Art installations engage viewers through thoughtfully arranged physical elements that invite contemplation and interaction within a defined space. Immersive experiences transcend traditional boundaries by enveloping participants in multi-sensory environments that foster emotional connection and active participation. Understanding the distinction helps art enthusiasts appreciate varying modes of artistic expression and audience engagement.
Table of Comparison
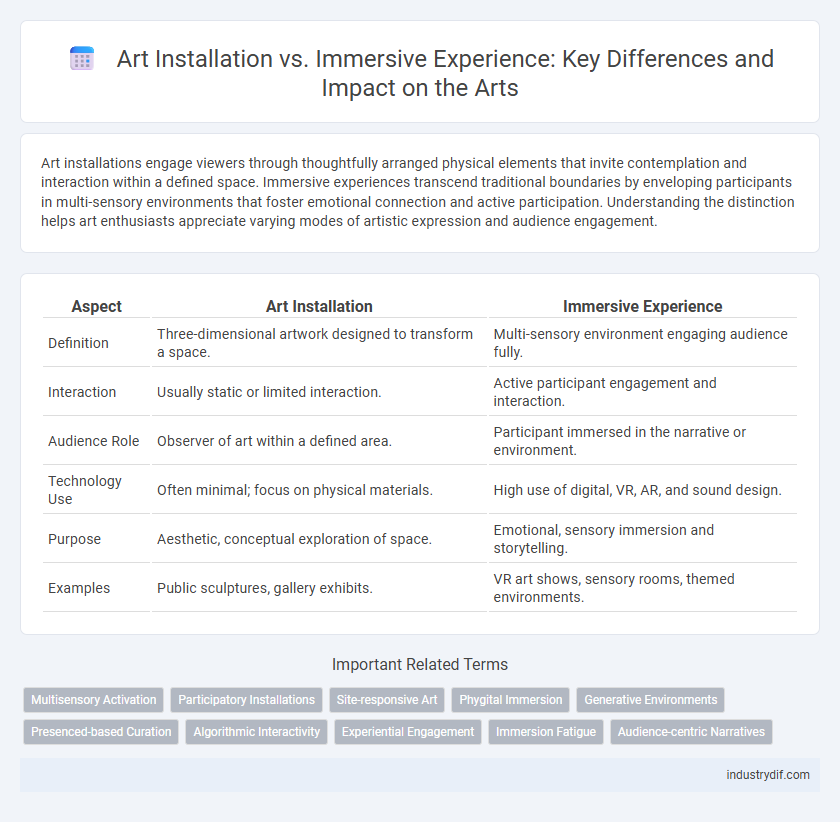
| Aspect | Art Installation | Immersive Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Three-dimensional artwork designed to transform a space. | Multi-sensory environment engaging audience fully. |
| Interaction | Usually static or limited interaction. | Active participant engagement and interaction. |
| Audience Role | Observer of art within a defined area. | Participant immersed in the narrative or environment. |
| Technology Use | Often minimal; focus on physical materials. | High use of digital, VR, AR, and sound design. |
| Purpose | Aesthetic, conceptual exploration of space. | Emotional, sensory immersion and storytelling. |
| Examples | Public sculptures, gallery exhibits. | VR art shows, sensory rooms, themed environments. |
Defining Art Installation and Immersive Experience
Art installation involves creating three-dimensional works designed to transform a viewer's perception of space using physical materials, spatial arrangement, and sensory elements. Immersive experience engages multiple senses through interactive and often digital environments, aiming to fully envelop participants in a narrative or conceptual world. Both prioritize sensory engagement but differ as art installations emphasize spatial transformation while immersive experiences focus on participant interaction and narrative immersion.
Historical Evolution of Art Installations
Art installations trace their origins to early 20th-century avant-garde movements such as Dada and Surrealism, evolving from static objects into dynamic, multi-sensory environments. By the 1960s and 70s, artists like Allan Kaprow pioneered "Happenings" that blurred boundaries between artwork and audience, laying groundwork for immersive experiences. This historical evolution reflects a shift from passive observation to active participation, emphasizing spatial interaction and sensory engagement in contemporary art installations.
The Rise of Immersive Experiences in Contemporary Art
Immersive experiences in contemporary art have surged in popularity, transforming traditional art installations into dynamic, multi-sensory environments that actively engage audience participation. Artists like teamLab and Yayoi Kusama utilize technology, light, and sound to create spaces that blur the boundaries between viewer and artwork. This evolution highlights a shift toward experiential art forms that emphasize emotional connection and interactive storytelling over static display.
Key Characteristics of Art Installations
Art installations are three-dimensional works designed to transform a space and engage viewers through visual, sensory, and spatial elements. They often combine various materials and media, emphasizing the relationship between the artwork, the environment, and the audience. Key characteristics include site-specificity, interactivity, and the ability to evoke emotional or intellectual responses within a confined or defined area.
Essential Elements of Immersive Experiences
Immersive experiences in art hinge on multisensory engagement, spatial design, and interactive elements that envelop viewers in a dynamic environment. Unlike traditional art installations, these experiences prioritize audience participation, incorporating technology such as VR, AR, and soundscapes to deepen emotional and cognitive connections. Key components include narrative structure, environmental interactivity, and real-time feedback, fostering a fully integrated and transformative art encounter.
