Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant root zone, minimizing wastage and promoting efficient water use in agriculture. Smart irrigation systems integrate sensors and weather data to automate watering schedules, optimizing water application based on real-time field conditions. Combining these technologies enhances crop yield, conserves water resources, and supports sustainable farming practices.
Table of Comparison
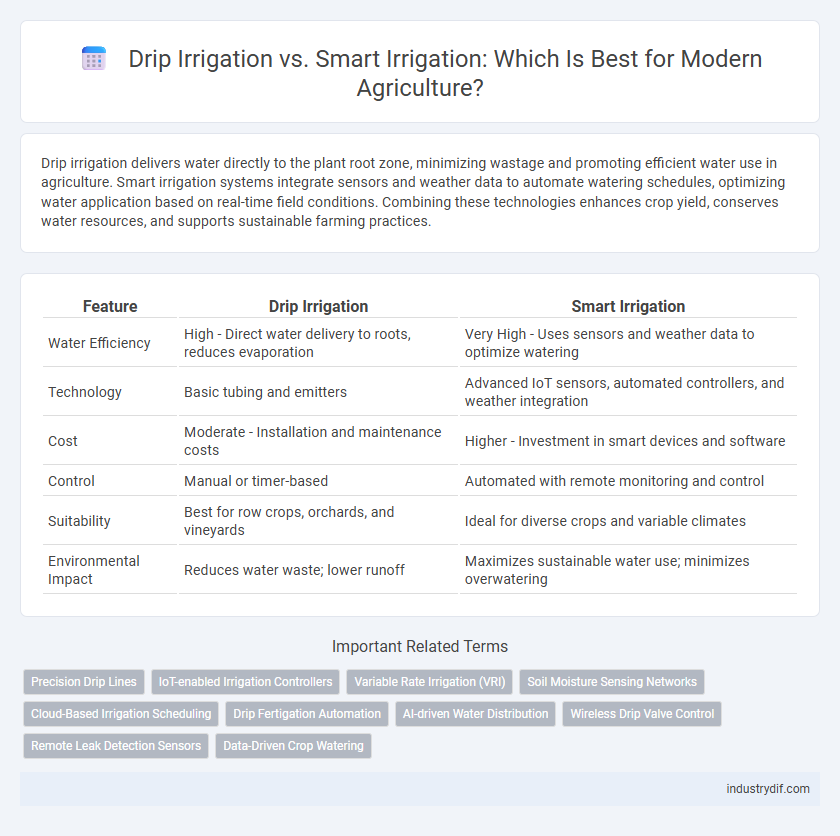
| Feature | Drip Irrigation | Smart Irrigation |
|---|---|---|
| Water Efficiency | High - Direct water delivery to roots, reduces evaporation | Very High - Uses sensors and weather data to optimize watering |
| Technology | Basic tubing and emitters | Advanced IoT sensors, automated controllers, and weather integration |
| Cost | Moderate - Installation and maintenance costs | Higher - Investment in smart devices and software |
| Control | Manual or timer-based | Automated with remote monitoring and control |
| Suitability | Best for row crops, orchards, and vineyards | Ideal for diverse crops and variable climates |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces water waste; lower runoff | Maximizes sustainable water use; minimizes overwatering |
Introduction to Drip and Smart Irrigation
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone through a network of valves, pipes, and emitters, minimizing water waste and enhancing crop yields by providing precise moisture control. Smart irrigation integrates advanced technologies such as soil moisture sensors, weather data, and automated controllers to optimize watering schedules, improving efficiency and reducing water consumption. Both systems revolutionize agricultural water management by promoting sustainability and resource conservation.
Key Differences Between Drip and Smart Irrigation
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone through a network of tubes and emitters, optimizing water use efficiency for specific crop types. Smart irrigation utilizes sensors and automated controls to adjust watering schedules based on real-time soil moisture, weather, and crop needs, enhancing precision and resource management. Key differences include drip irrigation's fixed delivery system versus smart irrigation's adaptive, data-driven approach that reduces water waste and supports sustainable farming practices.
Core Technologies Involved
Drip irrigation relies on micro-tubing and emitters that deliver water directly to the root zone, maximizing water efficiency through precise, low-pressure flow control. Smart irrigation integrates IoT sensors, weather data analytics, and automated valve controls to optimize irrigation schedules based on real-time soil moisture and climatic conditions. Core technologies in smart irrigation include wireless sensors, cloud computing platforms, and AI algorithms that enable adaptive water management, enhancing crop health and conservation efforts.
Water Efficiency and Conservation
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots through a network of tubes, minimizing evaporation and runoff, achieving water use efficiency rates of up to 90%. Smart irrigation leverages sensors and climate data to optimize watering schedules, reducing water waste by up to 30% compared to traditional methods. Combining drip technology with smart controls enhances water conservation efforts in agriculture by precisely targeting crop needs and adapting to environmental conditions.
Crop Yield and Growth Impacts
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant roots, significantly reducing water waste and promoting consistent moisture levels that enhance crop yield and growth uniformity. Smart irrigation systems use real-time data from soil moisture sensors and weather forecasts to optimize watering schedules, further improving resource efficiency and maximizing crop productivity. Studies show smart irrigation can increase crop yield by up to 20% compared to traditional drip irrigation by precisely matching water supply to plant needs throughout growth stages.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Drip irrigation systems require precise installation of tubing and emitters near crop roots, demanding careful layout planning to ensure uniform water distribution, while maintenance involves regular flushing to prevent clogging. Smart irrigation integrates sensors and automated controllers, necessitating skilled setup of electronic components and software calibration, with ongoing maintenance focused on sensor cleaning and firmware updates. Both systems aim to optimize water use but differ significantly in technical complexity and upkeep needs.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Drip irrigation systems typically involve lower initial installation costs but may require more manual monitoring and maintenance compared to smart irrigation, which integrates sensors and automated controls to optimize water usage. Smart irrigation systems can lead to significant water savings and higher crop yields by precisely applying water based on real-time soil moisture and weather data, justifying their higher upfront investment over time. The cost-benefit analysis favors smart irrigation for large-scale or high-value crops where efficiency gains translate into substantial economic returns, while drip irrigation remains cost-effective for smaller or resource-limited farms.
