Surface water, sourced from rivers, lakes, and reservoirs, provides a vital supply for drinking, agriculture, and industry but is vulnerable to pollution and seasonal fluctuations. Smart water systems use advanced sensors, data analytics, and IoT technology to monitor water quality, optimize distribution, and prevent wastage, enhancing the sustainability and efficiency of water management. By integrating real-time data, smart water solutions address challenges inherent in surface water reliance, ensuring safer and more reliable access.
Table of Comparison
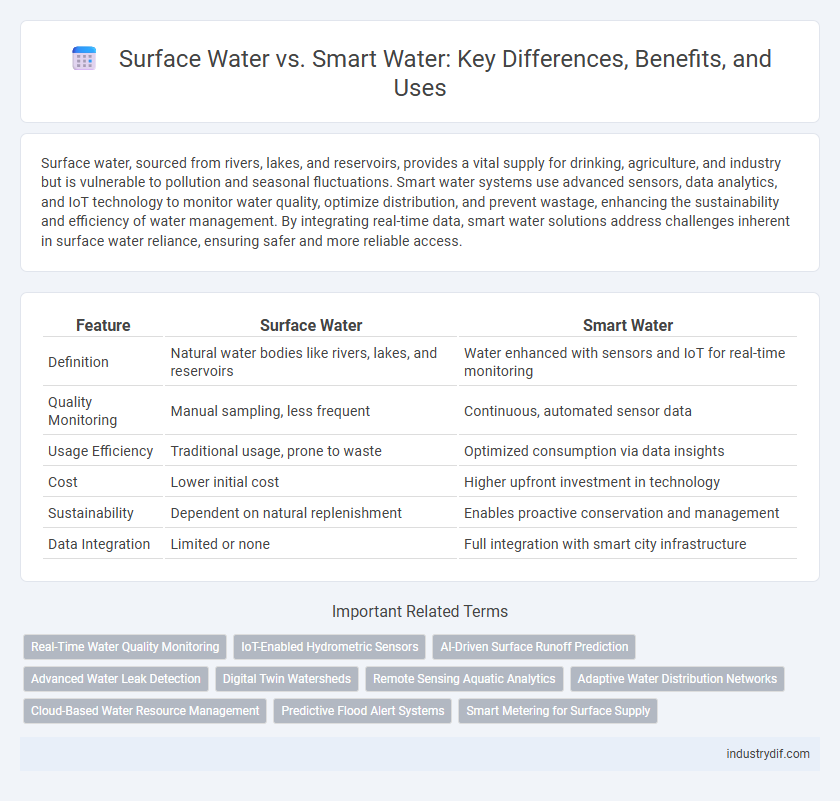
| Feature | Surface Water | Smart Water |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Natural water bodies like rivers, lakes, and reservoirs | Water enhanced with sensors and IoT for real-time monitoring |
| Quality Monitoring | Manual sampling, less frequent | Continuous, automated sensor data |
| Usage Efficiency | Traditional usage, prone to waste | Optimized consumption via data insights |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher upfront investment in technology |
| Sustainability | Dependent on natural replenishment | Enables proactive conservation and management |
| Data Integration | Limited or none | Full integration with smart city infrastructure |
Introduction to Surface Water and Smart Water
Surface water encompasses lakes, rivers, and reservoirs, serving as vital sources for drinking water, agriculture, and industrial use. Smart water integrates advanced technologies like sensors and IoT to monitor and manage water quality, distribution, and consumption in real time. This approach enhances efficiency, sustainability, and disaster response in water resource management.
Key Definitions: Surface Water vs Smart Water
Surface water refers to natural bodies of water such as rivers, lakes, and reservoirs that are accessible for various uses including irrigation, drinking, and industrial processes. Smart water involves the integration of advanced technologies like IoT sensors, data analytics, and automated control systems to monitor, manage, and optimize water resources in real time. Key differences highlight surface water as a physical resource and smart water as a technological approach enhancing water efficiency and sustainability.
Sources and Characteristics of Surface Water
Surface water primarily originates from natural sources such as rivers, lakes, reservoirs, and streams, characterized by its exposure to the environment and susceptibility to seasonal fluctuations and contamination. This water type typically contains organic matter, sediments, and varying levels of pollutants due to runoff and atmospheric deposition. Understanding the physical, chemical, and biological properties of surface water is crucial for effective management and treatment strategies in both conventional and smart water systems.
Technologies Behind Smart Water Systems
Smart water systems leverage advanced technologies like IoT sensors, real-time data analytics, and automated control mechanisms to optimize the management of surface water resources. These systems enable precise monitoring of water quality, flow rates, and consumption patterns, reducing waste and improving distribution efficiency. Integration of AI-driven predictive models further enhances decision-making for sustainable water resource management.
Water Quality: Surface Water Challenges vs Smart Water Solutions
Surface water often faces contamination from pollutants, pathogens, and sediment, leading to inconsistent water quality and posing risks to human health and ecosystems. Smart water technologies leverage real-time monitoring, data analytics, and IoT sensors to detect and address water quality issues promptly, ensuring safer and more reliable supply. These solutions enable proactive management of surface water challenges by optimizing treatment processes and reducing the impact of contaminants.
Environmental Impact: Surface Water vs Smart Water Management
Surface water management often leads to significant environmental challenges including habitat disruption, increased pollution runoff, and inefficient water use. Smart water management incorporates advanced technologies like IoT sensors and data analytics to optimize water distribution, reduce wastage, and minimize ecological footprints. This approach enhances the sustainability of water resources by promoting efficient consumption and real-time monitoring of environmental impacts.
