Raw water is untreated natural water containing impurities and microorganisms, requiring filtration or purification before use. Electrolyzed water undergoes electrolysis to produce a powerful disinfectant with enhanced antimicrobial properties, making it effective for sanitation without chemical additives. This transformation improves water safety and usability in various industrial and healthcare applications.
Table of Comparison
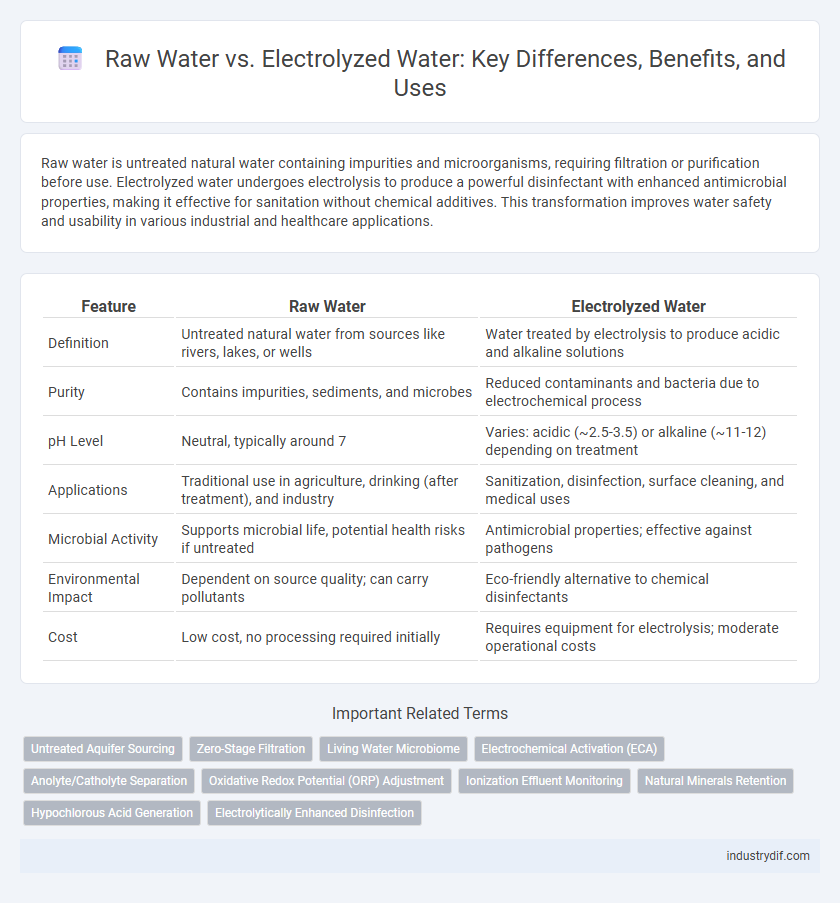
| Feature | Raw Water | Electrolyzed Water |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Untreated natural water from sources like rivers, lakes, or wells | Water treated by electrolysis to produce acidic and alkaline solutions |
| Purity | Contains impurities, sediments, and microbes | Reduced contaminants and bacteria due to electrochemical process |
| pH Level | Neutral, typically around 7 | Varies: acidic (~2.5-3.5) or alkaline (~11-12) depending on treatment |
| Applications | Traditional use in agriculture, drinking (after treatment), and industry | Sanitization, disinfection, surface cleaning, and medical uses |
| Microbial Activity | Supports microbial life, potential health risks if untreated | Antimicrobial properties; effective against pathogens |
| Environmental Impact | Dependent on source quality; can carry pollutants | Eco-friendly alternative to chemical disinfectants |
| Cost | Low cost, no processing required initially | Requires equipment for electrolysis; moderate operational costs |
Definition and Sources of Raw Water
Raw water refers to untreated water collected from natural sources such as rivers, lakes, groundwater, and rainwater, containing various impurities and microorganisms. It serves as the primary input for water treatment plants before undergoing processes like filtration, disinfection, or electrolysis. Electrolyzed water, produced by passing an electric current through saltwater or tap water, has antimicrobial properties but originates from treated or processed water, unlike raw water's natural and unprocessed sources.
