Municipal solid waste (MSW) primarily consists of everyday household and commercial refuse such as food scraps, packaging, and paper, whereas construction and demolition (C&D) waste includes materials like concrete, wood, metals, and bricks generated from building activities. Proper management of MSW focuses on recycling, composting, and reducing landfill disposal, while C&D waste requires specialized processing for material recovery and reuse in construction projects. Addressing both waste types effectively reduces environmental impact and promotes sustainable resource management.
Table of Comparison
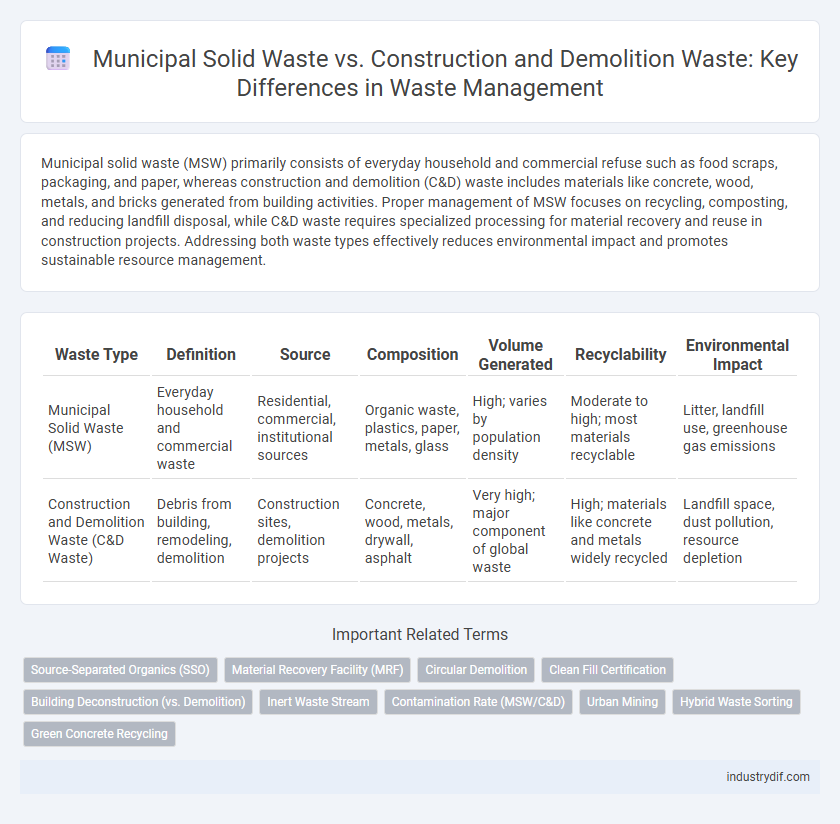
| Waste Type | Definition | Source | Composition | Volume Generated | Recyclability | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) | Everyday household and commercial waste | Residential, commercial, institutional sources | Organic waste, plastics, paper, metals, glass | High; varies by population density | Moderate to high; most materials recyclable | Litter, landfill use, greenhouse gas emissions |
| Construction and Demolition Waste (C&D Waste) | Debris from building, remodeling, demolition | Construction sites, demolition projects | Concrete, wood, metals, drywall, asphalt | Very high; major component of global waste | High; materials like concrete and metals widely recycled | Landfill space, dust pollution, resource depletion |
Defining Municipal Solid Waste (MSW)
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) consists of everyday household garbage, including food scraps, packaging, paper, and yard waste, generated by residential and commercial sources. It differs from Construction and Demolition (C&D) waste, which primarily includes materials like concrete, wood, metals, and drywall from building activities. Proper management of MSW is critical for reducing landfill use, promoting recycling, and minimizing environmental impact in urban areas.
Understanding Construction and Demolition (C&D) Waste
Construction and Demolition (C&D) waste consists primarily of materials such as concrete, wood, metals, bricks, and drywall generated during building construction, renovation, and demolition activities. Unlike Municipal Solid Waste (MSW), which includes everyday household garbage like food scraps, plastics, and paper, C&D waste often contains large volumes of recyclable materials that can be recovered and reused in new construction projects. Efficient management of C&D waste through sorting, recycling, and repurposing reduces landfill usage and environmental impact compared to the more heterogeneous composition of MSW.
