Painting captures artistic expression through color, texture, and brushwork on a flat surface, evoking emotion and storytelling. Data sculpture transforms complex information into three-dimensional physical forms, merging art with technology to visualize abstract data. Both mediums challenge perception but differ in their approach to representing reality and interpretation.
Table of Comparison
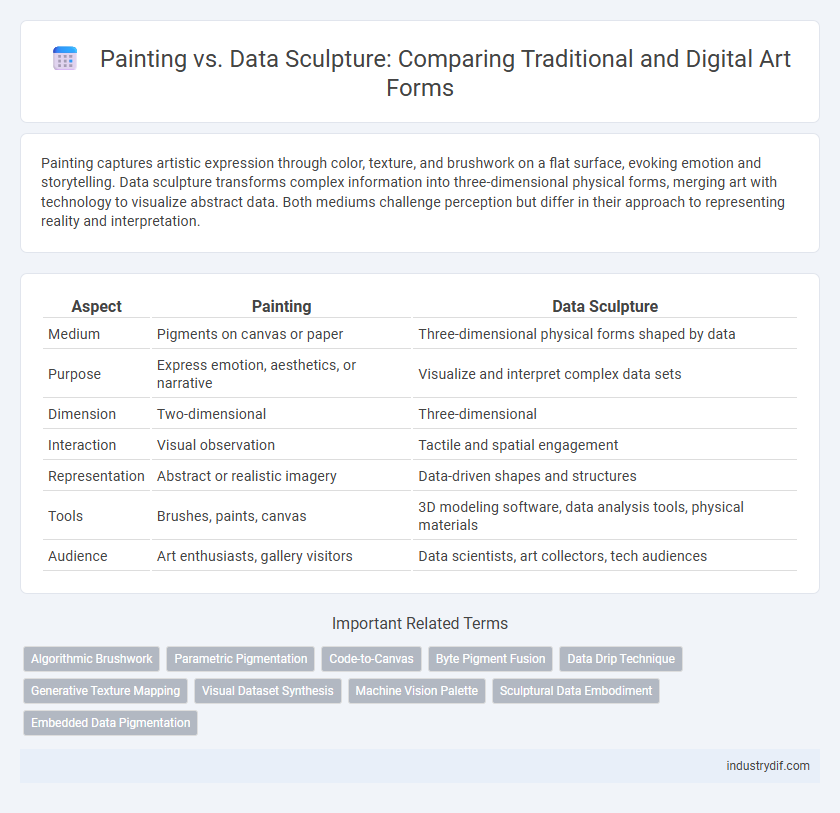
| Aspect | Painting | Data Sculpture |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Pigments on canvas or paper | Three-dimensional physical forms shaped by data |
| Purpose | Express emotion, aesthetics, or narrative | Visualize and interpret complex data sets |
| Dimension | Two-dimensional | Three-dimensional |
| Interaction | Visual observation | Tactile and spatial engagement |
| Representation | Abstract or realistic imagery | Data-driven shapes and structures |
| Tools | Brushes, paints, canvas | 3D modeling software, data analysis tools, physical materials |
| Audience | Art enthusiasts, gallery visitors | Data scientists, art collectors, tech audiences |
Understanding Painting: Traditional Art Explored
Traditional painting emphasizes the use of pigments on surfaces like canvas to convey emotions, narratives, and cultural expressions through color, texture, and composition. Techniques such as oil, watercolor, and acrylic highlight the artist's skill in manipulating light and shadow to create depth and realism. Understanding painting requires recognizing its historical evolution, from classical realism to abstract expressionism, reflecting societal changes and artistic innovation.
What is Data Sculpture? Definition and Origins
Data sculpture is an innovative art form that transforms complex datasets into three-dimensional physical representations, merging aesthetics with information visualization. Originating from the intersection of digital technology and contemporary art, data sculpture emerged in the early 21st century as artists sought new ways to interpret and materialize abstract data patterns. This practice redefines traditional sculpture by embedding data-driven narratives into tangible structures, expanding the boundaries of both art and data analysis.
Key Materials: Brushes vs Algorithms
Painting relies on brushes crafted from natural or synthetic fibers to manipulate pigments on a canvas, enabling tactile and expressive strokes that capture the artist's intent. Data sculpture employs algorithms as its primary material, transforming vast datasets into three-dimensional forms that reveal patterns and insights invisible to the naked eye. While brushes shape physical textures and colors, algorithms generate dynamic structures and interactive experiences grounded in computational logic.
Techniques in Painting vs Data Sculpture
Painting techniques rely on brushstrokes, color mixing, layering, and texture manipulation to create visual narratives on canvas. Data sculpture employs digital algorithms, 3D modeling, and interactive elements to transform complex datasets into tangible, spatial forms. While painting emphasizes manual skill and sensory perception, data sculpture integrates technology and data visualization to convey meaning through dimensionality and interactivity.
Role of Visual Storytelling in Both Forms
Visual storytelling in painting captures emotions and narratives through color, texture, and composition to evoke personal and cultural meanings. In data sculpture, visual storytelling translates complex datasets into tangible, spatial forms, enabling viewers to perceive patterns and insights physically. Both forms rely on visual elements to communicate stories, with painting emphasizing subjective interpretation and data sculpture highlighting objective information.