The Science Behind Electrolyzed Water
Electrolyzed water is generated through an electrochemical process that splits a saline solution into two distinct streams: acidic water with powerful disinfecting properties and alkaline water with cleaning capabilities. This reaction alters the molecular structure, producing reactive oxygen species and hypochlorous acid, which contribute to its strong antimicrobial effectiveness. The scientific basis of electrolyzed water lies in its ability to safely eliminate bacteria and viruses without harmful chemicals, making it an innovative alternative to traditional raw water treatment.
Key Differences: Raw Water vs Electrolyzed Water
Raw water contains all natural minerals, organic matter, and potential contaminants as it is untreated from its source, while electrolyzed water undergoes electrochemical activation, producing a solution with altered pH levels and disinfecting properties. Electrolyzed water is commonly used for sanitation, disinfection, and cleaning due to its antimicrobial activity, unlike raw water which requires further purification for safe consumption. The key difference lies in functionality and safety: raw water is unprocessed, whereas electrolyzed water is a treated solution designed to enhance hygiene and reduce microbial load.
Water Treatment Methods and Processes
Raw water contains natural impurities such as sediments, microorganisms, and organic matter that require filtration and disinfection in traditional water treatment methods. Electrolyzed water is generated through electrolysis, producing hypochlorous acid and hydroxide ions, which provide effective microbial disinfection without chemical additives. This process offers a sustainable alternative by reducing chemical usage and enhancing water quality through advanced oxidation and sanitization mechanisms.
Applications in Industrial Sectors
Raw water, sourced directly from natural bodies, serves primarily in industrial cooling, process water, and boiler feed applications due to its affordability and availability. Electrolyzed water, generated through electrolysis that splits water molecules into acidic and alkaline components, finds specialized use in sanitation, surface cleaning, and sterilization in food processing, pharmaceutical, and healthcare industries owing to its powerful antimicrobial properties. Industrial sectors prioritize electrolyzed water for eco-friendly and chemical-free disinfection, while raw water remains essential for bulk industrial processes where treatment costs must be minimized.
Health and Safety Considerations
Raw water often contains impurities and microorganisms that pose health risks, making it unsuitable for direct consumption without proper treatment. Electrolyzed water, produced through electrolysis, has been shown to have antimicrobial properties, enhancing safety by reducing pathogens and contaminants. This process results in a safer option for applications such as disinfection and wound care, aligning with stringent health and safety standards.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Raw water requires minimal processing, resulting in a lower immediate energy footprint but carries potential risks of contamination that can impact ecosystems if not managed properly. Electrolyzed water production involves electricity consumption and the generation of reactive species that can degrade pollutants, offering a chemical-free alternative for disinfection and cleaning, thus reducing reliance on hazardous chemicals and lowering secondary pollution. The environmental impact of electrolyzed water is often offset by its ability to minimize harmful chemical discharge into water bodies and soil, promoting sustainable water management practices in industrial and agricultural sectors.
Cost and Efficiency Analysis
Raw water requires minimal initial processing costs but often incurs higher long-term expenses due to filtration, treatment chemicals, and infrastructure maintenance. Electrolyzed water systems involve higher upfront investment for electrolysis equipment but offer greater efficiency by reducing chemical usage and enabling on-site generation, lowering operational costs over time. Cost efficiency analysis favors electrolyzed water in large-scale or continuous applications due to reduced reliance on external chemical supplies and enhanced antimicrobial properties.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Raw water must comply with local and international regulatory standards such as the EPA's Safe Drinking Water Act, which sets limits on contaminants like bacteria, heavy metals, and chemicals to ensure safety. Electrolyzed water, used primarily as a disinfectant, is regulated under agencies like the EPA and FDA to confirm residual chlorine levels and pH meet safety criteria for specific applications, including food processing and sanitation. Compliance with these regulations guarantees that both raw and electrolyzed water meet health and safety requirements for their intended uses.
