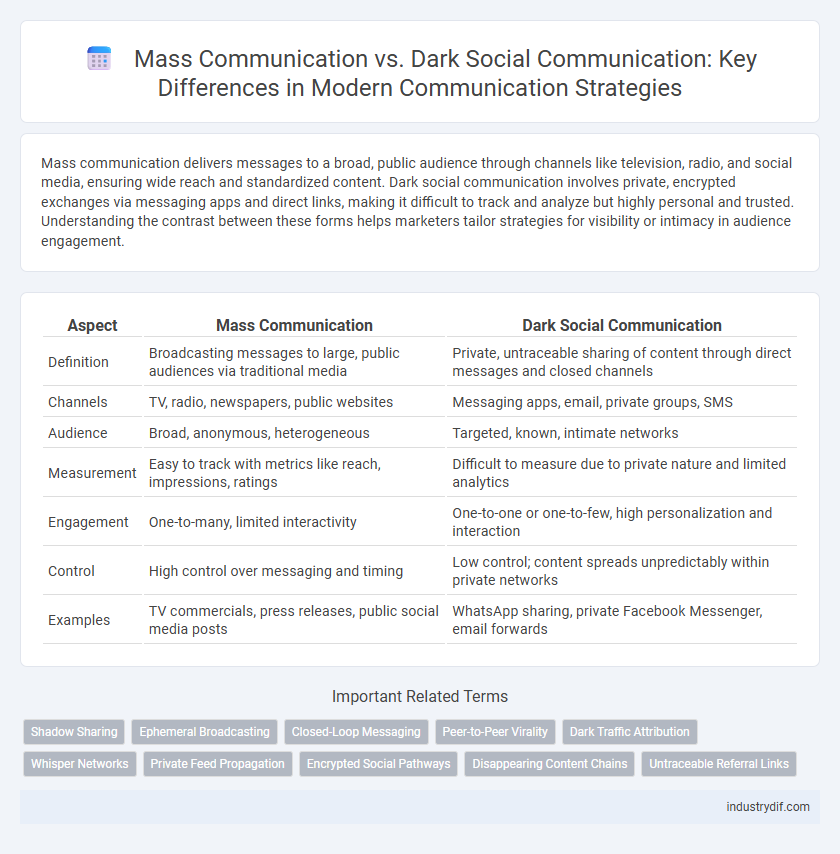
Mass communication delivers messages to a broad, public audience through channels like television, radio, and social media, ensuring wide reach and standardized content. Dark social communication involves private, encrypted exchanges via messaging apps and direct links, making it difficult to track and analyze but highly personal and trusted. Understanding the contrast between these forms helps marketers tailor strategies for visibility or intimacy in audience engagement.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mass Communication | Dark Social Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Broadcasting messages to large, public audiences via traditional media | Private, untraceable sharing of content through direct messages and closed channels |
| Channels | TV, radio, newspapers, public websites | Messaging apps, email, private groups, SMS |
| Audience | Broad, anonymous, heterogeneous | Targeted, known, intimate networks |
| Measurement | Easy to track with metrics like reach, impressions, ratings | Difficult to measure due to private nature and limited analytics |
| Engagement | One-to-many, limited interactivity | One-to-one or one-to-few, high personalization and interaction |
| Control | High control over messaging and timing | Low control; content spreads unpredictably within private networks |
| Examples | TV commercials, press releases, public social media posts | WhatsApp sharing, private Facebook Messenger, email forwards |
Defining Mass Communication
Mass communication refers to the process of disseminating information to a large, diverse audience through traditional media channels such as television, radio, newspapers, and digital platforms. It involves one-to-many communication that is often centralized and publicly accessible, aiming to reach a broad spectrum of people simultaneously. This contrasts sharply with dark social communication, which occurs through private channels like messaging apps and emails, making it less visible to public metrics and analytics.
Understanding Dark Social Communication
Dark Social Communication refers to the sharing of content through private channels such as messaging apps, email, and direct messaging, which are not easily tracked by traditional analytics tools. Unlike Mass Communication, which broadcasts messages to a broad audience via public platforms like TV, radio, and social media, Dark Social interactions are more personal and targeted, making them crucial for understanding genuine user engagement and referral traffic. Marketers and communicators must leverage Dark Social insights to capture the full impact of their content distribution and optimize strategies beyond visible metrics.
Key Differences Between Mass Communication and Dark Social
Mass communication involves broadcasting messages to large, diverse audiences through public channels like television, radio, and social media platforms, emphasizing reach and broad visibility. Dark social communication occurs through private, untraceable channels such as encrypted messaging apps, email, and direct sharing, characterized by personalized and discreet interactions. Key differences include transparency, measurement ability, and audience engagement; mass communication offers measurable metrics and public feedback, while dark social limits tracking but fosters trust and deeper personal connections.
Channels Used in Mass Communication
Mass communication primarily relies on traditional channels such as television, radio, newspapers, and magazines to disseminate information to a broad audience. Digital platforms like social media, websites, and streaming services have also become integral channels, enhancing the reach and immediacy of mass communication. These channels enable organizations to broadcast messages simultaneously to millions, contrasting with the private, peer-to-peer sharing typical of dark social communication.
The Role of Messaging Apps in Dark Social Communication
Messaging apps play a pivotal role in dark social communication by enabling private, one-to-one or small group conversations that evade traditional tracking methods used in mass communication channels. Platforms like WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, and Telegram facilitate seamless sharing of content, making it challenging for marketers to attribute traffic sources or measure engagement accurately. This shift emphasizes the need for advanced analytics and innovative strategies to understand audience behavior within these encrypted, private messaging ecosystems.