Audience Participation: Interaction in Both Formats
Art installations engage audiences through tactile and visual interaction, allowing viewers to explore physical spaces and manipulate elements within the artwork. Immersive experiences deepen this engagement by enveloping participants in multi-sensory environments that often include sound, light, and digital media, encouraging active involvement. Both formats prioritize audience participation, transforming spectators into co-creators and enhancing emotional and cognitive connections with the art.
Technological Influences on Art Presentation
Technological advancements such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and interactive sensors have revolutionized art installations by enabling dynamic, multisensory environments that engage audiences beyond traditional visual stimuli. Immersive experiences utilize these technologies to blur the boundaries between the viewer and the artwork, creating personalized narratives and spatial interactions that evolve in real-time. Digital platforms and projection mapping further enhance the scalability and accessibility of art presentations, transforming static displays into participatory, evolving ecosystems.
Notable Art Installations vs Immersive Experience Exhibits
Notable art installations like Yayoi Kusama's Infinity Mirror Rooms emphasize physical space manipulation and sensory engagement through sculptural and light-based elements. Immersive experience exhibits, such as teamLab Borderless, combine digital technology and interactivity to create dynamic, participatory environments that evolve with visitor interaction. Both forms blur traditional art boundaries but differ in their reliance on tangible materials versus virtual or augmented realities to evoke emotional and intellectual responses.
Impact on Viewer Perception and Engagement
Art installations transform physical spaces by integrating visual, tactile, and spatial elements, fostering active viewer participation and heightening sensory awareness. Immersive experiences envelop audiences through multisensory stimuli, including sound, light, and digital interaction, creating a dynamic environment that alters perception and emotional engagement. Both forms challenge traditional art boundaries, but immersive experiences often generate deeper psychological impact, promoting a holistic connection between the artwork and the viewer.
Future Trends: Blurring the Line Between Installation and Immersion
Emerging trends in the art world highlight a fusion of art installation and immersive experience, where spatial design and interactive technology converge to create multi-sensory environments. Advanced digital projection, augmented reality, and responsive soundscapes enable visitors to engage with artwork on a personalized level, dissolving traditional boundaries between observer and creation. This evolution drives a future where art transcends passive viewing, promoting active participation and emotional connectivity.
Related Important Terms
Multisensory Activation
Art installations engage viewers through spatial and visual elements, often emphasizing physical presence and environmental transformation. Immersive experiences enhance multisensory activation by integrating sound, touch, smell, and interactive technologies, creating a fully enveloping environment that stimulates emotional and cognitive responses.
Participatory Installations
Participatory installations emphasize audience interaction, transforming viewers into active contributors within the artwork, which distinguishes them from traditional art installations that often remain passive. Immersive experiences further amplify this engagement by enveloping participants in multisensory environments designed to blur the line between observer and creator, fostering deeper emotional and sensory involvement.
Site-responsive Art
Site-responsive art adapts and interacts with the specific characteristics of a location, creating a unique dialogue between the artwork and its environment, unlike immersive experiences that prioritize audience engagement through sensory stimulation. This approach emphasizes context, history, and spatial dynamics, resulting in installations that transform perception and deepen the connection to the physical site.
Phygital Immersion
Phygital immersion integrates physical art installations with digital elements to create multisensory environments that engage audiences beyond traditional boundaries. This fusion enhances interactive experiences by combining tangible artistic expressions with augmented reality, virtual reality, and sensor-based technologies.
Generative Environments
Generative environments in art installations utilize algorithmic processes to create dynamic, evolving visuals and sounds that transform physical spaces, engaging viewers through real-time interaction and sensory immersion. Immersive experiences expand on this by integrating multisensory elements such as spatial audio, haptic feedback, and augmented reality to envelop audiences fully within responsive, generative landscapes.
Presenced-based Curation
Presenced-based curation in art installations emphasizes the viewer's spatial and sensory presence, creating a dynamic interaction that transforms static artworks into immersive experiences. By integrating environmental elements and multisensory stimuli, this approach fosters deeper engagement and personal connection between the audience and the artwork.
Algorithmic Interactivity
Algorithmic interactivity in art installations involves programmed responses that adapt to viewers' actions, creating dynamic environments that evolve based on input data. Immersive experiences leverage algorithmic systems to generate seamless, multi-sensory engagement, enhancing audience participation through real-time feedback loops and personalized narrative pathways.
Experiential Engagement
Art installations create a physical space where viewers interact with static or dynamic components, emphasizing spatial perception and material engagement. Immersive experiences envelop participants through multisensory stimuli, fostering deeper emotional and cognitive involvement beyond traditional observation.
Immersion Fatigue
Immersive experiences in art installations demand continuous sensory engagement, often leading to immersion fatigue where viewers feel overwhelmed by constant stimuli. This fatigue can reduce the overall impact of the artwork, making traditional art installations with selective sensory focus more effective for sustained audience interaction.
Audience-centric Narratives
Art installations engage audiences through spatial and sensory elements that invite interpretation and personal connection, while immersive experiences envelop participants in interactive environments designed to evoke emotional and multisensory responses. Both prioritize audience-centric narratives by transforming viewers into active participants, fostering deeper engagement through individualized and collective storytelling.
Art Installation vs Immersive Experience Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com