Drinking water primarily serves to hydrate the body and maintain essential physiological functions, making it a vital component of daily health. Functional water is enhanced with added minerals, vitamins, or electrolytes to offer specific health benefits beyond basic hydration. Choosing between drinking water and functional water depends on individual health needs and lifestyle preferences.
Table of Comparison
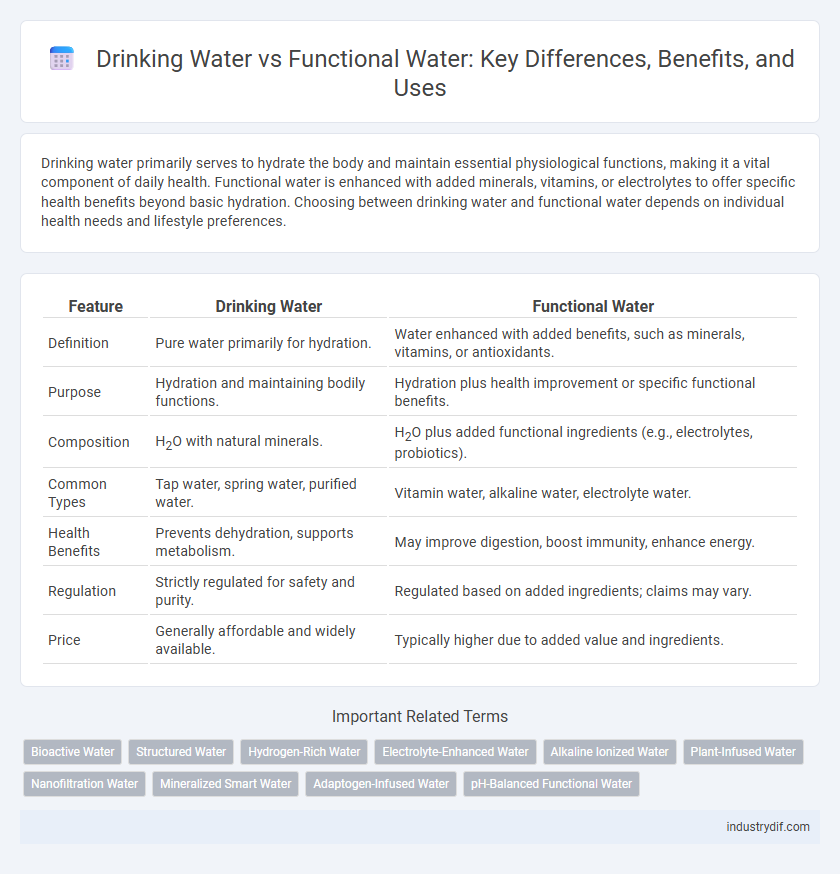
| Feature | Drinking Water | Functional Water |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pure water primarily for hydration. | Water enhanced with added benefits, such as minerals, vitamins, or antioxidants. |
| Purpose | Hydration and maintaining bodily functions. | Hydration plus health improvement or specific functional benefits. |
| Composition | H2O with natural minerals. | H2O plus added functional ingredients (e.g., electrolytes, probiotics). |
| Common Types | Tap water, spring water, purified water. | Vitamin water, alkaline water, electrolyte water. |
| Health Benefits | Prevents dehydration, supports metabolism. | May improve digestion, boost immunity, enhance energy. |
| Regulation | Strictly regulated for safety and purity. | Regulated based on added ingredients; claims may vary. |
| Price | Generally affordable and widely available. | Typically higher due to added value and ingredients. |
Understanding Drinking Water: Definition and Sources
Drinking water, defined as water safe for human consumption, primarily originates from surface water sources such as rivers, lakes, and reservoirs, as well as groundwater from wells and aquifers. This water undergoes treatment processes including filtration, disinfection, and purification to meet health standards set by organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO). Understanding the distinction between natural drinking water and enhanced functional water, which contains added minerals or health-promoting substances, highlights the fundamental role of untreated or minimally treated drinking water in daily hydration and safety.
What is Functional Water? Key Characteristics
Functional water is enhanced with additives such as minerals, vitamins, or electrolytes to provide specific health benefits beyond basic hydration. Key characteristics include improved mineral content, pH balance modification, and the inclusion of bioactive compounds designed to support bodily functions or boost immunity. Unlike regular drinking water, functional water aims to deliver targeted physiological effects, often marketed for wellness and therapeutic purposes.
Key Differences Between Drinking Water and Functional Water
Drinking water primarily serves hydration and basic bodily functions, ensuring purity standards are met to eliminate harmful contaminants. Functional water contains added minerals, electrolytes, or bioactive compounds designed to provide specific health benefits such as improved digestion, enhanced energy, or immune support. Regulatory classifications and manufacturing processes differ, with functional water often marketed as a health supplement beyond standard hydration.
Health Benefits of Drinking Water
Drinking water is essential for maintaining optimal hydration, supporting vital bodily functions such as temperature regulation, digestion, and nutrient absorption. Functional water, often infused with vitamins, minerals, or antioxidants, claims added health benefits but lacks consistent scientific evidence compared to pure drinking water. Prioritizing clean, untreated drinking water ensures efficient detoxification and promotes overall well-being without unnecessary additives.
Enhanced Health Claims of Functional Water
Functional water contains added minerals, electrolytes, or vitamins designed to improve hydration and support bodily functions beyond basic thirst quenching. Enhanced health claims include improved digestion, boosted immune response, and better muscle recovery due to ingredients like antioxidants, probiotics, and electrolytes. Unlike regular drinking water, functional water targets specific wellness benefits, making it a preferred choice for health-conscious consumers seeking more than simple hydration.
