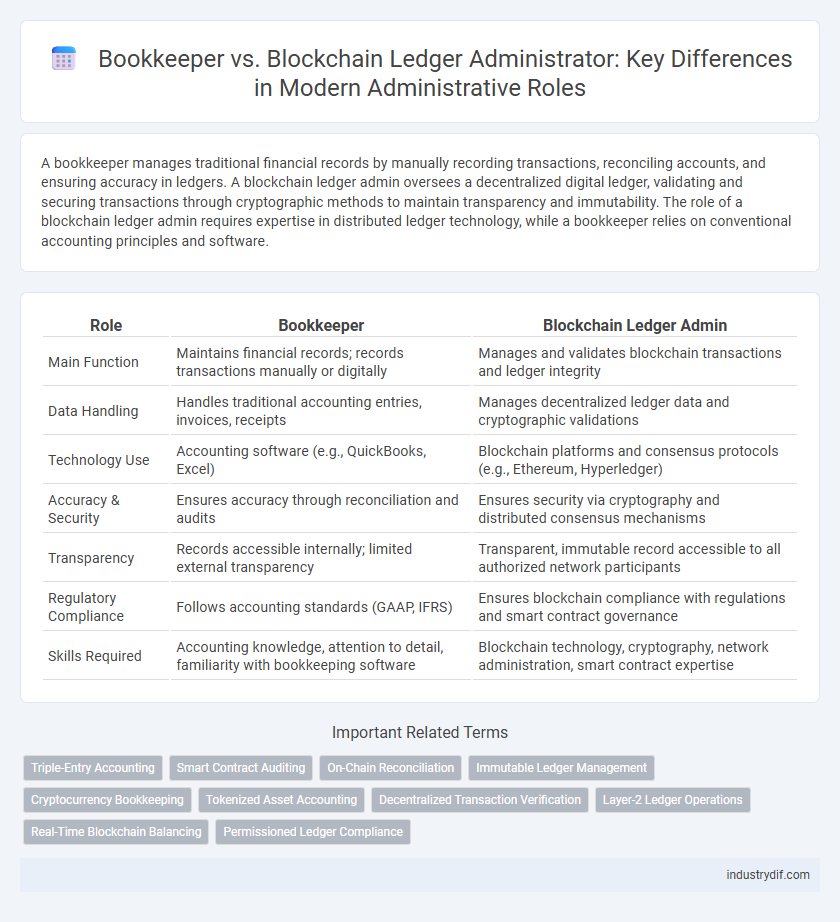
A bookkeeper manages traditional financial records by manually recording transactions, reconciling accounts, and ensuring accuracy in ledgers. A blockchain ledger admin oversees a decentralized digital ledger, validating and securing transactions through cryptographic methods to maintain transparency and immutability. The role of a blockchain ledger admin requires expertise in distributed ledger technology, while a bookkeeper relies on conventional accounting principles and software.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Bookkeeper | Blockchain Ledger Admin |
|---|---|---|
| Main Function | Maintains financial records; records transactions manually or digitally | Manages and validates blockchain transactions and ledger integrity |
| Data Handling | Handles traditional accounting entries, invoices, receipts | Manages decentralized ledger data and cryptographic validations |
| Technology Use | Accounting software (e.g., QuickBooks, Excel) | Blockchain platforms and consensus protocols (e.g., Ethereum, Hyperledger) |
| Accuracy & Security | Ensures accuracy through reconciliation and audits | Ensures security via cryptography and distributed consensus mechanisms |
| Transparency | Records accessible internally; limited external transparency | Transparent, immutable record accessible to all authorized network participants |
| Regulatory Compliance | Follows accounting standards (GAAP, IFRS) | Ensures blockchain compliance with regulations and smart contract governance |
| Skills Required | Accounting knowledge, attention to detail, familiarity with bookkeeping software | Blockchain technology, cryptography, network administration, smart contract expertise |
Understanding the Role of a Bookkeeper
A bookkeeper maintains accurate financial records by recording daily transactions, reconciling accounts, and managing invoices to ensure organizational transparency. Unlike a blockchain ledger administrator who oversees decentralized digital ledgers and ensures data immutability, the bookkeeper's role centers on traditional accounting practices and compliance. Mastery of accounting software and attention to detail are critical skills that define an effective bookkeeper's contributions to financial administration.
