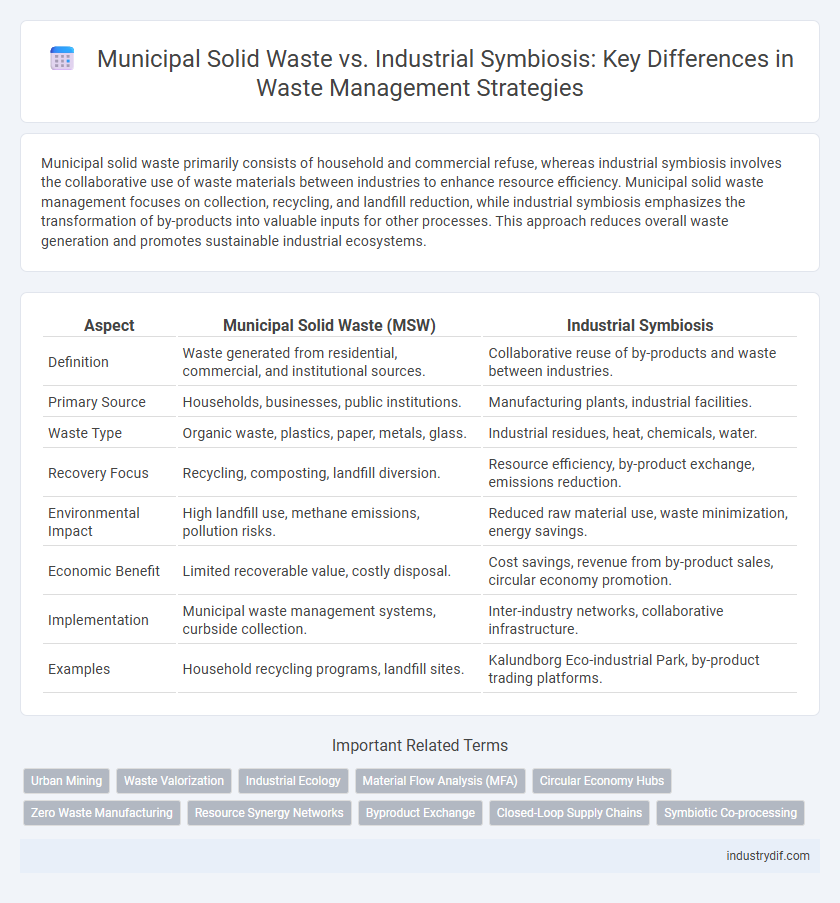
Municipal solid waste primarily consists of household and commercial refuse, whereas industrial symbiosis involves the collaborative use of waste materials between industries to enhance resource efficiency. Municipal solid waste management focuses on collection, recycling, and landfill reduction, while industrial symbiosis emphasizes the transformation of by-products into valuable inputs for other processes. This approach reduces overall waste generation and promotes sustainable industrial ecosystems.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) | Industrial Symbiosis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Waste generated from residential, commercial, and institutional sources. | Collaborative reuse of by-products and waste between industries. |
| Primary Source | Households, businesses, public institutions. | Manufacturing plants, industrial facilities. |
| Waste Type | Organic waste, plastics, paper, metals, glass. | Industrial residues, heat, chemicals, water. |
| Recovery Focus | Recycling, composting, landfill diversion. | Resource efficiency, by-product exchange, emissions reduction. |
| Environmental Impact | High landfill use, methane emissions, pollution risks. | Reduced raw material use, waste minimization, energy savings. |
| Economic Benefit | Limited recoverable value, costly disposal. | Cost savings, revenue from by-product sales, circular economy promotion. |
| Implementation | Municipal waste management systems, curbside collection. | Inter-industry networks, collaborative infrastructure. |
| Examples | Household recycling programs, landfill sites. | Kalundborg Eco-industrial Park, by-product trading platforms. |
Defining Municipal Solid Waste
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) refers to the everyday garbage or refuse generated by households, commercial establishments, and institutions, including food scraps, paper, plastics, and glass. MSW management involves collection, treatment, and disposal processes aimed at minimizing environmental impact and promoting recycling and recovery. In contrast, Industrial Symbiosis optimizes waste exchanges between industries to reduce raw material consumption and improve sustainability beyond traditional waste disposal methods.
