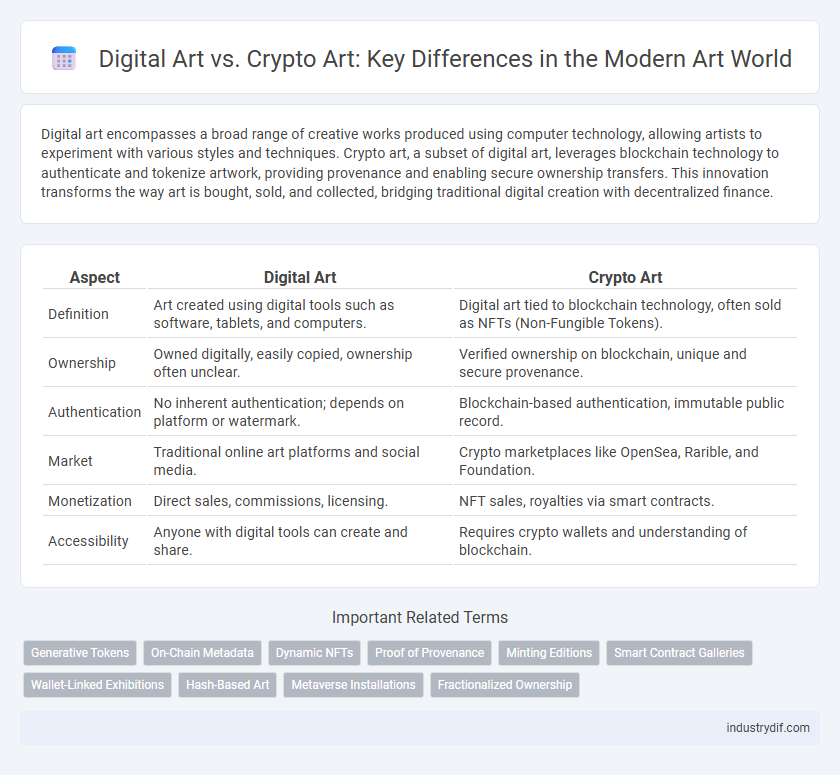
Digital art encompasses a broad range of creative works produced using computer technology, allowing artists to experiment with various styles and techniques. Crypto art, a subset of digital art, leverages blockchain technology to authenticate and tokenize artwork, providing provenance and enabling secure ownership transfers. This innovation transforms the way art is bought, sold, and collected, bridging traditional digital creation with decentralized finance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Digital Art | Crypto Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art created using digital tools such as software, tablets, and computers. | Digital art tied to blockchain technology, often sold as NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens). |
| Ownership | Owned digitally, easily copied, ownership often unclear. | Verified ownership on blockchain, unique and secure provenance. |
| Authentication | No inherent authentication; depends on platform or watermark. | Blockchain-based authentication, immutable public record. |
| Market | Traditional online art platforms and social media. | Crypto marketplaces like OpenSea, Rarible, and Foundation. |
| Monetization | Direct sales, commissions, licensing. | NFT sales, royalties via smart contracts. |
| Accessibility | Anyone with digital tools can create and share. | Requires crypto wallets and understanding of blockchain. |
Defining Digital Art: Origins and Evolution
Digital art originated in the 1960s with computer-generated images and evolved through advancements in software and hardware, becoming a broad category encompassing everything from digital painting to interactive media. As technology progressed, artists embraced digital tools to create, manipulate, and distribute artworks widely without physical constraints. This evolution paved the way for new artistic expressions, setting the foundation for subsequent developments like crypto art and blockchain-based digital ownership.
Understanding Crypto Art: Blockchain’s Impact on Creativity
Crypto art leverages blockchain technology to authenticate and verify the originality of digital artworks, creating unique, provably scarce assets known as NFTs (non-fungible tokens). This innovation transforms traditional digital art by enabling artists to securely monetize and distribute their creations directly to global audiences without intermediaries. Blockchain's transparency and immutability enhance provenance tracking, ensuring artists retain control over their work and receive royalties through smart contracts.
Key Differences Between Digital Art and Crypto Art
Digital art encompasses a broad range of artworks created using digital technologies, typically stored and displayed as standard image files, whereas crypto art is a subset of digital art that utilizes blockchain technology to establish provenance and ownership through non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Unlike traditional digital art, crypto art provides verifiable scarcity and authenticity, enabling artists to monetize their work within decentralized marketplaces. The key differences lie in the methods of distribution, ownership verification, and the integration of blockchain protocols unique to crypto art.
Authenticity and Ownership in Digital vs Crypto Art
Digital art authenticity relies on metadata, watermarks, and digital signatures to verify originality, but these methods can be vulnerable to duplication and forgery. Crypto art, secured by blockchain technology, offers immutable proof of ownership and provenance through unique non-fungible tokens (NFTs), ensuring transparent and verifiable authenticity. The decentralized ledger records every transaction and transfer, providing collectors with indisputable ownership rights compared to traditional digital verification systems.
Marketplaces: Selling and Buying Digital Art vs Crypto Art
Digital art marketplaces like Etsy and ArtStation offer artists platforms to sell traditional digital creations directly to buyers, emphasizing accessibility and broad audience reach. Crypto art, traded on blockchain-based marketplaces such as OpenSea and Rarible, leverages NFTs to guarantee provenance and scarcity, transforming ownership verification and resale royalties. Market dynamics reveal higher volatility and speculative pricing in crypto art markets compared to the relatively stable valuations in conventional digital art platforms.