Future Trends in Water Use and Technology
Raw water, sourced directly from natural bodies, faces increasing challenges due to contamination and resource scarcity, driving innovation in purification technologies. Electrolyzed water, created by applying electrical current to saline solutions, offers a sustainable alternative with potent disinfectant properties and minimal chemical residue. Future trends emphasize integrating electrolyzed water systems for agriculture, healthcare, and sanitation to enhance water efficiency and reduce reliance on harmful chemicals.
Related Important Terms
Untreated Aquifer Sourcing
Untreated aquifer sourcing provides raw water that contains natural minerals and organic materials, essential for environmental sustainability but requiring treatment for safe consumption. Electrolyzed water, produced through electrolysis, offers enhanced sterilization properties by generating reactive oxygen species that effectively eliminate contaminants without chemical additives.
Zero-Stage Filtration
Raw water contains natural impurities and contaminants that require zero-stage filtration for removal to ensure safety and quality before further treatment. Electrolyzed water, produced by passing filtered water through an electrolysis process, benefits from prior zero-stage filtration to enhance its purity and effectiveness in disinfection and cleaning applications.
Living Water Microbiome
Raw water contains a diverse living water microbiome essential for maintaining natural ecological balance and supporting skin and gut health through beneficial microbes. Electrolyzed water, while effective for sanitation and disinfection, often lacks this living microbiome, reducing its potential benefits for microbiome diversity and environmental sustainability.
Electrochemical Activation (ECA)
Electrolyzed Water, produced through Electrochemical Activation (ECA), involves applying electrical current to raw water containing salts to generate reactive oxygen species and free radicals with strong antimicrobial properties. This process enhances water disinfection efficiency by creating oxidizing agents such as hypochlorous acid, widely used in sanitation and sterilization applications.
Anolyte/Catholyte Separation
Electrolyzed water separates into anolyte and catholyte through electrolysis, where anolyte contains oxidizing agents such as hypochlorous acid for disinfection, and catholyte consists mostly of alkaline water rich in hydroxide ions. Raw water lacks this separation and antimicrobial properties, making electrolyzed water more effective for sterilization and cleaning applications.
Oxidative Redox Potential (ORP) Adjustment
Raw water typically exhibits a variable oxidative redox potential (ORP), often ranging from -100 to +200 millivolts depending on source and contamination levels, whereas electrolyzed water, produced through electrolysis, consistently shows elevated ORP values, commonly between +800 to +1200 millivolts, enhancing its oxidative properties. This significant ORP adjustment in electrolyzed water results in superior antimicrobial activity and oxidation potential compared to raw water, making it effective for disinfection and sanitation applications.
Ionization Effluent Monitoring
Ionization effluent monitoring of raw water involves tracking mineral and contaminant ion levels to ensure safe environmental discharge, whereas electrolyzed water monitoring focuses on controlling pH, oxidation-reduction potential (ORP), and residual chlorine concentrations to optimize disinfection efficacy and minimize harmful byproducts. Accurate ion analysis through advanced sensors and spectroscopic methods enables regulatory compliance and protects aquatic ecosystems in both raw and electrolyzed water treatment processes.
Natural Minerals Retention
Raw water retains natural minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium essential for health, while electrolyzed water undergoes electrochemical treatment that often reduces these beneficial mineral content. The mineral balance in raw water supports hydration and bodily functions better than the altered composition of electrolyzed water.
Hypochlorous Acid Generation
Raw water contains various impurities and microorganisms, while electrolyzed water is produced through the electrolysis process that generates hypochlorous acid, a powerful disinfectant effective against bacteria and viruses. Hypochlorous acid formation occurs when an electric current passes through a saline solution, converting chloride ions into this potent antimicrobial agent essential for water sanitization.
Electrolytically Enhanced Disinfection
Electrolyzed water, generated through electrolysis, exhibits potent antimicrobial properties by producing reactive oxygen species such as hypochlorous acid, enhancing disinfection efficiency compared to raw water. This electrolytically enhanced disinfection method reduces reliance on chemical disinfectants, offering an eco-friendly, effective solution for water treatment and pathogen control.
Raw Water vs Electrolyzed Water Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com