Understanding Industrial Symbiosis
Industrial Symbiosis involves the collaborative exchange of materials, energy, and by-products between different industries to reduce overall waste generation and resource consumption. Unlike typical Municipal Solid Waste management, which focuses on collecting and disposing of household and commercial waste, Industrial Symbiosis aims to create closed-loop systems that transform waste into valuable inputs for other processes. This approach enhances sustainability by minimizing landfill use, lowering environmental impact, and promoting efficient resource utilization across industrial sectors.
Key Differences Between Municipal Solid Waste and Industrial Symbiosis
Municipal solid waste primarily consists of everyday items discarded by households, such as food scraps, paper, and plastics, whereas industrial symbiosis involves the collaborative exchange of materials, energy, and by-products between industries to optimize resource use. Unlike municipal solid waste management, which focuses on collection, disposal, and recycling, industrial symbiosis aims to create closed-loop systems that reduce waste generation through synergy among factories. Key differences also include the scale and purpose, with municipal waste targeting urban living environments, while industrial symbiosis emphasizes economic and environmental benefits within industrial networks.
Waste Generation Sources in Urban Environments
Municipal solid waste primarily originates from household activities, commercial establishments, and public spaces within urban environments, contributing significantly to daily waste accumulation. Industrial symbiosis involves the collaboration between industries to repurpose by-products and waste streams, reducing overall waste generation at source in urban industrial clusters. Urban waste management strategies benefit from integrating municipal waste data with industrial symbiosis initiatives to optimize resource recovery and minimize landfill dependency.
Circular Economy Principles in Industrial Symbiosis
Industrial symbiosis promotes circular economy principles by enabling the exchange of municipal solid waste as raw materials among industries, reducing landfill dependency and conserving natural resources. This approach transforms waste streams into valuable inputs, fostering resource efficiency and minimizing environmental impact compared to traditional waste disposal methods. Municipal solid waste, when integrated into industrial symbiosis networks, supports closed-loop systems that enhance sustainability and economic resilience.
Environmental Impacts of Municipal Solid Waste
Municipal solid waste (MSW) significantly contributes to environmental degradation through methane emissions during organic waste decomposition, exacerbating climate change. Improper disposal of MSW leads to soil and water contamination from hazardous substances, impacting ecosystems and human health. Industrial symbiosis offers a sustainable alternative by promoting resource efficiency and waste minimization, thereby reducing the overall environmental footprint associated with MSW management.
Resource Recovery Through Industrial Symbiosis
Municipal solid waste (MSW) management primarily focuses on collection, recycling, and disposal, often missing opportunities for resource optimization across industries. Industrial symbiosis facilitates resource recovery by enabling the exchange of materials, energy, and by-products between industrial processes, reducing waste generation and enhancing circular economy practices. This collaborative approach decreases landfill dependency, lowers greenhouse gas emissions, and improves resource efficiency significantly compared to conventional MSW handling.
Technology and Innovation in Waste Management
Municipal solid waste management increasingly incorporates sensor technology and AI-driven sorting systems to enhance recycling rates and reduce landfill reliance. Industrial symbiosis employs digital platforms and real-time data analytics to facilitate the exchange of by-products, optimizing resource efficiency between industries. Advances in waste-to-energy technologies, including anaerobic digestion and plasma gasification, support both sectors by converting waste streams into renewable energy sources, promoting sustainable circular economy models.
Policy Frameworks Shaping Waste Strategies
Municipal solid waste management policies prioritize waste reduction, segregation, and recycling within urban populations, emphasizing extended producer responsibility and public participation to minimize landfill usage. Industrial symbiosis frameworks promote resource efficiency by encouraging collaboration among industries to exchange waste materials, supported by regulations incentivizing circular economy practices and emissions reduction targets. Effective policy frameworks integrate both approaches, fostering sustainable waste practices through regulatory measures, financial incentives, and stakeholder engagement to achieve holistic waste minimization and resource recovery.