Applications in Industry: Surface Water and Smart Water Use Cases
Surface water is commonly used in industries such as agriculture, manufacturing, and energy production for processes like irrigation, cooling, and cleaning, due to its availability and cost-effectiveness. Smart water systems leverage IoT sensors, automated controls, and data analytics to optimize water usage in industrial applications, minimizing waste and enhancing efficiency in sectors like chemical manufacturing and food processing. The integration of smart water technologies enables real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, driving sustainable water management practices in industries dependent on surface water sources.
Efficiency and Sustainability: Comparing Surface Water and Smart Water
Surface water systems often face challenges with efficiency due to high evaporation rates and contamination risks, impacting sustainable water management. Smart water technologies optimize resource use by employing IoT sensors and real-time data analytics to reduce waste and improve distribution accuracy. Integrating smart water solutions enhances sustainability by enabling precise monitoring, leak detection, and adaptive management compared to traditional surface water methods.
Regulatory Standards: Surface Water Management vs Smart Water Compliance
Surface water management is governed by regulatory standards such as the Clean Water Act in the United States, which sets limits on pollutants, discharge permits, and water quality criteria to protect natural water bodies. Smart water systems must comply with additional compliance frameworks that emphasize data security, real-time monitoring accuracy, and interoperability with IoT devices, ensuring efficient water usage and contamination prevention. Regulatory compliance for smart water solutions often involves meeting industry standards like ISO 24518 for smart water management and EPA guidelines for automated water quality reporting.
Future Trends: Evolving Roles of Surface Water and Smart Water
Surface water management is increasingly integrating smart water technologies, utilizing real-time data analytics and IoT sensors to optimize resource allocation and improve water quality monitoring. Future trends emphasize the convergence of traditional surface water systems with smart infrastructure to enhance sustainability and resilience against climate change impacts. Advanced predictive models and automated control systems will redefine water distribution and conservation efforts, ensuring more efficient, adaptive management of surface water resources.
Related Important Terms
Real-Time Water Quality Monitoring
Surface water sources such as rivers, lakes, and reservoirs are susceptible to contamination, making real-time water quality monitoring critical for ensuring safety and compliance with environmental standards. Smart water technologies integrate IoT sensors and data analytics to continuously track parameters like pH, turbidity, and pollutant levels, enabling rapid detection of contaminants and proactive management.
IoT-Enabled Hydrometric Sensors
Surface water management increasingly relies on IoT-enabled hydrometric sensors to provide real-time data on water levels, flow rates, and quality, enhancing flood forecasting and resource allocation. Smart water systems integrate these sensors with cloud analytics to optimize surface water monitoring, reduce wastage, and improve sustainability in water distribution networks.
AI-Driven Surface Runoff Prediction
AI-driven surface runoff prediction leverages advanced machine learning algorithms and real-time sensor data to optimize the management of surface water resources, reducing flood risks and improving water quality. Smart water systems integrate IoT devices and predictive analytics to monitor runoff patterns, enabling proactive infrastructure planning and efficient water distribution.
Advanced Water Leak Detection
Smart water systems utilize advanced water leak detection technologies such as IoT sensors and AI analytics to monitor surface water pipelines in real-time, significantly reducing water loss and improving resource management. These intelligent solutions enable quick identification and precise localization of leaks compared to traditional surface water monitoring methods, enhancing infrastructure efficiency and sustainability.
Digital Twin Watersheds
Surface water management is revolutionized by Digital Twin Watersheds, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive analytics for rivers, lakes, and reservoirs. Smart water systems integrate sensor networks and IoT devices to create dynamic digital replicas that optimize water quality, flood control, and resource allocation in watershed management.
Remote Sensing Aquatic Analytics
Surface water monitoring leverages remote sensing technologies to collect real-time data on water quality, temperature, and contamination levels across lakes, rivers, and reservoirs. Smart water systems integrate aquatic analytics with IoT sensors and satellite imagery, enhancing predictive modeling and efficient water resource management for sustainable environmental planning.
Adaptive Water Distribution Networks
Adaptive water distribution networks leverage smart water technologies to optimize surface water use by monitoring real-time demand, pressure, and leakage, enhancing efficiency and sustainability. These systems integrate sensors and automated controls to dynamically adjust flow and reduce water loss, contrasting with traditional surface water networks that rely on fixed infrastructure and manual management.
Cloud-Based Water Resource Management
Cloud-based water resource management leverages real-time data and analytics to optimize surface water usage, ensuring efficient monitoring of reservoirs, rivers, and lakes. Smart water systems integrate IoT sensors and advanced algorithms to predict demand, detect leaks, and improve distribution, enhancing sustainability and reducing wastage in surface water management.
Predictive Flood Alert Systems
Surface water sources such as rivers and lakes are vulnerable to rapid changes in water levels, making communities prone to flooding. Smart water management employs predictive flood alert systems using real-time data and AI algorithms to analyze surface water conditions, enabling timely warnings and reducing flood risks effectively.
Smart Metering for Surface Supply
Smart metering for surface water supply enhances real-time monitoring and data accuracy, enabling efficient management of water resources and reducing losses through leakage detection. Integration of IoT sensors and advanced analytics in smart meters supports sustainable water distribution and demand forecasting for surface water systems.
Surface Water vs Smart Water Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com