Canvas art offers a tangible and traditional medium that invites close inspection of texture and brushwork, allowing viewers to appreciate fine details in a personal setting. Immersive installations transform the space into an interactive environment that surrounds and engages the audience, often integrating multiple sensory elements like sound, light, and movement. Each approach delivers a unique artistic experience, with canvas emphasizing craftsmanship and immersive installations prioritizing spatial interaction.
Table of Comparison
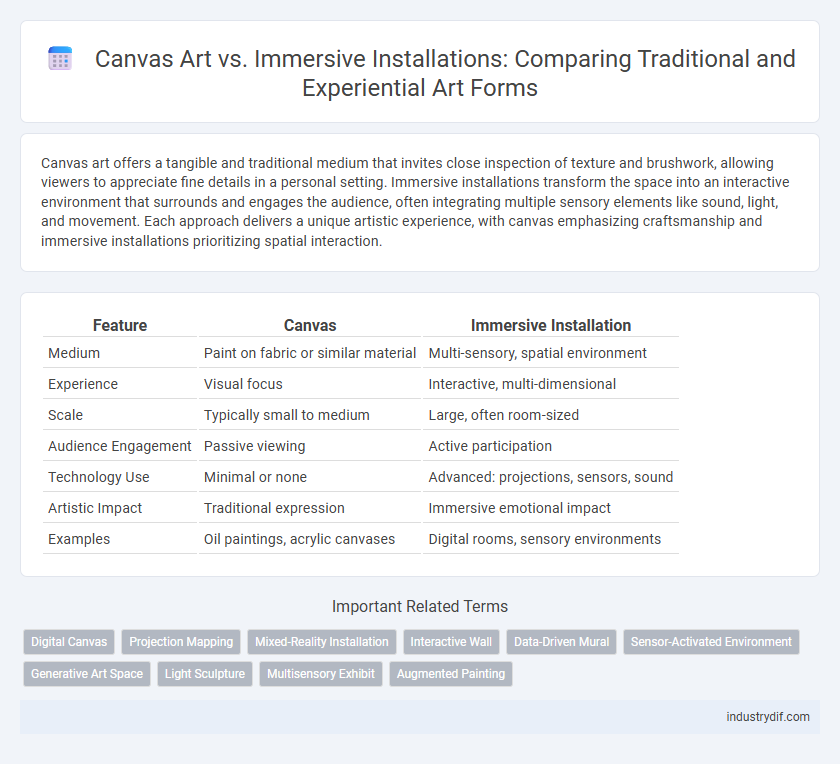
| Feature | Canvas | Immersive Installation |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Paint on fabric or similar material | Multi-sensory, spatial environment |
| Experience | Visual focus | Interactive, multi-dimensional |
| Scale | Typically small to medium | Large, often room-sized |
| Audience Engagement | Passive viewing | Active participation |
| Technology Use | Minimal or none | Advanced: projections, sensors, sound |
| Artistic Impact | Traditional expression | Immersive emotional impact |
| Examples | Oil paintings, acrylic canvases | Digital rooms, sensory environments |
Definition of Canvas Art and Immersive Installations
Canvas art involves creating visual artworks on fabric stretched over a frame, traditionally using mediums like oil or acrylic paints, offering a tangible, two-dimensional surface for artistic expression. Immersive installations integrate physical space, light, sound, and sometimes digital technology to envelop viewers in a multi-sensory experience, transforming the perception of environment and art. Both forms emphasize different interaction levels: canvas art centers on the aesthetic appreciation of a static piece, while immersive installations aim for participatory engagement and spatial transformation.
Historical Evolution of Canvas in Art
Canvas has been a fundamental medium in art since the Renaissance, revolutionizing painting by providing artists like Leonardo da Vinci and Titian a durable, portable surface suitable for oil paints. The historical evolution of canvas marked a shift from wooden panels to a fabric base, enabling larger and more expressive compositions throughout the 17th and 18th centuries. This transformation laid the groundwork for contemporary art forms, contrasting sharply with the multisensory, spatial experiences characteristic of immersive installations.
Rise of Immersive Installations in Contemporary Spaces
Immersive installations have surged in popularity within contemporary art spaces, blending technology, sound, and physical interaction to engage audiences beyond the static experience of traditional canvas art. These installations transform galleries into dynamic environments, enabling viewers to participate actively and experience art through multisensory stimuli. The rise of immersive art reflects a shift towards experiential engagement, challenging conventional boundaries and expanding creative expression in modern exhibitions.
Key Differences in Artistic Techniques
Canvas art typically emphasizes two-dimensional compositions created with paints or mixed media on fabric surfaces, allowing for precise brushwork and color layering techniques. Immersive installations engage multiple senses through three-dimensional, spatial environments, incorporating elements like lighting, sound, and physical objects to create an interactive experience. The primary artistic difference lies in the static, visual-centric nature of canvas paintings versus the dynamic, experiential focus of immersive installations.
Audience Engagement: Passive vs. Participatory
Canvas art primarily offers a passive audience experience, where viewers observe the artwork without direct interaction, fostering contemplative engagement through visual appreciation. Immersive installations transform audience participation by encouraging active involvement, allowing visitors to interact physically or emotionally with the environment, thereby creating a dynamic and memorable experience. This participatory engagement enhances emotional connection and sparks personal interpretation, significantly altering the traditional art consumption model.