Interactivity: Static Paintings vs Dynamic Data Sculptures
Static paintings offer a fixed visual experience, engaging viewers through color, texture, and composition without altering over time. Dynamic data sculptures incorporate real-time data, enabling interactive and evolving representations that respond to environmental or user input. This interactivity transforms passive observation into an immersive experience, merging technology with artistic expression.
Audience Engagement and Interpretation
Painting captivates audiences through rich visual narratives and emotional depth, allowing viewers to interpret themes subjectively based on color, texture, and composition. Data sculpture, by contrast, engages audiences through interactive and immersive experiences that reveal patterns and insights from complex datasets, encouraging analytical interpretation and active participation. Both mediums foster unique modes of audience engagement, with painting emphasizing aesthetic appreciation and data sculpture promoting intellectual exploration.
Preservation and Longevity: Canvas vs Code
Canvas paintings offer centuries-old preservation with physical durability and natural aging processes that enhance artistic value, supported by climate-controlled environments and restoration techniques. Data sculptures rely on digital code, which faces challenges of software obsolescence, hardware dependency, and data corruption, necessitating continuous updates and migration to maintain longevity. Preservation strategies for data sculptures include using standardized file formats, digital archiving platforms, and robust cybersecurity measures to ensure the artwork's survival in evolving technological landscapes.
Influence of Technology on Art Practices
Advancements in digital tools and software have transformed traditional painting techniques, enabling artists to integrate augmented reality and interactive elements into their canvases. Data sculpture, emerging from big data visualization, leverages 3D printing and algorithmic design to create tangible representations of abstract information. This technological fusion expands artistic expression by merging sensory experience with empirical data, redefining how contemporary art communicates meaning.
Future Trends: Where Painting Meets Data Sculpture
Emerging trends in the art world showcase a fusion where traditional painting techniques intersect with data sculpture, creating hybrid forms that merge visual storytelling with interactive data visualization. Innovations in digital technology enable artists to embed complex datasets within layered paint textures, transforming canvases into dynamic, information-rich experiences. Future artworks will increasingly leverage algorithms and real-time data feeds, blurring boundaries between static paintings and evolving data sculptures, pushing the frontier of contemporary artistic expression.
Related Important Terms
Algorithmic Brushwork
Algorithmic brushwork bridges traditional painting and data sculpture by using code-driven processes to generate dynamic visual patterns that mimic brushstrokes, blending artistic intuition with computational precision. This fusion allows artists to explore complex data sets through expressive, textured surfaces that evolve beyond static images into interactive, algorithmically-enhanced artworks.
Parametric Pigmentation
Parametric pigmentation in painting manipulates color through algorithmic adjustments to create dynamic visual textures, contrasting with data sculptures where pigmentation encodes datasets into three-dimensional forms. This fusion of computational design and artistic expression highlights the evolving interplay between traditional brushstrokes and data-driven aesthetics in contemporary art.
Code-to-Canvas
Code-to-Canvas innovation bridges traditional painting techniques with data sculpture by transforming complex datasets into visual art through algorithmic processing and digital rendering. This fusion enables artists to create dynamic, interactive canvases that embody both aesthetic expression and informative data visualization.
Byte Pigment Fusion
Byte Pigment Fusion redefines artistic expression by integrating digital data streams with traditional painting mediums, creating multidimensional canvases that translate binary code into vivid pigment patterns. This synergy between painting and data sculpture bridges tactile brushwork and immersive data visualization, pushing boundaries in contemporary art innovation.
Data Drip Technique
Data Drip Technique in painting involves layering vibrant pigments to capture fluid motion, contrasting with data sculpture's three-dimensional form which visualizes complex datasets through spatial arrangements. This method emphasizes dynamic paint application to translate abstract data patterns into expressive, two-dimensional art.
Generative Texture Mapping
Generative texture mapping in painting enhances surface complexity by algorithmically applying patterns that evolve with brushstrokes, creating dynamic visual depth. In contrast, data sculpture uses generative texture mapping to transform abstract datasets into three-dimensional tactile forms, revealing hidden structures through layered digital textures.
Visual Dataset Synthesis
Visual dataset synthesis in painting leverages traditional techniques to create expressive, hand-crafted imagery rich in texture and emotion, while data sculpture employs computational algorithms to transform complex datasets into three-dimensional, interactive forms that reveal patterns and insights. Both approaches redefine the boundaries of visual art by integrating subjective creativity with objective data representation.
Machine Vision Palette
Painting traditionally captures visual narratives through brushstrokes and color blending, while data sculpture leverages machine vision palettes to translate complex datasets into three-dimensional forms. Machine vision palettes analyze color and texture patterns algorithmically, enabling artists to create dynamic, data-driven sculptures that visualize information beyond two-dimensional constraints.
Sculptural Data Embodiment
Sculptural data embodiment transforms abstract datasets into tangible three-dimensional forms, enabling immersive interaction and enhanced comprehension of complex information patterns. This approach contrasts with traditional painting by prioritizing spatial representation and multisensory engagement, bridging art and data visualization through materiality and form.
Embedded Data Pigmentation
Embedded data pigmentation in painting integrates layers of color infused with informational patterns, creating a tactile narrative that merges traditional artistry with digital encoding. In contrast, data sculpture transforms raw datasets into three-dimensional forms, emphasizing spatial relationships and materiality to represent information, prioritizing tangible interaction over pigment-based expression.
Painting vs Data Sculpture Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com