Graphic design emphasizes creativity and human intuition to craft visually compelling artwork, relying heavily on manual skills and artistic judgment. Algorithmic design utilizes computational methods and mathematical algorithms to generate complex patterns and structures efficiently with high precision. Combining graphic design with algorithmic design offers innovative possibilities, blending aesthetic appeal with automated scalability and consistency.
Table of Comparison
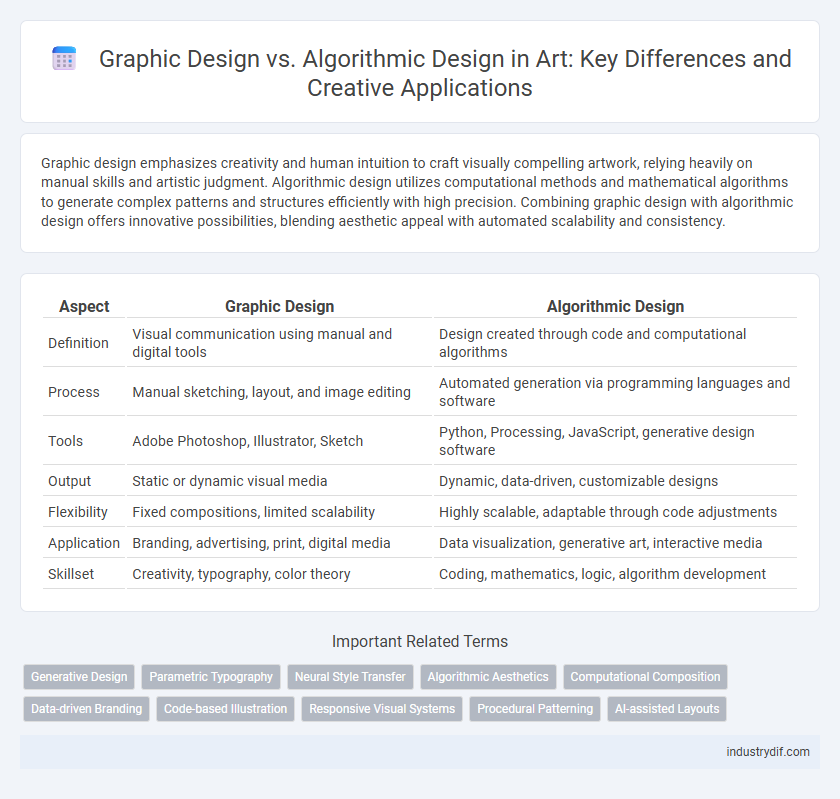
| Aspect | Graphic Design | Algorithmic Design |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Visual communication using manual and digital tools | Design created through code and computational algorithms |
| Process | Manual sketching, layout, and image editing | Automated generation via programming languages and software |
| Tools | Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, Sketch | Python, Processing, JavaScript, generative design software |
| Output | Static or dynamic visual media | Dynamic, data-driven, customizable designs |
| Flexibility | Fixed compositions, limited scalability | Highly scalable, adaptable through code adjustments |
| Application | Branding, advertising, print, digital media | Data visualization, generative art, interactive media |
| Skillset | Creativity, typography, color theory | Coding, mathematics, logic, algorithm development |
Defining Graphic Design and Algorithmic Design
Graphic design involves creating visual content using traditional tools and software to communicate messages through typography, imagery, and color. Algorithmic design relies on computational processes and mathematical algorithms to generate visuals, often enabling dynamic and complex patterns beyond manual creation. Both approaches shape modern aesthetics but differ in their methods of production and conceptual frameworks.
Historical Evolution of Graphic and Algorithmic Design
Graphic design evolved from traditional hand-drawn techniques to digital tools, beginning with early printmaking and typography advancements in the 15th century and expanding through the 20th-century adoption of computers. Algorithmic design emerged in the late 20th century with the rise of computer science, utilizing code-based processes to generate complex visual patterns and forms beyond manual creation. Both disciplines reflect shifting technological capabilities, where graphic design emphasizes aesthetic composition and visual communication, while algorithmic design integrates computational logic to innovate artistic expression.
Core Principles: Creative Process vs Computational Logic
Graphic design emphasizes a creative process driven by human intuition, visual storytelling, and emotional resonance, prioritizing aesthetics, composition, and color theory to convey messages effectively. Algorithmic design relies on computational logic and mathematical algorithms to generate patterns, structures, and visuals based on predefined rules, enabling scalability and precision in design output. Both approaches integrate core principles but differ fundamentally in their methodology: one rooted in artistic creativity, the other in systematic computation.
Tools and Technologies in Graphic vs Algorithmic Design
Graphic design primarily employs tools like Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, and CorelDRAW, emphasizing manual creativity and visual storytelling through intuitive interfaces and vector-based graphics. Algorithmic design leverages programming languages such as Python, Processing, and JavaScript alongside generative design software like Grasshopper and Houdini, enabling the creation of complex patterns and adaptive visuals through code-driven processes. Both fields integrate emerging technologies like AI and machine learning to enhance precision and innovation, but algorithmic design distinctly relies on computational algorithms to automate and evolve artistic creation.
The Role of Human Intuition and Machine Intelligence
Graphic design relies heavily on human intuition to craft visually compelling and emotionally resonant images, leveraging creativity and cultural understanding. Algorithmic design harnesses machine intelligence to analyze data patterns and generate complex, precise visuals at scale, often optimizing efficiency and consistency. The interplay of human intuition and machine intelligence enables innovative design outcomes that blend personalized artistry with computational power.
