers (MFCs)
Micro-Fulfillment Centers (MFCs) bridge the gap between traditional warehousing and dark stores by enabling rapid, localized order fulfillment through advanced automation and optimized inventory management. These facilities enhance last-mile delivery efficiency by strategically placing small-scale warehouses closer to urban consumers, reducing transit times and operational costs.
Hyperlocal Warehousing
Hyperlocal warehousing optimizes last-mile delivery by strategically positioning inventory closer to end consumers, enhancing speed and reducing transportation costs compared to traditional warehousing. Dark stores serve as localized fulfillment centers exclusively for online orders, leveraging hyperlocal warehousing to streamline e-commerce logistics and improve delivery efficiency in urban areas.
Ghost Warehousing
Ghost warehousing leverages smaller, strategically located fulfillment centers designed exclusively for fast e-commerce order processing, minimizing delivery times compared to traditional warehousing. These facilities operate without storefronts, optimizing inventory management and enabling seamless last-mile logistics in urban environments.
On-Demand Fulfillment
Warehousing supports bulk inventory storage with longer lead times, while dark stores optimize on-demand fulfillment by serving as localized mini-distribution centers for rapid order processing and last-mile delivery. Dark stores enhance urban logistics efficiency by reducing delivery times and enabling real-time inventory visibility, critical for meeting consumer expectations in e-commerce.
Urban Logistics Hubs
Urban logistics hubs optimize last-mile delivery by utilizing warehousing facilities for bulk inventory storage, while dark stores serve as localized distribution centers designed for rapid order fulfillment and increased delivery speed. Efficient integration of warehousing and dark stores within urban logistics networks reduces transit times, lowers transportation costs, and enhances customer satisfaction in densely populated areas.
Last-Mile Distribution Points
Warehousing facilities serve as centralized hubs for bulk storage and inventory management, supporting longer supply chains, while dark stores function as localized mini-fulfillment centers designed to expedite last-mile delivery by enabling faster order processing and reducing delivery times. Optimizing last-mile distribution points through dark stores significantly enhances e-commerce fulfillment efficiency by bringing inventory closer to end consumers, minimizing transportation costs and delivery delays.
Dark Picking Facilities
Dark picking facilities optimize last-mile delivery by operating as automated, technology-driven hubs that streamline order fulfillment without customer foot traffic, contrasting traditional warehousing which primarily stores bulk inventory. These facilities leverage real-time inventory management and robotics to enhance efficiency, reduce order processing time, and support rapid e-commerce growth within urban logistics networks.
Automated Dark Stores
Automated dark stores optimize last-mile delivery by integrating robotics and AI-driven inventory management, significantly reducing order fulfillment time compared to traditional warehousing. Their strategic urban locations enhance supply chain efficiency and enable rapid response to consumer demand in e-commerce and food delivery sectors.
Click-and-Collect Nodes
Warehousing facilities optimize inventory storage and bulk distribution, while dark stores function as local fulfillment centers specifically designed for rapid pick-up in click-and-collect operations. Click-and-collect nodes situated in dark stores enhance last-mile delivery efficiency by reducing travel time and enabling immediate customer access to ordered goods.
Inventory-Only Hubs
Inventory-only hubs like dark stores optimize urban last-mile delivery by acting as specialized warehouses dedicated solely to fulfilling online orders, reducing delivery times and improving inventory accuracy. Warehousing facilities, while essential for bulk storage and distribution, often lack the rapid accessibility and localized inventory management that dark stores provide in dense metropolitan areas.
Warehousing vs Dark Stores Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com