Scalability for Different Farm Sizes
Drip irrigation offers high scalability for different farm sizes by delivering water directly to the root zone, minimizing wastage and enabling precise control in both small and large fields. Smart irrigation systems enhance scalability through integration with IoT sensors and data analytics, allowing real-time adjustments that optimize water usage across varied crop types and terrain sizes. Both systems support sustainable agriculture, but smart irrigation provides greater flexibility and automation for expanding farm operations.
Environmental Sustainability
Drip irrigation minimizes water wastage by delivering precise amounts of water directly to plant roots, reducing runoff and evaporation, which enhances environmental sustainability. Smart irrigation systems use sensor data and weather forecasts to optimize watering schedules, further conserving water resources and reducing energy consumption. Both methods significantly improve water use efficiency compared to traditional irrigation, supporting sustainable agricultural practices and reducing environmental impact.
Future Trends in Agricultural Irrigation
Drip irrigation continues to advance with innovations in emitter design and water efficiency, enabling precise nutrient delivery to crops and reducing water waste. Smart irrigation integrates IoT sensors, weather forecasts, and AI algorithms to automate and optimize watering schedules, enhancing crop yield and resource management. Future trends emphasize combining these technologies to create adaptive, data-driven systems that promote sustainable agriculture and resilience to climate variability.
Related Important Terms
Precision Drip Lines
Precision drip lines in drip irrigation deliver targeted water directly to plant roots, minimizing water wastage and enhancing crop yield. Smart irrigation integrates sensors and automated controls with precision drip lines to optimize water use based on real-time soil moisture and weather data, significantly improving irrigation efficiency and sustainability.
IoT-enabled Irrigation Controllers
IoT-enabled irrigation controllers in smart irrigation systems optimize water usage by delivering precise amounts based on real-time soil moisture and weather data, significantly reducing water waste compared to traditional drip irrigation. These controllers enable remote monitoring and automated adjustments, enhancing crop health and increasing agricultural efficiency through data-driven decision-making.
Variable Rate Irrigation (VRI)
Variable Rate Irrigation (VRI) enhances water efficiency by delivering precise amounts of water to specific field zones based on real-time crop needs, outperforming traditional drip irrigation systems that apply uniform water distribution. Smart irrigation technologies integrating VRI leverage soil moisture sensors, weather data, and GPS mapping to optimize water use, increase crop yield, and reduce water waste in sustainable agriculture.
Soil Moisture Sensing Networks
Drip irrigation systems deliver water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff, while smart irrigation integrates soil moisture sensing networks to precisely monitor soil hydration levels, enabling real-time adjustments that optimize water use efficiency. Soil moisture sensing networks employ sensors placed at various root zones to gather data, enhancing irrigation scheduling by reducing water waste and improving crop yield under varying environmental conditions.
Cloud-Based Irrigation Scheduling
Drip irrigation delivers precise water directly to plant roots, maximizing efficiency with minimal waste, while cloud-based smart irrigation scheduling leverages real-time data and IoT sensors to optimize water usage dynamically across agricultural fields. Integrating cloud technology enhances irrigation systems by enabling remote monitoring, predictive analytics, and automated adjustments, leading to improved crop yields and water conservation.
Drip Fertigation Automation
Drip fertigation automation integrates precise nutrient delivery with water-saving drip irrigation technology, enhancing crop yield and resource efficiency by delivering fertilizers directly to the root zone at controlled rates. Smart irrigation systems use sensors and data analytics to optimize water usage but often lack the seamless nutrient integration and real-time fertilization control provided by advanced drip fertigation automation.
AI-driven Water Distribution
AI-driven water distribution in smart irrigation systems optimizes crop hydration by analyzing real-time data on soil moisture, weather patterns, and plant needs, enhancing water-use efficiency compared to traditional drip irrigation. Machine learning algorithms adjust water delivery precisely, reducing waste and improving yield sustainability through targeted irrigation schedules.
Wireless Drip Valve Control
Wireless drip valve control enhances drip irrigation by enabling precise water delivery through remote management, reducing water waste and improving crop yield. Smart irrigation systems integrate sensors and wireless valves to automate irrigation schedules, optimizing soil moisture levels and promoting sustainable water use in agriculture.
Remote Leak Detection Sensors
Remote leak detection sensors in drip irrigation systems enable precise water delivery by identifying leaks swiftly, reducing water wastage and preventing crop damage. Smart irrigation integrates these sensors with IoT technology for real-time monitoring and automated adjustments, enhancing efficiency and resource management in modern agriculture.
Data-Driven Crop Watering
Drip irrigation delivers precise water directly to plant roots, minimizing waste and optimizing soil moisture levels, while smart irrigation integrates real-time data from sensors, weather forecasts, and soil conditions to automate watering schedules for enhanced crop yield and resource efficiency. Data-driven crop watering through smart irrigation systems enables dynamic adjustment of water usage, reducing over-irrigation and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
Drip Irrigation vs Smart Irrigation Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com