Aesthetic Outcomes: Manual Creativity vs Generated Patterns
Graphic design emphasizes manual creativity, where designers craft unique visual elements that reflect personal expression and cultural context, resulting in highly customized and emotionally resonant aesthetics. Algorithmic design generates patterns through computational processes, producing intricate, mathematically driven visuals that often showcase symmetry, repetition, and complexity beyond manual capability. The aesthetic outcome of graphic design tends to prioritize originality and subjective interpretation, while algorithmic design favors precision, scalability, and novel pattern formation grounded in data and code.
Efficiency and Scalability: Handcrafted vs Automated Design
Graphic design relies on handcrafted creativity, offering nuanced aesthetics but limited scalability and time efficiency compared to algorithmic design. Algorithmic design automates repetitive tasks, enabling rapid production of scalable visuals that adapt seamlessly to various formats and platforms. This automation enhances workflow efficiency, making it ideal for large-scale projects requiring consistent output.
Industry Applications: From Branding to Data Visualization
Graphic design excels in creating visually compelling branding materials that communicate a company's identity through color theory, typography, and imagery, making it essential for marketing and advertising industries. Algorithmic design harnesses computational processes to generate complex patterns and data-driven visualizations, revolutionizing fields such as data science, architecture, and interactive media. The fusion of graphic and algorithmic design enhances industry applications by combining creativity with precision, enabling dynamic branding solutions and insightful data visualization tools.
Collaboration: Designers, Developers, and AI Systems
Collaboration between graphic designers, developers, and AI systems bridges creativity and technology, enhancing design innovation and efficiency. Graphic design emphasizes human intuition and visual storytelling, while algorithmic design leverages computational power to generate dynamic, data-driven visuals. Integrating AI tools enables seamless interaction, allowing teams to co-create adaptive designs that respond to user behavior and market trends.
Future Trends in Graphic and Algorithmic Design Integration
Future trends in graphic and algorithmic design integration emphasize the rise of AI-driven creativity, enabling designers to generate complex visual patterns with minimal manual input. Adaptive algorithms will facilitate personalized design experiences, optimizing aesthetics based on user data and behavioral insights. The convergence of procedural generation and traditional graphic techniques promises more dynamic, interactive, and context-aware visual content in digital media.
Related Important Terms
Generative Design
Generative design harnesses algorithms and AI to create complex, unique visuals that evolve from set parameters, contrasting traditional graphic design's manual, intuition-driven approach. This fusion of computational power and artistic input pushes creative boundaries, enabling designers to explore infinite variations and optimize aesthetics with precision.
Parametric Typography
Parametric typography leverages algorithms to generate dynamic letterforms that adapt based on defined variables, contrasting traditional graphic design which relies on static, manually crafted typefaces. By integrating computational rules, parametric typography enables innovative, data-driven visuals that evolve in real-time, enhancing customization and interactivity in digital art.
Neural Style Transfer
Neural Style Transfer bridges the gap between graphic design and algorithmic design by using deep learning algorithms to blend artistic styles with digital images, enhancing creativity and automation. This technique transforms traditional graphic design workflows by enabling the generation of unique visuals that combine the aesthetics of classical art with computational precision.
Algorithmic Aesthetics
Algorithmic aesthetics in design harnesses computational processes to generate visually compelling patterns and structures that evolve through mathematical rules, diverging from traditional graphic design's manual creativity. This approach enables the exploration of complex forms and dynamic interactions, producing unique, data-driven visuals that adapt and respond to evolving inputs.
Computational Composition
Graphic design emphasizes aesthetic principles and human creativity to craft visually compelling compositions, while algorithmic design leverages computational methods and algorithms to generate dynamic, data-driven visuals. Computational composition in algorithmic design enables precise control over complex patterns and iterations, often producing unique, scalable art forms unattainable through traditional graphic techniques.
Data-driven Branding
Graphic design emphasizes creative visual communication through handcrafted elements, while algorithmic design leverages data-driven processes and computational techniques to generate adaptive brand identities. Data-driven branding optimizes audience targeting and personalization by analyzing consumer behavior patterns, enhancing brand consistency and engagement across digital platforms.
Code-based Illustration
Graphic design centers on visual communication through manual or software-based tools emphasizing creativity and aesthetics, while algorithmic design leverages computational processes and code to generate dynamic, complex illustrations. Code-based illustration in algorithmic design enables precision, scalability, and unique generative art patterns that traditional graphic design techniques may not achieve.
Responsive Visual Systems
Graphic design emphasizes handcrafted aesthetics and user-focused layouts, while algorithmic design leverages code-driven processes to generate adaptive visuals. Responsive visual systems integrate these approaches by dynamically adjusting design elements based on user interaction and device parameters for optimized engagement.
Procedural Patterning
Procedural patterning in graphic design leverages algorithmic rules to generate intricate, repeatable patterns that enhance visual complexity and consistency, contrasting with manual graphic design methods reliant on individual creativity and intuition. Algorithmic design enables scalable pattern variations and automatised adjustments, optimizing workflow efficiency and precision in creating dynamic, adaptable visual compositions.
AI-assisted Layouts
AI-assisted layouts in graphic design leverage machine learning algorithms to automate composition, color schemes, and typography choices, enhancing creativity while saving time. Algorithmic design integrates computational processes to generate dynamic and adaptive visuals, offering precision and scalability that traditional graphic design methods may lack.
Graphic Design vs Algorithmic Design Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com