Key Differences Between MSW and C&D Waste
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) primarily consists of household garbage, packaging, food scraps, and everyday discarded materials, while Construction and Demolition (C&D) Waste includes debris from building sites such as concrete, wood, metals, bricks, and drywall. MSW is typically generated by residential, commercial, and institutional sources and requires different handling and treatment methods compared to C&D waste, which often involves bulky, heavy materials with high recycling potential. Regulatory frameworks and disposal strategies differ substantially, reflecting the distinct composition, volume, and environmental impact of MSW versus C&D waste streams.
Major Sources of Municipal Solid Waste
Major sources of Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) include residential households, commercial establishments, and institutional facilities, accounting for diverse waste types such as food scraps, paper, plastics, and textiles. Construction and Demolition (C&D) Waste primarily originates from building sites, including debris like concrete, wood, metals, and drywall, which differ significantly in composition and management from MSW. Effective waste management requires understanding the distinct origins and material characteristics of MSW and C&D waste to optimize recycling, disposal, and resource recovery strategies.
Primary Sources of Construction and Demolition Waste
Construction and demolition waste primarily originates from building sites, including debris from renovations, demolitions, and new construction projects. Key sources include concrete, wood, metals, bricks, and drywall generated during the dismantling or updating of structures. These materials differ significantly from municipal solid waste, which consists mainly of household refuse, organic waste, and packaging materials collected from residential, commercial, and institutional sources.
Material Composition Comparison: MSW vs C&D Waste
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) primarily consists of organic materials, plastics, paper, and glass, reflecting residential and commercial discard patterns. Construction and Demolition (C&D) Waste is predominantly composed of concrete, wood, metals, bricks, and gypsum drywall, originating from building sites and renovation projects. The distinct material composition of MSW and C&D waste necessitates specialized recycling and disposal strategies tailored to their respective physical and chemical characteristics.
Waste Management Practices for MSW
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) primarily consists of everyday household and commercial refuse, requiring systematic waste management practices such as source segregation, recycling, composting, and sanitary landfilling. Effective MSW management emphasizes reducing landfill reliance through advanced technologies like Material Recovery Facilities (MRFs) and anaerobic digestion to convert organic waste into biogas. In contrast, Construction and Demolition Waste (C&DW) demands specialized handling involving on-site sorting, crushing, and repurposing materials for construction aggregates, highlighting distinct operational strategies from MSW management.
C&D Waste Recycling and Recovery Methods
Construction and demolition (C&D) waste recycling employs mechanical sorting, crushing, and screening to recover valuable materials such as concrete, wood, metals, and gypsum. Advanced methods like on-site separation and use of mobile processing units enhance recovery rates, reducing landfill dependency compared to municipal solid waste management. Recycled C&D materials are increasingly utilized in road base, aggregate substitutes, and new construction products, promoting circular economy principles in the construction sector.
Environmental Impacts: MSW versus C&D Waste
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) primarily includes household and commercial refuse, generating significant greenhouse gas emissions from landfills due to organic decomposition, while Construction and Demolition (C&D) Waste consists of concrete, wood, metals, and other materials with higher potential for recycling but substantial environmental risks from improper disposal. MSW contributes to water and air pollution through leachate and methane production, whereas C&D waste poses hazards like soil contamination and resource depletion if not managed sustainably. Effective segregation, recycling, and treatment strategies for both waste types are crucial to mitigating soil degradation, reducing landfill volumes, and minimizing carbon footprints associated with waste management processes.
Regulatory Frameworks Governing MSW and C&D Waste
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) is regulated under frameworks such as the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) in the United States, which emphasizes waste reduction, recycling, and safe disposal practices. Construction and Demolition (C&D) Waste is governed by separate regulations that often prioritize material recovery and landfill diversion, including specific guidelines from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and local building codes. Compliance with these regulatory frameworks ensures environmental protection, resource conservation, and public health safety in managing both MSW and C&D waste streams.