Future Trends in Municipal and Industrial Waste Management
Future trends in municipal solid waste management emphasize advanced sorting technologies, increased recycling rates, and the integration of smart infrastructure to optimize collection and reduce landfill dependency. Industrial symbiosis promotes resource sharing and waste exchange between industries, fostering circular economy principles that minimize raw material consumption and environmental impact. Emerging innovations include digital platforms for waste tracking and enhanced material recovery, driving collaboration between municipal and industrial sectors towards sustainable waste management systems.
Related Important Terms
Urban Mining
Municipal solid waste (MSW) primarily consists of everyday household refuse, while industrial symbiosis involves the collaborative reuse of waste materials between industries, optimizing resources through urban mining. Urban mining recovers valuable metals and materials from MSW and industrial by-products, reducing landfill use and promoting sustainable circular economies in urban areas.
Waste Valorization
Municipal solid waste (MSW) valorization transforms everyday household refuse into valuable resources through processes like recycling, composting, and energy recovery, reducing landfill reliance and environmental impact. Industrial symbiosis enhances waste valorization by facilitating the exchange of by-products and energy between industries, optimizing resource efficiency and promoting circular economy principles.
Industrial Ecology
Industrial ecology leverages the principles of industrial symbiosis to minimize municipal solid waste by promoting resource efficiency and material reuse across interconnected industries. This holistic approach transforms waste streams from municipal waste into valuable inputs, reducing environmental impact and fostering sustainable urban ecosystems.
Material Flow Analysis (MFA)
Material Flow Analysis (MFA) of municipal solid waste reveals inefficiencies in waste segregation and resource recovery, emphasizing the need for improved waste management strategies. Industrial symbiosis optimizes material flows by facilitating the exchange of by-products between industries, significantly reducing waste generation and promoting circular economy principles.
Circular Economy Hubs
Municipal solid waste management transforms urban refuse into valuable resources, while industrial symbiosis facilitates material and energy exchanges among industries, both driving Circular Economy Hubs that optimize resource efficiency and minimize landfill dependency. These hubs integrate waste streams and by-products, promoting sustainable urban development and reducing environmental impact through closed-loop systems.
Zero Waste Manufacturing
Municipal solid waste (MSW) primarily consists of everyday household refuse, whereas industrial symbiosis leverages by-products and waste streams from different industries to achieve zero waste manufacturing. By integrating industrial symbiosis practices, manufacturers can minimize landfill dependency and convert waste into valuable raw materials, fostering sustainable production cycles and reducing environmental impact.
Resource Synergy Networks
Municipal solid waste management primarily focuses on collection, segregation, and disposal within urban environments, often leading to resource recovery challenges. Industrial symbiosis leverages Resource Synergy Networks to transform waste streams from one industrial process into valuable inputs for another, enhancing circular economy practices and reducing environmental impacts.
Byproduct Exchange
Municipal solid waste (MSW) primarily consists of everyday household refuse, typically destined for landfills or incineration, creating significant environmental challenges. Industrial symbiosis, by contrast, emphasizes the byproduct exchange where waste materials from one industrial process become raw inputs for another, reducing overall waste generation and promoting sustainable resource efficiency.
Closed-Loop Supply Chains
Municipal solid waste management primarily relies on traditional disposal methods, whereas industrial symbiosis promotes closed-loop supply chains by enabling multiple industries to exchange waste materials as resources, significantly reducing landfill use and environmental impact. Closed-loop supply chains in industrial symbiosis optimize resource efficiency through waste reuse, recovery, and recycling, fostering sustainable waste management and circular economy practices.
Symbiotic Co-processing
Symbiotic co-processing integrates municipal solid waste with industrial by-products to enhance resource efficiency and reduce landfill dependency through collaborative material recovery and energy extraction. This approach optimizes waste valorization by combining diverse waste streams, promoting sustainable industrial ecosystems and lowering overall environmental footprints.
Municipal Solid Waste vs Industrial Symbiosis Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com