What is a Blockchain Ledger Admin?
A Blockchain Ledger Admin manages and verifies transactions within a distributed ledger system, ensuring data integrity and security through cryptographic protocols. Unlike traditional bookkeeping, this role involves monitoring decentralized ledgers, executing consensus mechanisms, and facilitating transparent, tamper-proof record-keeping. This position requires expertise in blockchain technology, smart contracts, and compliance with regulatory frameworks.
Key Responsibilities: Bookkeeper vs Blockchain Ledger Admin
A Bookkeeper is responsible for recording daily financial transactions, maintaining accurate ledgers, and reconciling accounts to ensure the integrity of financial data. In contrast, a Blockchain Ledger Admin oversees the maintenance and security of distributed ledger technology, validates transactions, and manages network permissions to ensure transparency and immutability. Key responsibilities for the Blockchain Ledger Admin also include monitoring consensus protocols and troubleshooting ledger discrepancies within the blockchain ecosystem.
Required Skills: Manual Records vs Digital Ledgers
Bookkeepers require strong attention to detail, proficiency in manual record-keeping techniques, and familiarity with traditional accounting software to accurately maintain physical financial records. Blockchain ledger administrators need expertise in distributed ledger technology, cryptographic security measures, and smart contract management to oversee digital transactions on decentralized platforms. Mastery of data integrity protocols and real-time auditing tools is essential for blockchain ledger administration, contrasting with the manual reconciliation and data entry skills prioritized in bookkeeping.
Data Accuracy and Error Management
Bookkeepers ensure data accuracy by manually recording and reconciling financial transactions, relying on periodic reviews to identify and correct errors. Blockchain Ledger Administrators leverage decentralized ledger technology with cryptographic validation, enabling real-time immutable records that reduce human errors and enhance error detection automatically. The contrast highlights traditional manual error management against automated, tamper-proof data integrity mechanisms in blockchain systems.
Security Protocols in Traditional vs Blockchain Administration
Bookkeepers in traditional administration rely on centralized databases with access controls and audit trails to ensure data security, but these systems remain vulnerable to insider threats and unauthorized alterations. Blockchain ledger administrators implement decentralized security protocols, using cryptographic hashes and consensus mechanisms to provide immutable transaction records and resistance to fraud. The inherent transparency and encryption in blockchain technology significantly enhance data integrity and reduce risks associated with manipulation compared to conventional bookkeeping methods.
Cost and Efficiency Comparison
Bookkeepers traditionally handle manual data entry and reconciliations, incurring higher labor costs and time delays in financial record maintenance. Blockchain ledger administrators utilize distributed ledger technology, reducing transaction costs by automating verification processes and enhancing real-time data transparency. The decentralized nature of blockchain significantly improves operational efficiency by minimizing errors and streamlining audit trails compared to conventional bookkeeping methods.
Compliance Requirements: Bookkeeper and Blockchain Admin
Bookkeepers manage financial records by ensuring accurate data entry and adherence to traditional accounting standards and regulatory compliance such as GAAP or IFRS. Blockchain ledger admins maintain decentralized ledgers with enhanced security protocols and real-time transaction verification, ensuring compliance with blockchain-specific regulations like AML and KYC requirements. Both roles require meticulous record-keeping but differ in technology use and regulatory frameworks tailored to centralized versus decentralized financial systems.
Career Paths and Industry Demand
Bookkeepers primarily manage traditional financial records and transactions, offering stability in small to medium businesses with steady demand. Blockchain ledger administrators specialize in overseeing decentralized digital ledgers, a rapidly growing field driven by the expanding adoption of blockchain technology in finance, supply chain, and cybersecurity sectors. Career paths in blockchain administration often require tech expertise and command higher salaries due to the scarcity of skilled professionals compared to conventional bookkeeping roles.