Materiality and Technology Integration
Canvas art emphasizes traditional materiality, using physical surfaces like linen or cotton that interact directly with paint pigments, creating tangible textures and color depth. Immersive installations integrate advanced technologies such as projection mapping, sensors, and augmented reality, transforming physical space into interactive environments that engage multiple senses. This fusion of material and digital elements in immersive works redefines audience interaction, contrasting the static, tactile experience offered by canvas.
Spatial Experience and Environment
Canvas art offers a two-dimensional spatial experience confined to the artwork's physical boundaries, emphasizing texture, color, and composition on a fixed plane. Immersive installations transform the environment into an interactive, multi-sensory space, engaging viewers through spatial depth, movement, and surrounding stimuli. This dynamic environment elevates audience participation, creating a holistic experience beyond traditional canvas limitations.
Impact on Art Market and Collectors
Canvas art remains a dominant medium in the traditional art market due to its tangible, collectible nature and established valuation metrics. Immersive installations disrupt conventional art sales by emphasizing experiential engagement over physical ownership, attracting collectors interested in innovative, large-scale works that challenge display norms. This shift expands investment opportunities but complicates provenance, storage, and resale, prompting new market models and collector approaches.
Notable Artists and Iconic Works
Notable artists like Jackson Pollock and Mark Rothko revolutionized traditional canvas art with iconic works such as *No. 5, 1948* and *Orange, Red, Yellow*, emphasizing color and abstract expression. In contrast, immersive installations by artists like Yayoi Kusama and Olafur Eliasson transform space with interactive experiences, exemplified by Kusama's *Infinity Mirror Rooms* and Eliasson's *The Weather Project*. These immersive works challenge the boundaries of art by engaging audiences directly, creating multisensory environments beyond the static canvas.
Future Trends in Art Presentation
Canvas remains a timeless medium for art presentation, but immersive installations are rapidly shaping the future by integrating technology such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) to create dynamic, multifaceted experiences. These installations engage audiences through interactive environments, blending digital and physical elements to transform traditional art consumption. As artists and galleries increasingly adopt AI-driven and sensor-based technologies, immersive art is poised to redefine narrative possibilities and audience participation in exhibitions.
Related Important Terms
Digital Canvas
Digital canvas integrates advanced technology with traditional artistic techniques, offering dynamic, interactive visuals that evolve in real-time. Unlike immersive installations, digital canvases focus on transforming flat surfaces into versatile digital displays, enhancing accessibility and versatility in contemporary art exhibitions.
Projection Mapping
Projection mapping transforms traditional canvas art by projecting dynamic visuals onto surfaces, creating immersive installations that engage viewers through multidimensional experiences. This technique leverages spatial geometry and light manipulation to blur boundaries between physical and digital art, offering a richer sensory interaction than static canvas displays.
Mixed-Reality Installation
Mixed-reality installations blend physical and digital elements, offering a dynamic art experience beyond traditional canvas paintings by integrating interactive virtual components into real-world environments. These installations enhance viewer engagement through real-time sensory feedback and multi-dimensional storytelling, pushing the boundaries of traditional art forms.
Interactive Wall
An interactive wall transforms traditional canvas art by incorporating digital technology that responds to viewer engagement, creating a dynamic and immersive experience. Unlike static canvas, immersive installations leverage sensors, projection mapping, and real-time interaction to deepen audience participation and redefine spatial storytelling in contemporary art.
Data-Driven Mural
Data-driven murals transform traditional canvas artwork by integrating interactive technology and real-time data visualization, creating dynamic and evolving visual narratives. Immersive installations leverage spatial design and sensory inputs to engage viewers in multi-dimensional experiences, blending physical art with digital interactivity for profound audience impact.
Sensor-Activated Environment
Sensor-activated environments in immersive installations engage audiences through interactive technology, creating dynamic, multisensory experiences that extend beyond the static visuals of traditional canvas art. These environments use motion sensors, infrared detectors, and spatial tracking to respond to viewers' presence and movements, fostering personalized and evolving artistic interactions.
Generative Art Space
Canvas-based generative art offers a traditional medium where algorithmically created visuals are confined to two-dimensional surfaces, emphasizing intricate detail and controlled viewing angles. Immersive installations extend generative art into three-dimensional, interactive environments, enabling multisensory engagement and real-time audience participation within expansive digital spaces.
Light Sculpture
Light sculptures in immersive installations transform spaces by integrating dynamic, multidimensional illumination with physical elements, creating interactive environments that engage viewers on a sensory level. In contrast, canvas-based light art typically emphasizes static or two-dimensional expressions, relying on painted or projected light effects confined within a flat surface.
Multisensory Exhibit
Canvas artworks engage viewers primarily through visual stimuli, offering detailed, static representations that invite close examination of texture and brushwork. Immersive installations create multisensory experiences by integrating sound, light, scent, and tactile elements, enveloping the audience in an interactive environment that transforms perception and emotional response.
Augmented Painting
Augmented painting combines traditional canvas techniques with immersive installation elements, utilizing digital overlays and interactive technology to enhance the viewer's sensory experience. This fusion transforms static art into dynamic environments, allowing audiences to engage with the artwork beyond physical boundaries through augmented reality applications.
Canvas vs Immersive Installation Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com