Copyright, Licensing, and Intellectual Property Concerns
Digital art spans a broad range of creative works produced or enhanced through digital technology, where copyright laws generally protect the original artwork and grant artists licensing control over reproduction and distribution. Crypto art, a subset of digital art tied to blockchain technology, introduces unique intellectual property challenges due to the decentralized nature of non-fungible tokens (NFTs), which authenticate ownership but do not inherently transfer copyright unless explicitly stated. Artists must navigate licensing agreements carefully to ensure that rights are preserved and that digital or crypto art buyers understand the scope of their usage, highlighting ongoing complexities in intellectual property enforcement within digital and crypto art markets.
Community and Culture: Digital Art vs Crypto Art Ecosystems
Digital Art ecosystems thrive on diverse online communities that celebrate creativity across multiple platforms, fostering open collaboration without central gatekeepers. Crypto Art communities are tightly knit around blockchain technology and NFT marketplaces, where provenance and ownership verification play a crucial role in cultural value and artist empowerment. The cultural dynamics of Crypto Art emphasize scarcity and digital asset trading, contrasting with Digital Art's broader, more inclusive network of shared artistic expression and accessibility.
Environmental Considerations: Sustainability and NFTs
Digital art creation typically involves software and hardware with minimal direct environmental impact, whereas crypto art, often tied to NFTs, depends on blockchain technology that can consume significant energy due to proof-of-work mechanisms. The minting and trading of NFTs on platforms like Ethereum contribute to carbon emissions, raising sustainability concerns within the art community. Emerging solutions such as proof-of-stake blockchains and layer-2 scaling aim to reduce the ecological footprint of crypto art while maintaining decentralization and provenance features.
Investment Potential: Value Trends in Digital and Crypto Art
Digital art has demonstrated steady appreciation as artists leverage technology for innovative creations, attracting traditional collectors and institutional investors. Crypto art, often represented as NFTs on blockchain platforms, exhibits volatile but sometimes explosive value growth driven by scarcity, provenance, and market hype. While digital art investment relies on artistic merit and market recognition, crypto art's value trends are heavily influenced by blockchain adoption, rarity, and investor sentiment.
The Future of Artistic Expression: Digital Art and Crypto Art Integration
Digital art and crypto art are increasingly converging, shaping the future of artistic expression by leveraging blockchain technology to authenticate and monetize digital creations securely. The integration enables artists to reach global audiences, establish provenance through NFTs, and unlock new revenue streams, transforming traditional art markets. This fusion promotes innovation in digital creativity, fostering decentralized art communities and novel interactive experiences.
Related Important Terms
Generative Tokens
Generative tokens in digital art use algorithmic processes to create evolving, unique pieces that continuously engage collectors through dynamic visuals and interaction. Crypto art incorporates blockchain technology to verify authenticity and ownership, with generative tokens representing a cutting-edge fusion that enhances provenance and incentivizes creator participation in decentralized art markets.
On-Chain Metadata
Digital art often relies on external servers for metadata storage, which risks loss or manipulation, whereas crypto art utilizes on-chain metadata embedded directly within blockchain transactions, ensuring permanence and authenticity. This on-chain approach enhances provenance transparency and secures artists' rights through immutable records accessible to collectors and platforms.
Dynamic NFTs
Dynamic NFTs in digital art provide an innovative platform where artwork evolves over time or reacts to external data, offering a more interactive and mutable experience compared to traditional static digital art. Crypto art leverages blockchain technology to authenticate ownership and provenance, but dynamic NFTs push these boundaries by enabling artists to create living pieces that change based on real-world events or user engagement.
Proof of Provenance
Digital art relies on traditional metadata and watermarking to establish authenticity, while crypto art uses blockchain technology to provide immutable proof of provenance and ownership. This decentralized ledger system ensures transparent, tamper-proof verification, enhancing trust and value in digital creations.
Minting Editions
Digital art editions are typically minted as high-resolution files distributed without blockchain verification, allowing unlimited reproductions and flexible ownership. Crypto art editions utilize blockchain technology to mint limited, verifiable tokens as unique digital assets, ensuring scarcity and provenance through smart contracts on platforms like Ethereum.
Smart Contract Galleries
Smart Contract Galleries revolutionize the display and ownership of digital art by leveraging blockchain technology to authenticate and securely trade pieces without intermediaries. These platforms enhance transparency and provenance in Crypto Art, distinguishing it from traditional Digital Art through embedded smart contracts that automate royalties and ownership transfers.
Wallet-Linked Exhibitions
Wallet-linked exhibitions in digital art enable artists and collectors to showcase pieces tied directly to blockchain wallets, ensuring provenance and ownership transparency. Crypto art leverages this technology by integrating NFTs, facilitating unique displays where each artwork's authenticity and transaction history are verifiable through decentralized ledger systems.
Hash-Based Art
Hash-based art leverages cryptographic hash functions to create unique, verifiable digital artworks that emphasize data integrity and provenance within the crypto art space. This method contrasts traditional digital art by embedding immutable hashes directly into the artwork's metadata, ensuring authenticity and resistance to forgery.
Metaverse Installations
Digital art encompasses a broad spectrum of creative works produced or enhanced through digital technology, often showcased in immersive metaverse installations that blur the line between physical and virtual realities. Crypto art, a subset of digital art authenticated through blockchain technology as non-fungible tokens (NFTs), leverages metaverse spaces to offer exclusive, tradeable art experiences that emphasize provenance and ownership within virtual exhibitions.
Fractionalized Ownership
Digital art encompasses a broad range of artworks created using digital technology, while crypto art specifically refers to digital artworks authenticated and traded on blockchain platforms. Fractionalized ownership in crypto art allows multiple investors to hold shares of a single digital asset through tokens, enabling increased accessibility and liquidity compared to traditional digital art ownership.
Digital Art vs Crypto Art Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com