Common Types of Functional Water Products
Functional water products include alkaline water, ionized water, and mineral-enriched water, each designed to provide specific health benefits beyond basic hydration. Alkaline water typically has a higher pH, which may help neutralize acid in the body, while ionized water contains altered molecular structures purported to improve antioxidant capacity. Mineral-enriched waters are fortified with essential minerals like calcium and magnesium to support bodily functions and promote overall wellness.
Regulatory Standards: Drinking Water vs Functional Water
Drinking water must meet strict regulatory standards set by agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) or the World Health Organization (WHO), ensuring safety through limits on contaminants like lead, bacteria, and chemical pollutants. Functional water, often marketed with added minerals, vitamins, or probiotics, may not be subject to the same rigorous regulations, resulting in variability in quality and safety requirements across different countries. Understanding these regulatory differences is crucial for consumers prioritizing health and safety in their choice between drinking water and functional water products.
Consumer Trends: Why Choose Functional Water?
Functional water is rapidly gaining popularity among health-conscious consumers due to its added benefits such as enhanced hydration, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that go beyond basic thirst quenching. Market studies indicate a growing preference for enhanced waters that support wellness, energy, and immunity, appealing especially to millennials and Gen Z demographics. This trend is driven by increasing consumer awareness about health, convenience, and the desire for beverages that contribute to overall vitality.
Price Comparison and Market Availability
Drinking water typically costs between $0.50 to $2.00 per liter and is widely available in supermarkets, convenience stores, and vending machines globally. Functional water, infused with vitamins, minerals, or probiotics, commands higher prices ranging from $2.00 to $5.00 per liter, reflecting added health benefits and premium positioning. Market availability of functional water is growing rapidly in urban and health-conscious markets but remains limited compared to the ubiquitous presence of standard drinking water.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Drinking water sourced from natural supplies requires minimal processing, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced carbon emissions compared to functional water, which often involves added minerals and advanced filtration technologies with higher environmental costs. Functional water products typically generate more plastic waste due to specialized packaging, whereas sustainable drinking water initiatives emphasize reusable containers and local distribution to minimize ecological footprints. Prioritizing sustainable drinking water solutions supports water conservation, reduces pollution, and helps maintain ecosystem balance, essential for long-term environmental health.
Related Important Terms
Bioactive Water
Bioactive water, a subset of functional water, contains added minerals, antioxidants, or probiotics designed to promote health benefits beyond hydration. Unlike regular drinking water, bioactive water supports metabolic functions, boosts immune response, and enhances cellular hydration through its enriched composition.
Structured Water
Drinking water primarily serves to hydrate the body and maintain essential physiological functions, while functional water, such as structured water, is claimed to have altered molecular arrangements that enhance cellular absorption and promote improved metabolic activity. Structured water's unique hexagonal clusters are believed to optimize hydration at the cellular level, potentially offering superior antioxidant properties compared to regular drinking water.
Hydrogen-Rich Water
Hydrogen-rich water contains dissolved molecular hydrogen (H2) known for its antioxidant properties, which may help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation compared to regular drinking water. Functional water like hydrogen-rich variants offers potential health benefits beyond basic hydration, supporting cellular health and enhancing energy metabolism.
Electrolyte-Enhanced Water
Electrolyte-enhanced water contains essential minerals like sodium, potassium, and magnesium that support hydration and muscle function, distinguishing it from regular drinking water which primarily serves to quench thirst. Functional water with added electrolytes improves fluid balance and can aid in recovery during intense physical activity or dehydration.
Alkaline Ionized Water
Alkaline ionized water, a subset of functional water, offers enhanced antioxidant properties and higher pH levels compared to regular drinking water, potentially aiding in neutralizing acid in the bloodstream and improving hydration. Scientific studies suggest that consuming alkaline ionized water may support detoxification processes and promote better metabolic function beyond basic hydration benefits of standard drinking water.
Plant-Infused Water
Plant-infused water enhances drinking water by adding natural antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that support hydration and overall health. Unlike regular drinking water, functional plant-infused water leverages botanicals such as mint, cucumber, and lemon to improve detoxification and boost metabolism.
Nanofiltration Water
Nanofiltration water offers a superior purification process by effectively removing contaminants while retaining essential minerals, distinguishing it from regular drinking water that may lack such precision in filtration. Functional water enhanced through nanofiltration provides targeted health benefits like improved hydration and detoxification, surpassing the basic hydration properties of standard drinking water.
Mineralized Smart Water
Mineralized smart water enhances hydration by incorporating essential electrolytes like calcium, magnesium, and potassium, which support bodily functions beyond basic hydration found in regular drinking water. This functional water promotes improved nutrient absorption and electrolyte balance, offering benefits such as increased energy and better muscle function compared to standard purified water.
Adaptogen-Infused Water
Adaptogen-infused water combines hydrating properties with botanical extracts like ashwagandha and rhodiola, enhancing physical and mental resilience against stress. Unlike regular drinking water, this functional water supports immune function, reduces fatigue, and promotes overall well-being through natural adaptogenic compounds.
pH-Balanced Functional Water
pH-balanced functional water is specifically engineered to maintain an optimal pH level, typically between 7.4 and 8.5, supporting the body's natural acid-base balance and promoting better hydration compared to regular drinking water. Enriched with minerals and electrolytes, this type of water enhances alkalinity and offers potential health benefits such as improved digestion, detoxification, and increased energy levels.
Drinking Water vs Functional Water Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com