Audience Reach: Mass vs. Dark Social
Mass communication leverages traditional and digital media platforms to reach large, diverse audiences at scale, utilizing channels such as television, radio, and social networks to broadcast messages widely. Dark social communication occurs through private channels like messaging apps, email, and encrypted platforms, resulting in more limited but highly targeted and intimate audience engagement. While mass communication prioritizes quantity and broad visibility, dark social emphasizes quality interactions and trust-driven sharing within smaller, closed communities.
Measuring Engagement in Mass and Dark Social Communication
Measuring engagement in mass communication relies on quantifiable metrics such as reach, impressions, click-through rates, and audience demographics captured through analytics platforms. Dark social communication, characterized by private sharing via messaging apps, email, and closed groups, presents challenges in tracking due to the lack of visible engagement data and reliance on indirect attribution methods like link tagging and surveys. Effective measurement strategies for dark social require integrating qualitative insights and advanced tracking technologies to capture its impact on brand awareness and customer interactions.
Privacy and Anonymity Concerns
Mass communication distributes information to broad audiences through public channels, often exposing user data to tracking and profiling, which raises significant privacy concerns. Dark social communication occurs via private channels like messaging apps and email, offering greater anonymity and control over shared content by limiting data exposure to third parties. Privacy-focused users prefer dark social methods as they reduce digital footprints and minimize risks associated with data breaches and surveillance.
Brand Strategies for Navigating Both Channels
Mass communication leverages broad channels like television, radio, and social media ads to amplify brand visibility and shape public perception on a large scale. Dark social communication, encompassing private messaging apps, email, and closed groups, demands brands implement personalized, trust-building strategies to engage users in authentic conversations. Effective brand strategies integrate data analytics and content customization to balance mass reach with the intimacy of dark social interactions, optimizing audience engagement across both platforms.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Mass and Dark Social Communication
Mass communication continues to evolve with the rise of AI-driven personalization and immersive technologies like augmented reality, enhancing audience engagement on public platforms. Dark social communication, characterized by private sharing via messaging apps and encrypted channels, is gaining prominence as users seek privacy and authenticity, challenging traditional metrics and advertising models. Future trends indicate a convergence where mass communication integrates secure, personalized dark social elements to create more intimate yet scalable conversations.
Related Important Terms
Shadow Sharing
Mass communication reaches broad audiences through public channels like TV and social media, whereas dark social communication involves private sharing via encrypted messages and closed groups, often termed shadow sharing. Shadow sharing significantly influences consumer behavior and content virality by bypassing traditional analytics and tracking tools.
Ephemeral Broadcasting
Mass communication leverages broad, one-to-many channels like television and radio to disseminate information rapidly, while dark social communication involves private, ephemeral sharing through direct messages and closed groups, complicating tracking and measurement. Ephemeral broadcasting in dark social emphasizes fleeting, time-limited content distribution, enhancing user privacy but challenging traditional mass communication analytics.
Closed-Loop Messaging
Mass communication reaches broad audiences through public channels like television, radio, and social media platforms, generating measurable engagement data for closed-loop messaging strategies. Dark social communication occurs in private, encrypted spaces such as messaging apps and email, posing challenges for tracking but offering high trust and personalized interactions critical for targeted marketing efforts.
Peer-to-Peer Virality
Mass communication leverages broad channels like television, radio, and social media platforms to reach vast audiences simultaneously, emphasizing one-to-many messaging for wide-scale brand visibility. Dark social communication relies on private, peer-to-peer sharing through messaging apps and closed networks, driving organic virality via trusted personal connections and increased message authenticity.
Dark Traffic Attribution
Dark social communication refers to the sharing of content through private channels such as messaging apps, email, and direct messaging, which eludes traditional web analytics and creates significant challenges for mass communication attribution. Accurate dark traffic attribution requires advanced tracking techniques that analyze URL parameters and user behavior patterns to uncover hidden referral sources and better inform content strategies.
Whisper Networks
Whisper networks operate within dark social communication, leveraging private, encrypted channels to share sensitive information discreetly, contrasting with mass communication's broad, public broadcasting through mainstream media and social platforms. These covert networks enable targeted dissemination of critical insights, enhancing confidentiality and trust among specific social groups often excluded from mass communication's wide reach.
Private Feed Propagation
Mass communication relies on public channels like TV, radio, and social media platforms to disseminate information broadly, whereas dark social communication occurs through private feeds such as encrypted messaging apps and direct shares, making content propagation less visible but highly personalized and influential. Private feed propagation leverages intimate networks to amplify messages via closed groups, direct messages, and private communities, resulting in organic reach that often outperforms traditional mass communication in engagement and trust.
Encrypted Social Pathways
Mass communication relies on broad, public channels such as television, radio, and social media platforms to disseminate information widely, whereas dark social communication involves private, encrypted social pathways like messaging apps and email that enable secure, untraceable exchanges between individuals. Encrypted social pathways prioritize user privacy and data security, limiting tracking and analytics while fostering direct, confidential interactions that contrast with the open visibility of mass communication channels.
Disappearing Content Chains
Mass communication relies on broad distribution channels such as television and social media platforms, creating permanent or widely archived content chains that can be tracked and analyzed. In contrast, dark social communication involves private messaging apps and disappearing content chains that bypass public visibility, making measurement and attribution of engagement significantly more challenging for marketers.
Untraceable Referral Links
Mass communication relies on traceable referral links to measure audience reach across platforms, whereas dark social communication uses untraceable referral links that prevent marketers from tracking user engagement and sharing behaviors. This lack of transparency in dark social channels significantly challenges the attribution of traffic sources and the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
Mass Communication vs Dark Social Communication Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com