Future Trends in Administrative Accounting
Future trends in administrative accounting highlight the increasing integration of blockchain ledger administration alongside traditional bookkeeping roles. Blockchain ledger admins leverage decentralized, tamper-proof ledgers to enhance transparency and security in financial records, surpassing the manual reconciliation tasks typical of bookkeepers. Emerging technologies like AI-driven smart contracts are expected to further transform administrative accounting by automating verification and auditing processes within blockchain systems.
Related Important Terms
Triple-Entry Accounting
Bookkeepers manage traditional double-entry accounting by recording debits and credits, ensuring accurate financial statements and compliance with standard accounting principles. Blockchain ledger administrators oversee triple-entry accounting systems, utilizing cryptographic verification and decentralized ledgers to enhance transparency, immutability, and fraud reduction in financial record-keeping.
Smart Contract Auditing
Bookkeepers manage traditional financial records, ensuring accuracy and compliance with accounting standards, while blockchain ledger administrators oversee decentralized databases with a focus on verifying transactions through smart contract auditing to prevent vulnerabilities. Smart contract auditing involves systematically analyzing code to detect risks, errors, and security flaws that could compromise blockchain integrity or lead to financial loss.
On-Chain Reconciliation
Bookkeepers manage financial records using traditional accounting methods, while Blockchain Ledger Administrators oversee on-chain reconciliation by verifying and validating transactions directly on the distributed ledger, ensuring real-time accuracy and transparency. On-chain reconciliation leverages smart contracts and cryptographic verification to automate and secure the matching of entries, reducing errors compared to manual bookkeeping processes.
Immutable Ledger Management
Bookkeepers manage traditional financial records through manual entries and periodic reconciliations, whereas blockchain ledger administrators oversee immutable ledger management by maintaining decentralized, tamper-proof transaction records secured with cryptographic hashing. Immutable ledger management on blockchain enhances transparency, reduces fraud risk, and automates audit trails compared to conventional bookkeeping systems.
Cryptocurrency Bookkeeping
Cryptocurrency bookkeeping requires specialized knowledge of blockchain ledger administration, enabling accurate tracking of digital asset transactions and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Unlike traditional bookkeepers, blockchain ledger admins utilize decentralized ledger technology to provide transparent, tamper-proof records essential for cryptocurrency accounting.
Tokenized Asset Accounting
Bookkeepers manage traditional financial records by accurately recording transactions and reconciling accounts, ensuring compliance with accounting standards, while Blockchain Ledger Administrators oversee decentralized, immutable ledgers that track tokenized asset ownership and transactions in real time. Tokenized asset accounting demands integration of cryptographic verification, smart contract auditing, and transparent ledger maintenance for enhanced security and traceability.
Decentralized Transaction Verification
Bookkeepers manage financial records through centralized databases, ensuring accuracy via manual reconciliation and audits, whereas Blockchain Ledger Administrators oversee decentralized transaction verification using cryptographic algorithms and consensus protocols. This decentralized approach enhances transparency, reduces fraud risk, and allows real-time, tamper-resistant record-keeping across distributed networks.
Layer-2 Ledger Operations
Bookkeepers manage traditional financial records with manual entry and reconciliation processes, while Blockchain Ledger Administrators oversee Layer-2 ledger operations that ensure scalability, faster transaction settlement, and enhanced data integrity through off-chain transaction handling. Layer-2 solutions reduce network congestion and lower fees by processing transactions off the main blockchain, which requires specialized administrative skills in cryptographic validation and smart contract monitoring.
Real-Time Blockchain Balancing
Bookkeepers ensure accurate financial records through manual transaction entry and periodic reconciliation, while blockchain ledger administrators oversee real-time blockchain balancing by instantly validating and updating transactions across decentralized ledgers. Real-time blockchain balancing enhances transparency and reduces errors compared to traditional bookkeeping methods by providing continuous synchronization of financial data.
Permissioned Ledger Compliance
Bookkeepers manage traditional financial records with manual controls ensuring compliance, while Blockchain Ledger Administrators oversee permissioned ledgers using cryptographic permissions and consensus protocols to enhance data integrity and regulatory adherence. Permissioned ledger compliance requires stringent access controls and audit trails that blockchain administrators implement through role-based permissions, providing real-time transparency and tamper-evident records essential for financial audits.
Bookkeeper vs Blockchain Ledger Admin Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com