Drinking water quality is crucial for public health, requiring rigorous treatment and monitoring to ensure safety and taste. In contrast, a smart water grid integrates advanced sensors and real-time data analytics to optimize water distribution, reduce waste, and detect leaks quickly. This technology enhances the efficiency and sustainability of drinking water systems, ensuring reliable access while conserving resources.
Table of Comparison
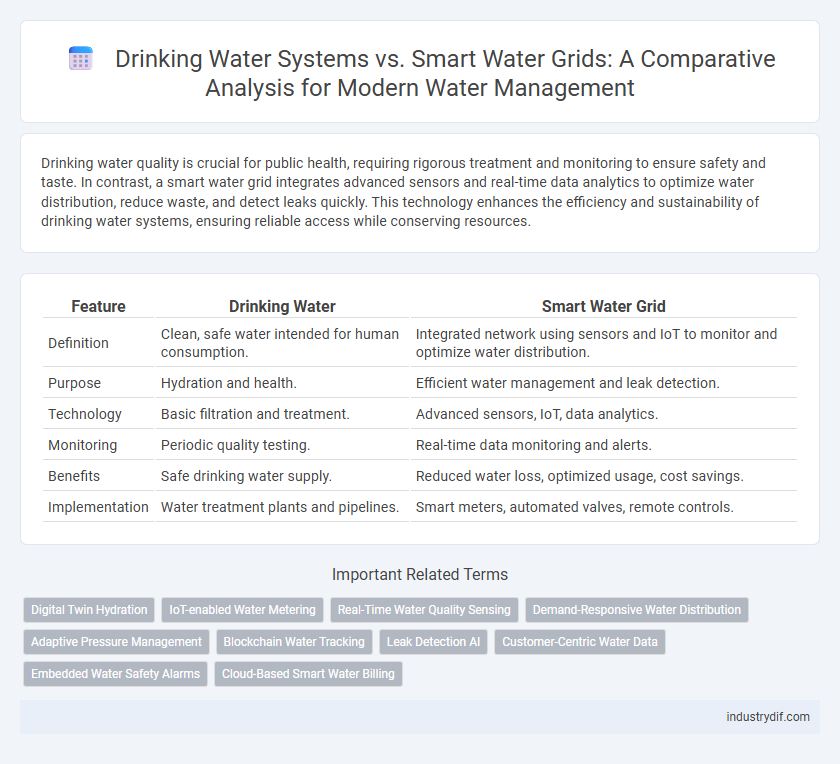
| Feature | Drinking Water | Smart Water Grid |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Clean, safe water intended for human consumption. | Integrated network using sensors and IoT to monitor and optimize water distribution. |
| Purpose | Hydration and health. | Efficient water management and leak detection. |
| Technology | Basic filtration and treatment. | Advanced sensors, IoT, data analytics. |
| Monitoring | Periodic quality testing. | Real-time data monitoring and alerts. |
| Benefits | Safe drinking water supply. | Reduced water loss, optimized usage, cost savings. |
| Implementation | Water treatment plants and pipelines. | Smart meters, automated valves, remote controls. |
Introduction to Drinking Water and Smart Water Grids
Drinking water, essential for human health, is treated to meet strict safety standards ensuring it is free from contaminants and pathogens. Smart water grids utilize advanced sensors and IoT technology to monitor water quality, detect leaks, and optimize distribution in real-time. Integrating smart water grids enhances the management of drinking water systems by improving efficiency, reducing waste, and ensuring consistent delivery of safe potable water to communities.
Defining Drinking Water Quality Standards
Drinking water quality standards are established by regulatory agencies such as the EPA to ensure water is free from harmful contaminants and safe for human consumption. These standards specify maximum allowable levels for chemicals, microorganisms, and radioactive substances, directly impacting public health outcomes. In contrast, smart water grids integrate real-time monitoring and advanced analytics to optimize water distribution but rely on these defined quality benchmarks to maintain safe drinking water compliance.
What is a Smart Water Grid?
A Smart Water Grid integrates advanced sensors, real-time data analytics, and automated control systems to efficiently monitor and manage water distribution networks. Unlike traditional drinking water systems that rely on manual inspections, a smart grid detects leaks, optimizes pressure, and ensures consistent water quality through continuous feedback mechanisms. This technology enhances sustainability, reduces water loss, and improves the resilience of urban water infrastructure.
Key Differences: Traditional vs Smart Water Management
Traditional drinking water systems rely on manual monitoring, fixed schedules, and physical infrastructure maintenance, often resulting in inefficiencies and delayed leak detection. Smart water grids integrate IoT sensors, real-time data analytics, and automated controls to optimize water distribution, reduce waste, and enhance water quality management. The key differences lie in proactive system management, predictive maintenance capabilities, and enhanced resource sustainability offered by smart water technologies.
Technologies Powering Smart Water Grids
Smart water grids leverage advanced technologies such as IoT sensors, real-time data analytics, and AI algorithms to optimize water distribution and quality monitoring. These systems enable predictive maintenance, reduce water loss, and enhance resource management compared to traditional drinking water supply methods. Integrating GIS mapping, automated valves, and cloud computing facilitates efficient decision-making and sustainable water infrastructure development.
