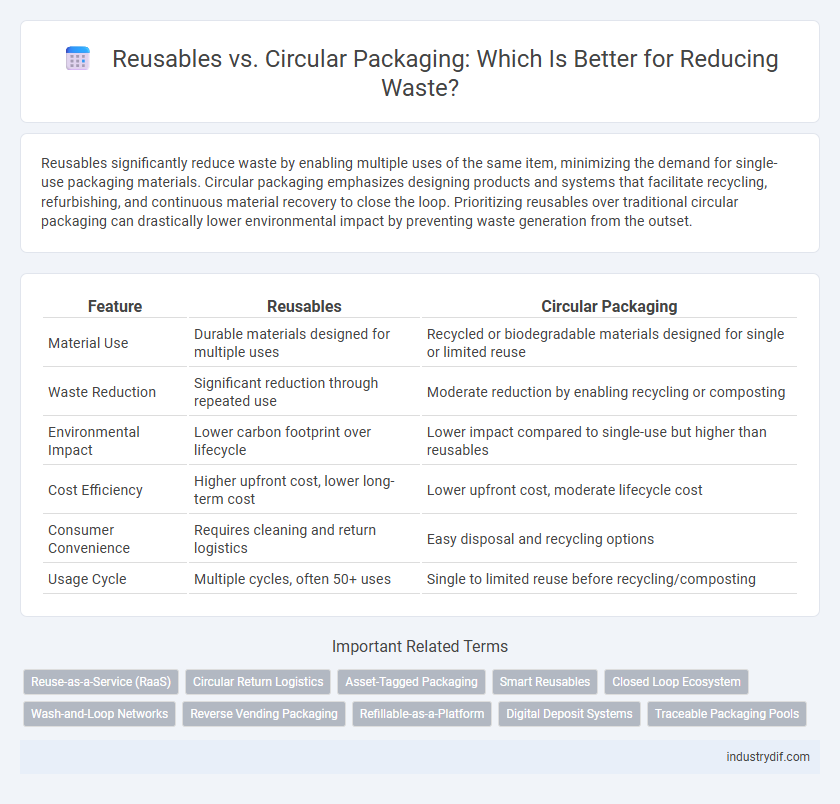
Reusables significantly reduce waste by enabling multiple uses of the same item, minimizing the demand for single-use packaging materials. Circular packaging emphasizes designing products and systems that facilitate recycling, refurbishing, and continuous material recovery to close the loop. Prioritizing reusables over traditional circular packaging can drastically lower environmental impact by preventing waste generation from the outset.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Reusables | Circular Packaging |
|---|---|---|
| Material Use | Durable materials designed for multiple uses | Recycled or biodegradable materials designed for single or limited reuse |
| Waste Reduction | Significant reduction through repeated use | Moderate reduction by enabling recycling or composting |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint over lifecycle | Lower impact compared to single-use but higher than reusables |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher upfront cost, lower long-term cost | Lower upfront cost, moderate lifecycle cost |
| Consumer Convenience | Requires cleaning and return logistics | Easy disposal and recycling options |
| Usage Cycle | Multiple cycles, often 50+ uses | Single to limited reuse before recycling/composting |
Understanding Reusables in Waste Management
Reusables play a crucial role in waste management by significantly reducing single-use packaging waste and promoting resource efficiency. Circular packaging systems emphasize the design of durable products intended for multiple lifecycles, enhancing environmental sustainability and minimizing landfill contributions. Understanding the lifecycle impact and logistics of reusables enables businesses to optimize waste reduction and support a closed-loop economy.
What is Circular Packaging?
Circular packaging is designed to be part of a closed-loop system where materials are continuously reused, recycled, or composted, minimizing waste and environmental impact. Unlike single-use or traditional packaging, circular packaging prioritizes durability, recyclability, and resource efficiency, aiming to extend the lifecycle of materials. This approach supports sustainable consumption by reducing the need for virgin resources and diverting packaging from landfills.
Environmental Impact: Reusables vs Circular Packaging
Reusables significantly reduce waste generation by minimizing single-use items, leading to lower carbon emissions and decreased landfill burden over their lifecycle. Circular packaging emphasizes material recovery and regeneration, promoting closed-loop systems that enhance resource efficiency and decrease environmental pollution. Both strategies contribute to sustainability, with reusables focusing on durability and longevity, while circular packaging optimizes material reuse and recycling processes.
Material Lifecycles in Reusable and Circular Solutions
Reusable packaging extends material lifecycles by enabling multiple uses before recycling, significantly reducing raw material demand and waste generation. Circular packaging prioritizes closed-loop systems, designing materials that are fully recyclable or compostable to re-enter production cycles efficiently. Both solutions enhance resource efficiency, with reusables emphasizing durability and repeated use, while circular packaging focuses on material recovery and regeneration.
Economic Benefits of Reusables and Circular Packaging
Reusables and circular packaging significantly reduce costs by minimizing the need for raw materials and lowering waste management expenses. Businesses save on procurement and disposal fees while benefiting from increased product lifespan and enhanced brand loyalty associated with sustainable practices. These economic advantages drive long-term profitability and promote resource efficiency in the waste management sector.