Related Important Terms
Source-Separated Organics (SSO)
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) typically contains a higher proportion of Source-Separated Organics (SSO), such as food scraps and yard waste, which are crucial for effective composting and waste diversion programs. In contrast, Construction and Demolition (C&D) Waste consists mainly of inert materials like concrete and wood, with minimal SSO content, making it less suitable for organic recycling processes.
Material Recovery Facility (MRF)
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) and Construction and Demolition (C&D) waste require specialized Material Recovery Facilities (MRFs) designed to efficiently sort and recycle diverse materials such as plastics, metals, wood, and concrete debris. Advanced MRF technologies enhance recovery rates by employing automated sorting systems, which maximize the extraction of valuable recyclables from both MSW and C&D waste streams, reducing landfill burden and promoting sustainable resource management.
Circular Demolition
Municipal solid waste (MSW) primarily consists of everyday household and commercial refuse, whereas construction and demolition (C&D) waste includes materials such as concrete, wood, metals, and drywall generated from building activities; Circular Demolition focuses on maximizing resource recovery by systematically deconstructing buildings to salvage reusable materials, significantly reducing landfill disposal and promoting sustainable construction practices. This approach enhances the circular economy by prioritizing material reuse, recycling, and minimizing environmental impact compared to traditional demolition methods.
Clean Fill Certification
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) consists primarily of everyday household and commercial refuse requiring comprehensive disposal and recycling strategies, whereas Construction and Demolition (C&D) Waste encompasses materials like concrete, wood, and metals that can often be repurposed or disposed of through specialized methods such as Clean Fill Certification. Clean Fill Certification ensures that inert C&D waste meets strict environmental standards for non-contaminating disposal, reducing landfill impact and promoting sustainable construction practices.
Building Deconstruction (vs. Demolition)
Building deconstruction maximizes material recovery and minimizes environmental impact by carefully dismantling structures to salvage reusable components, unlike traditional demolition, which generates mixed municipal solid waste and construction and demolition (C&D) debris that often end up in landfills. This selective process reduces municipal solid waste contamination, lowers landfill diversion costs, and supports sustainable waste management practices in urban development projects.
Inert Waste Stream
Municipal solid waste primarily consists of organic materials, plastics, and household refuse, whereas construction and demolition waste is largely composed of inert materials such as concrete, bricks, and asphalt that do not readily decompose. Inert waste streams from construction and demolition activities require specialized recycling and disposal methods due to their minimal biological activity and potential for reuse in infrastructure projects.
Contamination Rate (MSW/C&D)
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) typically exhibits a lower contamination rate of around 10-15%, whereas Construction and Demolition (C&D) waste often shows contamination rates exceeding 30% due to the presence of mixed materials like wood, metal, and hazardous substances. Effective sorting and processing strategies are essential to reduce contamination in C&D waste streams to improve recycling efficiency and environmental outcomes.
Urban Mining
Municipal solid waste primarily consists of everyday consumer materials such as food scraps, packaging, and household items, whereas construction and demolition waste includes debris like concrete, wood, metals, and bricks from building activities. Urban mining leverages the recycling potential of construction and demolition waste to recover valuable metals and materials, reducing landfill usage and promoting sustainable resource management in urban environments.
Hybrid Waste Sorting
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) primarily comprises everyday household refuse such as food scraps, paper, and plastics, whereas Construction and Demolition (C&D) Waste includes concrete, wood, metals, and drywall generated from building activities. Hybrid waste sorting systems optimize the separation process by integrating mechanical and manual sorting technologies, enhancing resource recovery efficiency across both MSW and C&D waste streams.
Green Concrete Recycling
Municipal solid waste primarily consists of everyday household and commercial refuse, while construction and demolition waste includes debris from building sites such as concrete, wood, and metals. Green concrete recycling repurposes construction and demolition concrete waste into eco-friendly building materials, reducing landfill use and lowering carbon emissions by minimizing the need for traditional cement production.
Municipal Solid Waste vs Construction and Demolition Waste Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com