Benefits of Smart Water Grids for Drinking Water Systems
Smart water grids enhance drinking water systems by enabling real-time monitoring and leak detection, which significantly reduces water losses and ensures high-quality water delivery. Advanced sensors and automated controls improve resource management and operational efficiency, leading to cost savings and sustainable water usage. Integrating smart grids facilitates rapid response to contamination events, safeguarding public health and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Challenges in Implementing Smart Water Grids
Implementing Smart Water Grids faces challenges including high infrastructure costs, data integration complexities, and cybersecurity risks. Maintaining water quality standards while deploying advanced sensors requires robust calibration and monitoring protocols. The variability in water sources and consumption patterns demands adaptive algorithms to optimize distribution and detect leaks effectively.
Drinking Water Safety and Real-time Monitoring
Drinking water safety relies on rigorous testing and treatment processes to eliminate contaminants and ensure compliance with health standards. Smart water grids enhance safety by integrating real-time monitoring technologies that detect pollutants, leaks, and pressure changes instantly. These advanced systems enable prompt responses to potential hazards, reducing health risks and improving the reliability of safe drinking water supply.
Sustainability and Resource Efficiency
Drinking water quality hinges on sustainable sourcing and efficient distribution to reduce waste and environmental impact. Smart water grids enhance resource efficiency by integrating sensors and data analytics that monitor consumption, detect leaks, and optimize supply in real-time. These advanced systems contribute to sustainable water management by minimizing loss and ensuring equitable access to clean drinking water.
Future Trends in Drinking Water and Smart Grid Integration
Future trends in drinking water emphasize advanced purification technologies and real-time quality monitoring to ensure safe, sustainable supplies amid growing demand. Smart water grids integrate IoT sensors and AI analytics to optimize water distribution, detect leaks, and manage resources efficiently. These innovations drive enhanced water conservation, reduced operational costs, and resilient infrastructure for urban water systems.
Related Important Terms
Digital Twin Hydration
Drinking water quality and availability are increasingly managed through Smart Water Grid systems featuring Digital Twin technology, which simulates real-time hydration dynamics to optimize distribution and reduce waste. This advanced modeling enhances resource efficiency, ensuring safer, more reliable hydration solutions aligned with urban consumption patterns.
IoT-enabled Water Metering
IoT-enabled water metering in smart water grids enhances real-time monitoring and management of drinking water distribution, reducing waste and ensuring quality control. These advanced meters provide precise consumption data, enabling utility providers to optimize resource allocation and detect leaks promptly.
Real-Time Water Quality Sensing
Real-time water quality sensing in smart water grids enables continuous monitoring of drinking water parameters such as pH, turbidity, and contaminant levels, ensuring safer and more reliable water supply. This technology detects anomalies instantly, allowing for prompt intervention and minimizing health risks associated with contaminated drinking water.
Demand-Responsive Water Distribution
Demand-responsive water distribution in smart water grids uses real-time data and IoT sensors to optimize drinking water delivery, reducing waste and ensuring consistent supply during peak demand. This technology enhances traditional drinking water systems by dynamically adjusting flows based on consumption patterns and infrastructure conditions.
Adaptive Pressure Management
Drinking water systems benefit significantly from adaptive pressure management within smart water grids, which optimizes water distribution by adjusting pressure based on real-time demand and reducing leakages. This technology enhances water efficiency, lowers energy consumption, and ensures consistent water quality from treatment facilities to end-users.
Blockchain Water Tracking
Blockchain water tracking enhances drinking water management by providing transparent, tamper-proof records of water quality and distribution from source to tap. Integrating blockchain within smart water grids enables real-time data verification, reducing contamination risks and ensuring safer, more efficient drinking water supply systems.
Leak Detection AI
Leak detection AI in smart water grids leverages advanced sensors and machine learning algorithms to identify anomalies and pinpoint leaks in real time, significantly reducing water loss compared to traditional drinking water systems. This technology enhances operational efficiency by enabling proactive maintenance and minimizing costly infrastructure damage in municipal water supply networks.
Customer-Centric Water Data
Customer-centric water data in drinking water systems enhances real-time monitoring of water quality and consumption patterns, enabling personalized service and efficient resource management. Smart water grids leverage advanced sensors and analytics to provide detailed insights, empowering utilities to anticipate demand, detect leaks, and ensure optimal water delivery tailored to individual customer needs.
Embedded Water Safety Alarms
Drinking water quality can be significantly enhanced through smart water grids equipped with embedded water safety alarms that detect contaminants in real-time, ensuring continuous monitoring and rapid response to potential hazards. These advanced alarm systems integrate sensors and IoT technology to maintain safe water standards and prevent public health risks by alerting authorities instantly upon detection of impurities.
Cloud-Based Smart Water Billing
Cloud-based smart water billing integrates real-time consumption data with automated meter readings, enhancing accuracy and reducing billing disputes for drinking water users. This technology enables utilities to optimize water distribution, monitor usage patterns, and implement dynamic pricing through a centralized smart water grid platform.
Drinking Water vs Smart Water Grid Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com