Barriers to Adoption: Challenges in Industry
Major barriers to adopting reusables and circular packaging in the waste management industry include high initial costs, logistical complexities, and limited infrastructure for collection and sanitation. Consumer behavior and lack of regulatory incentives further hinder widespread implementation. Overcoming these challenges requires collaboration across manufacturers, policymakers, and consumers to create scalable, cost-effective solutions.
Innovations Driving Reusables and Circular Packaging
Innovations driving reusables and circular packaging include advanced materials such as biodegradable polymers and smart packaging integrated with QR codes for enhanced tracking and consumer engagement. Companies leverage IoT technology to monitor product lifecycles, enabling efficient collection and reuse systems that minimize waste. These technological advancements contribute to reducing landfill dependency while promoting sustainable supply chains and zero-waste initiatives.
Regulatory Trends Influencing Packaging Choices
Regulatory trends increasingly favor circular packaging as governments implement stricter waste reduction mandates and extended producer responsibility (EPR) laws. Standards such as the European Union's Single-Use Plastics Directive promote reusables but emphasize materials that integrate seamlessly into circular economies, encouraging manufacturers to shift toward recyclable, compostable, or refillable packaging solutions. Compliance with evolving policies drives innovation in sustainable packaging technologies, impacting corporate sustainability strategies and reducing landfill dependency.
Case Studies: Successful Reuse and Circular Models
Case studies from global brands like Loop and TerraCycle demonstrate the effectiveness of reusable containers in drastically reducing single-use plastic waste while enhancing consumer engagement through deposit-return systems. Circular packaging initiatives by companies such as Nestle and Unilever showcase scalable models integrating recycled materials and closed-loop supply chains that minimize environmental impact. These examples confirm that adopting reusable and circular packaging solutions significantly contributes to sustainable waste management and resource conservation goals.
Future Directions in Waste Reduction Packaging
Future directions in waste reduction packaging emphasize the integration of reusables and circular packaging systems to minimize environmental impact. Innovations include scalable refillable containers and materials designed for multiple life cycles to reduce single-use waste. Harnessing advanced recycling technologies and digital tracking enhances the efficiency and transparency of circular supply chains, promoting sustainable consumption.
Related Important Terms
Reuse-as-a-Service (RaaS)
Reuse-as-a-Service (RaaS) platforms streamline the adoption of reusable packaging by providing businesses with scalable, cost-effective solutions that reduce single-use waste and promote circular economy principles. By integrating smart tracking and return logistics, RaaS enhances product lifecycle management, minimizes environmental impact, and drives consumer engagement in sustainable packaging practices.
Circular Return Logistics
Circular return logistics optimize waste reduction by enabling the repeated collection, cleaning, and redistribution of packaging materials, significantly lowering the demand for single-use containers. Implementing advanced tracking systems and efficient reverse supply chains enhances the scalability and sustainability of circular packaging solutions in diverse industries.
Asset-Tagged Packaging
Asset-tagged packaging enhances traceability and accountability in reusable systems, reducing waste by enabling efficient tracking and management of packaging lifecycle within circular economy models. This technology supports sustainable waste reduction by facilitating the return, refurbishment, and redeployment of packaging assets, thereby promoting resource efficiency and minimizing environmental impact.
Smart Reusables
Smart reusables integrate digital tracking and real-time usage data to enhance efficiency in circular packaging systems, reducing waste by enabling precise inventory management and user accountability. These intelligent solutions optimize resource cycles and minimize environmental impact through automated return incentives and seamless reuse logistics.
Closed Loop Ecosystem
Closed loop ecosystems in circular packaging maximize resource efficiency by continuously reusing materials, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact compared to traditional disposable packaging. Reusables within these systems promote sustainability through repeated cycles of collection, cleaning, and refilling, which significantly lower carbon footprints and conserve raw materials.
Wash-and-Loop Networks
Wash-and-loop networks enhance circular packaging by enabling efficient cleaning and rapid reuse of containers in supply chains, significantly reducing waste and resource consumption. These systems support scalable reuse models by integrating advanced washing technologies and real-time tracking to maintain hygiene standards and optimize logistics in sustainable packaging.
Reverse Vending Packaging
Reverse vending packaging systems drive circular packaging by incentivizing consumers to return reusable containers, significantly reducing waste and promoting resource recovery. This approach enhances sustainability by closing the materials loop, minimizing landfill contributions, and supporting efficient recycling processes.
Refillable-as-a-Platform
Refillable-as-a-Platform integrates reusable packaging solutions with circular economy principles, enabling brands to reduce waste by promoting multi-use containers designed for repeated filling and extended product life cycles. This approach not only minimizes single-use plastic waste but also supports sustainable consumption patterns through efficient collection, cleaning, and redistribution systems.
Digital Deposit Systems
Digital deposit systems enhance the efficiency of reusables by tracking and managing packaging returns, promoting circular packaging through data-driven consumer incentives and reducing waste. These systems optimize resource use and foster sustainable consumption by enabling seamless deposit refunds and real-time monitoring of reusable containers.
Traceable Packaging Pools
Traceable packaging pools enhance circular packaging by enabling real-time monitoring of reusable containers, reducing waste through efficient collection and redistribution systems. This technology supports robust data analytics that optimize asset utilization, minimize packaging loss, and promote sustainable supply chains.
Reusables vs Circular Packaging Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com