Wholesale involves bulk purchasing from manufacturers or distributors, enabling retailers to stock large quantities at reduced prices. An end-to-end marketplace integrates sourcing, sales, and logistics on a single platform, streamlining the entire supply chain process for buyers and sellers. This approach enhances efficiency by reducing intermediaries and providing real-time inventory and order tracking.
Table of Comparison
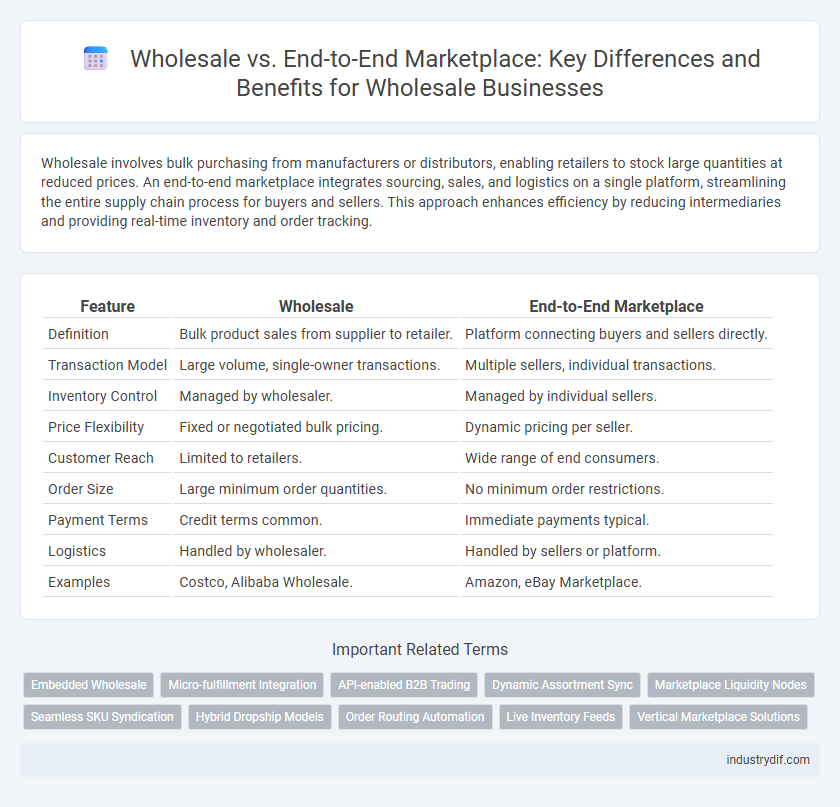
| Feature | Wholesale | End-to-End Marketplace |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bulk product sales from supplier to retailer. | Platform connecting buyers and sellers directly. |
| Transaction Model | Large volume, single-owner transactions. | Multiple sellers, individual transactions. |
| Inventory Control | Managed by wholesaler. | Managed by individual sellers. |
| Price Flexibility | Fixed or negotiated bulk pricing. | Dynamic pricing per seller. |
| Customer Reach | Limited to retailers. | Wide range of end consumers. |
| Order Size | Large minimum order quantities. | No minimum order restrictions. |
| Payment Terms | Credit terms common. | Immediate payments typical. |
| Logistics | Handled by wholesaler. | Handled by sellers or platform. |
| Examples | Costco, Alibaba Wholesale. | Amazon, eBay Marketplace. |
Understanding Wholesale: Definition and Key Features
Wholesale involves selling goods in large quantities at reduced prices to retailers or other businesses rather than directly to consumers. Key features include bulk purchasing, lower per-unit costs, and streamlined supply chain management that supports efficient distribution to multiple resellers. Unlike end-to-end marketplaces, wholesale centers on B2B transactions focused on volume and cost efficiency rather than direct consumer engagement.
What is an End-to-End Marketplace?
An end-to-end marketplace integrates all stages of the transaction process, from product discovery and ordering to payment and delivery, within a single platform. Unlike traditional wholesale models that often require separate steps and intermediaries, this streamlined approach enhances efficiency and transparency for both buyers and sellers. Features such as real-time inventory management, automated invoicing, and direct communication channels promote seamless end-to-end trade execution.
Core Differences Between Wholesale and End-to-End Marketplaces
Wholesale involves bulk purchasing from suppliers to resell products, typically emphasizing volume discounts and direct supplier relationships. End-to-end marketplaces facilitate transactions between buyers and sellers on a single platform, handling everything from product listing to payment, shipping, and customer service. Key differences include the level of operational integration and control, with wholesale focusing on inventory management and end-to-end marketplaces streamlining the entire purchase workflow for multiple vendors.
Supply Chain Management in Wholesale vs End-to-End Platforms
Wholesale supply chain management emphasizes bulk inventory handling, supplier relationships, and cost efficiency to streamline distribution to retailers. End-to-end marketplaces integrate these functions with advanced technology for real-time inventory tracking, automated order fulfillment, and seamless communication across suppliers and buyers. This integration enhances visibility and agility in managing supply chain operations from procurement to final delivery, reducing lead times and operational costs.
Pricing Structures: Bulk Discounts vs Dynamic Pricing
Wholesale pricing structures typically rely on bulk discounts, offering fixed price reductions based on the volume of goods purchased, which incentivizes large-scale buying and simplifies cost forecasting. End-to-end marketplaces employ dynamic pricing models that adjust prices in real-time according to demand, competition, and inventory levels, maximizing revenue opportunities and market responsiveness. Businesses choosing between wholesale and end-to-end marketplace strategies must consider the trade-offs between predictable bulk discount savings and the flexibility of dynamic price optimization.
