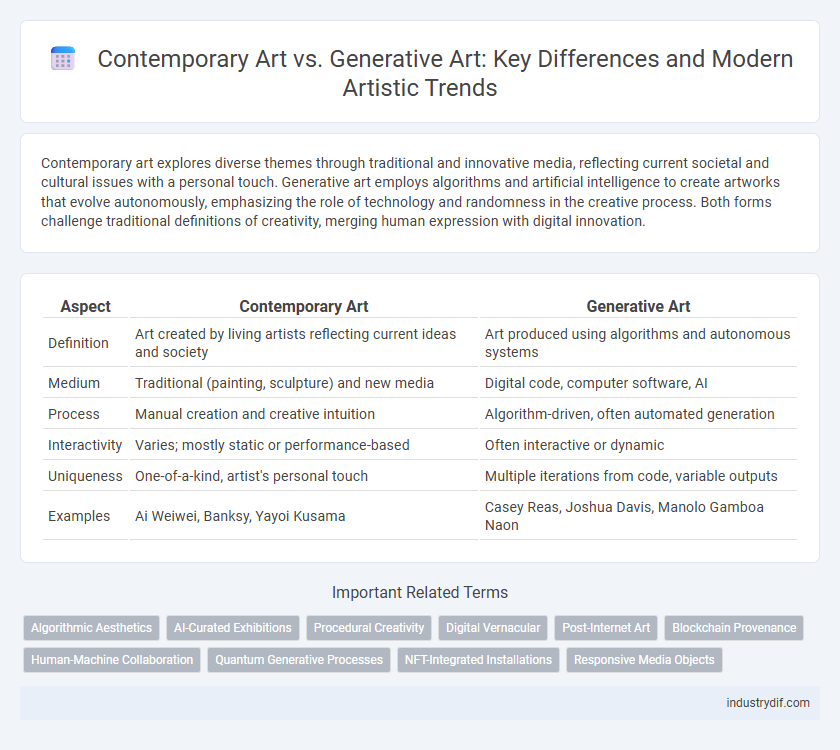
Contemporary art explores diverse themes through traditional and innovative media, reflecting current societal and cultural issues with a personal touch. Generative art employs algorithms and artificial intelligence to create artworks that evolve autonomously, emphasizing the role of technology and randomness in the creative process. Both forms challenge traditional definitions of creativity, merging human expression with digital innovation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Contemporary Art | Generative Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art created by living artists reflecting current ideas and society | Art produced using algorithms and autonomous systems |
| Medium | Traditional (painting, sculpture) and new media | Digital code, computer software, AI |
| Process | Manual creation and creative intuition | Algorithm-driven, often automated generation |
| Interactivity | Varies; mostly static or performance-based | Often interactive or dynamic |
| Uniqueness | One-of-a-kind, artist's personal touch | Multiple iterations from code, variable outputs |
| Examples | Ai Weiwei, Banksy, Yayoi Kusama | Casey Reas, Joshua Davis, Manolo Gamboa Naon |
Defining Contemporary Art: Key Characteristics
Contemporary art is characterized by its reflection of current social, political, and cultural issues, often challenging traditional boundaries and embracing diverse media and techniques. It prioritizes conceptual depth, experimentation, and viewer engagement, making it fluid and dynamic in response to contemporary life. Unlike generative art, which relies on algorithmic processes, contemporary art emphasizes human creativity and critical discourse.
The Evolution of Generative Art
Generative art has evolved from traditional contemporary art by integrating advanced algorithms and artificial intelligence to create autonomous, dynamic works that continuously change and respond to their environment. This evolution marks a shift from human-centric creation to collaborative interaction between artists and technology, expanding the boundaries of creativity and artistic expression. Key developments include the use of machine learning, neural networks, and code-based systems, which drive the generation of complex, unpredictable visual and auditory experiences.
Artistic Techniques: Manual vs. Algorithmic Creation
Contemporary art predominantly showcases manual artistic techniques such as painting, sculpture, and mixed media, emphasizing human expression and tactile skill. In contrast, generative art relies on algorithmic creation, utilizing computer code and artificial intelligence to produce evolving visual patterns and forms. This divergence highlights the contrast between handcrafted traditions and the innovative use of technology in artistic production.
Influential Artists in Contemporary and Generative Art
Influential artists in contemporary art include Jeff Koons, known for his large-scale sculptures that challenge popular culture, and Yayoi Kusama, whose immersive installations explore themes of infinity and repetition. In generative art, artists like Casey Reas and Mario Klingemann have pioneered the use of algorithms and artificial intelligence to create dynamic, evolving artworks. Both movements redefine artistic expression by blending traditional techniques with innovative technology and conceptual frameworks.
Visual Aesthetics: Contrasts and Convergences
Contemporary art explores diverse media and styles, emphasizing originality, conceptual depth, and cultural commentary, while generative art leverages algorithms and computational processes to create dynamic, often unpredictable visual outcomes. Visual aesthetics in contemporary art often hinge on human emotion and intentionality, contrasting with generative art's reliance on mathematical precision and automation, yet both share an evolving relationship with technology that challenges traditional boundaries of creativity. The convergence occurs as artists integrate generative techniques into contemporary practices, fostering hybrid aesthetics that blend human subjectivity with algorithmic innovation.
Technology’s Role in Modern Art Forms
Contemporary art embraces diverse media and explores technology as a tool for expression, often integrating digital platforms, interactive installations, and multimedia to challenge traditional boundaries. Generative art specifically leverages algorithms and artificial intelligence to autonomously create dynamic and evolving artworks, reflecting advancements in computational creativity and machine learning. The fusion of technology in these modern art forms transforms artistic processes, enabling real-time creativity and expanding the possibilities for innovation within the art world.
Audience Interaction and Engagement
Contemporary art often engages audiences through immersive installations and participatory experiences that evoke emotional and intellectual responses. Generative art leverages algorithms and real-time data to create dynamic, evolving works that respond directly to viewer input, enhancing interactivity and personalized engagement. Both forms prioritize audience involvement but differ in approach, with generative art emphasizing automated creativity and continual transformation.
Art Market Trends: Collecting Contemporary vs. Generative Works
Contemporary art maintains strong demand in the global art market, driven by established artists and well-known galleries, whereas generative art is rapidly gaining traction due to its innovation in algorithmic creativity and digital scarcity. Collectors increasingly view generative art as a valuable asset class, supported by blockchain provenance and NFT platforms, which enhance transparency and authenticity. Market analyses indicate rising auction prices and expanding collector bases for generative artworks, signaling a shift in investment trends that balance traditional collectability with digital innovation.
Preservation and Authenticity Challenges
Contemporary art faces preservation challenges due to the diverse use of mixed media and ephemeral installations that degrade over time, complicating authenticity verification. Generative art introduces unique issues as its digital code and algorithm-driven processes require preservation of both the software environment and original data sets, raising concerns about long-term accessibility and originality. The authenticity of generative art often depends on cryptographic signatures or blockchain technology to ensure provenance, distinguishing it from traditional contemporary pieces that rely on physical documentation and artist verification.
Future Directions in Contemporary and Generative Art
Emerging trends in contemporary and generative art emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and immersive technologies, enabling unprecedented interactive experiences and expanding creative boundaries. Artists are increasingly exploring algorithmic processes to produce dynamic, evolving artworks that challenge traditional notions of authorship and originality. Future directions prioritize sustainability and ethical considerations, fostering a dialogue between technology, society, and artistic expression.
Related Important Terms
Algorithmic Aesthetics
Contemporary art encompasses diverse practices emphasizing conceptual and cultural contexts, while generative art leverages algorithmic aesthetics to create dynamic, evolving visuals through coded systems and autonomous processes. Algorithmic aesthetics in generative art prioritize computational rules and mathematical structures, producing unique, often unpredictable outputs that challenge traditional notions of authorship and creativity.
AI-Curated Exhibitions
AI-curated exhibitions in contemporary art showcase the dynamic interplay between human creativity and machine intelligence, highlighting how generative art algorithms produce novel visuals while redefining artistic authorship. These exhibitions leverage deep learning models to select and arrange artworks, offering fresh perspectives that challenge traditional curation methods and expand the boundaries of cultural expression.
Procedural Creativity
Contemporary art explores diverse materials and concepts, while generative art leverages algorithmic processes to autonomously produce visual forms, emphasizing procedural creativity as a core mechanism. This procedural creativity employs coding, algorithms, and computational systems to generate evolving, non-static artworks that continuously redefine artistic authorship and creative expression.
Digital Vernacular
Contemporary art explores diverse digital vernaculars through human creativity and cultural narratives, while generative art employs algorithmic processes to produce evolving digital expressions. The intersection of these forms highlights a dynamic dialogue between traditional artistic intent and machine-driven innovation in the digital age.
Post-Internet Art
Post-Internet Art reflects the digital condition of contemporary society, emphasizing the impact of the internet on visual culture and social interactions, while Generative Art utilizes algorithmic processes and artificial intelligence to create dynamic, evolving artworks. Both art forms challenge traditional boundaries by integrating technology, but Post-Internet Art critiques digital life and consumerism, whereas Generative Art explores the creative autonomy of machines.
Blockchain Provenance
Contemporary art increasingly integrates blockchain provenance to certify authenticity and track ownership, enhancing transparency in art transactions. Generative art leverages blockchain technology to create unique, algorithmically-produced pieces with verifiable provenance, ensuring original authorship and preventing forgery in digital and physical formats.
Human-Machine Collaboration
Contemporary art often emphasizes human creativity and emotional expression, while generative art relies on algorithms and machine processes to create evolving visual forms. This human-machine collaboration redefines artistic authorship by blending human intent with computational innovation, resulting in dynamic artworks that challenge traditional boundaries.
Quantum Generative Processes
Quantum generative processes in contemporary art utilize quantum computing principles to create complex, unpredictable visual patterns, pushing the boundaries of generative art beyond traditional algorithmic methods. This fusion enables artists to explore new dimensions of creativity by harnessing quantum superposition and entanglement, resulting in artworks with novel structural and aesthetic properties.
NFT-Integrated Installations
NFT-integrated installations merge contemporary art's experiential focus with generative art's algorithmic creativity, creating dynamic, blockchain-verified digital artworks. These installations redefine ownership and interactivity by embedding unique NFTs within evolving visual and spatial compositions, offering collectors provable scarcity alongside immersive artistic experiences.
Responsive Media Objects
Contemporary art encompasses diverse media and often incorporates interactive elements, but generative art specifically utilizes algorithms and computational processes to create responsive media objects that evolve based on real-time data or viewer interaction. Responsive media objects in generative art blur the boundary between creator and audience, enabling dynamic, ever-changing artworks that adapt to environmental inputs and user engagement.
Contemporary Art vs Generative Art Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com