Buyer and Seller Relationships: Direct vs Platform-Mediated
Wholesale typically involves direct buyer and seller relationships, enabling personalized negotiations, bulk pricing agreements, and long-term partnerships that foster trust and reliability. End-to-end marketplaces mediate transactions through a digital platform, offering streamlined access to multiple sellers but often limiting direct communication and customized terms. This platform-mediated approach provides efficiency and broad product selection, while wholesale emphasizes relationship-driven deals and bespoke arrangements.
Technology Integration in Wholesale and Marketplaces
Wholesale leverages robust ERP and inventory management systems to streamline bulk transactions and optimize supply chain efficiency. End-to-end marketplaces integrate CRM, payment gateways, and AI-driven analytics to create seamless customer experiences from order placement to delivery. Technology integration in wholesale prioritizes scalability and backend automation, whereas marketplaces focus on user interface and real-time data synchronization for buyer-seller interactions.
Scalability and Market Reach Comparison
Wholesale models offer scalable growth by enabling bulk transactions with established buyers, reducing customer acquisition costs and streamlining inventory management. End-to-end marketplaces expand market reach by connecting a vast network of sellers and buyers, facilitating diverse product offerings and real-time price competition. Scalability in wholesale is often limited by warehouse capacity and buyer relationships, while marketplaces leverage technology platforms to scale rapidly and access global audiences.
Risk Management and Quality Control
Wholesale operations require stringent risk management protocols and robust quality control systems to ensure product integrity across bulk transactions. End-to-end marketplaces integrate these mechanisms within a unified platform, offering real-time monitoring and automated compliance checks that reduce fraud and defects. Leveraging advanced analytics, these marketplaces enhance transparency and traceability, mitigating operational risks more effectively than traditional wholesale models.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business
Choosing the right model between wholesale and end-to-end marketplace depends on your business goals, product type, and target audience. Wholesale offers bulk purchasing at lower prices, ideal for businesses focused on volume sales and long-term partnerships, while end-to-end marketplaces provide direct-to-consumer access with broader reach and flexibility. Evaluating factors such as inventory management, customer engagement, and pricing strategy ensures alignment with operational capabilities and market demand.
Related Important Terms
Embedded Wholesale
Embedded wholesale integrates directly within digital marketplaces, streamlining bulk purchasing by connecting suppliers and buyers without intermediaries. This approach enhances efficiency and scalability compared to traditional wholesale models and end-to-end marketplaces that often separate procurement stages.
Micro-fulfillment Integration
Wholesale models benefit from micro-fulfillment integration by streamlining inventory management and reducing delivery times, enhancing operational efficiency. End-to-end marketplaces leverage micro-fulfillment centers to connect multiple suppliers directly with consumers, enabling faster order processing and localized distribution.
API-enabled B2B Trading
API-enabled B2B trading in wholesale streamlines bulk transactions by integrating real-time inventory, pricing, and order management across multiple suppliers, enhancing operational efficiency compared to traditional end-to-end marketplaces. This technology fosters seamless data exchange and automation, reducing manual errors and accelerating the procurement cycle in wholesale environments.
Dynamic Assortment Sync
Dynamic assortment sync in wholesale enables real-time inventory updates and seamless coordination between suppliers and retailers, reducing stockouts and overstock issues. End-to-end marketplaces also offer assortment synchronization but typically involve more complex integrations across multiple platforms, impacting update frequency and accuracy.
Marketplace Liquidity Nodes
Marketplace Liquidity Nodes in wholesale environments enable efficient transaction flows by aggregating diverse suppliers and buyers, enhancing inventory turnover and price competitiveness. Unlike traditional end-to-end marketplaces, these nodes optimize supply chain connectivity and reduce friction by facilitating real-time matching of demand and supply across multiple channels.
Seamless SKU Syndication
Wholesale platforms enable seamless SKU syndication by integrating vast product catalogs directly with retailers' inventory systems, streamlining order fulfillment and reducing manual entry errors. End-to-end marketplaces offer a centralized ecosystem where SKU data is consistently updated across suppliers and buyers, ensuring real-time accuracy and faster market response.
Hybrid Dropship Models
Hybrid dropship models combine wholesale inventory access with end-to-end marketplace technology, enabling retailers to offer a broad product range without holding stock. This approach leverages seamless integration between suppliers and e-commerce platforms, optimizing order fulfillment efficiency and reducing overhead costs.
Order Routing Automation
Wholesale platforms leverage order routing automation to efficiently manage large volumes of B2B transactions by directing orders to the appropriate suppliers based on criteria like inventory levels and shipping locations. End-to-end marketplaces integrate automated order routing within a single ecosystem, streamlining procurement by connecting buyers and sellers while optimizing fulfillment processes in real-time.
Live Inventory Feeds
Live inventory feeds in wholesale enable real-time stock updates directly from suppliers, reducing order inaccuracies and enhancing supply chain efficiency. End-to-end marketplaces integrate live inventory with order processing and fulfillment, providing a seamless customer experience and streamlining operations across multiple vendors.
Vertical Marketplace Solutions
Vertical marketplace solutions streamline wholesale operations by connecting specialized suppliers and buyers within specific industries, enhancing product discoverability and transaction efficiency. Compared to end-to-end marketplaces, these tailored platforms offer deeper category expertise and customized workflows that better address sector-specific compliance and logistics demands.
Wholesale vs End-to-End Marketplace Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com