Armored vehicles provide robust physical barriers that absorb and deflect ballistic impacts, ensuring crew safety through reinforced hulls and materials. Active Protection Systems (APS) enhance defense by detecting and intercepting incoming threats such as rockets and missiles before they reach the vehicle. Combining armored vehicles with APS technology creates a multi-layered defense strategy, maximizing survivability on the battlefield.
Table of Comparison
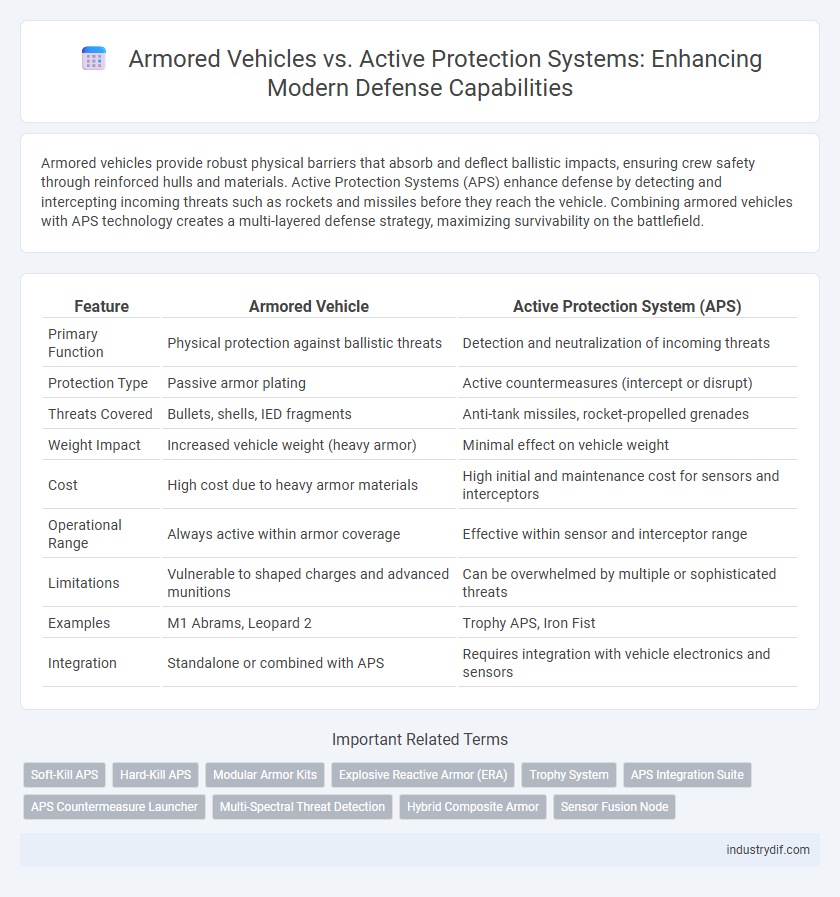
| Feature | Armored Vehicle | Active Protection System (APS) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Physical protection against ballistic threats | Detection and neutralization of incoming threats |
| Protection Type | Passive armor plating | Active countermeasures (intercept or disrupt) |
| Threats Covered | Bullets, shells, IED fragments | Anti-tank missiles, rocket-propelled grenades |
| Weight Impact | Increased vehicle weight (heavy armor) | Minimal effect on vehicle weight |
| Cost | High cost due to heavy armor materials | High initial and maintenance cost for sensors and interceptors |
| Operational Range | Always active within armor coverage | Effective within sensor and interceptor range |
| Limitations | Vulnerable to shaped charges and advanced munitions | Can be overwhelmed by multiple or sophisticated threats |
| Examples | M1 Abrams, Leopard 2 | Trophy APS, Iron Fist |
| Integration | Standalone or combined with APS | Requires integration with vehicle electronics and sensors |
Introduction to Armored Vehicles and Active Protection Systems
Armored vehicles are military transport units fortified with heavy armor plating to provide protection against ballistic threats, explosive devices, and shrapnel on the battlefield. Active Protection Systems (APS) are advanced defense mechanisms integrated into armored vehicles, designed to detect, intercept, and neutralize incoming anti-tank weapons such as RPGs and guided missiles before they strike. The integration of APS enhances survivability by complementing the passive armor, reducing the vulnerability of armored vehicles against modern anti-armor threats.
Evolution of Armored Vehicle Technology
The evolution of armored vehicle technology has been significantly shaped by the integration of Active Protection Systems (APS), which enhance survivability against modern anti-tank threats such as guided missiles and rocket-propelled grenades. These systems utilize radar, sensors, and interceptors to detect and neutralize incoming projectiles before impact, transforming traditional armor from passive defense to dynamic threat engagement. The continuous development in APS technology, including soft-kill and hard-kill measures, is driving a paradigm shift in armored vehicle design and battlefield strategy.
Fundamentals of Active Protection Systems (APS)
Active Protection Systems (APS) enhance armored vehicle survivability by detecting, tracking, and neutralizing incoming threats such as anti-tank guided missiles and rocket-propelled grenades before impact. Key components include radar or infrared sensors for threat acquisition, a central processing unit for threat evaluation, and countermeasures like kinetic interceptors or directed energy to disrupt or destroy the threat. APS integration significantly improves armored vehicle defense capabilities, reducing vulnerability against modern anti-armor weapons.
Key Components of Modern Armored Vehicles
Modern armored vehicles integrate advanced armor plating, high-performance engines, and sophisticated communication systems to enhance battlefield survivability and operational efficiency. Key components include reinforced hulls made from composite or reactive armor, sensor arrays for situational awareness, and modular weapon stations for versatile engagement capabilities. Active Protection Systems (APS) complement these features by employing radar detection, interception mechanisms, and countermeasure deployment to neutralize incoming threats before impact.
APS: Types and Operating Principles
Active Protection Systems (APS) in armored vehicles include hard-kill and soft-kill types; hard-kill APS intercept and destroy incoming threats like anti-tank guided missiles using kinetic countermeasures, while soft-kill APS employ electronic warfare techniques to disrupt or mislead target guidance. Operating principles of APS rely on radar, infrared, or laser sensors to detect incoming projectiles and activate countermeasures within milliseconds, ensuring the armored vehicle's survivability against modern anti-armor threats. Integration of APS with vehicle sensors enhances situational awareness and enables real-time threat neutralization, reducing vulnerability on the battlefield.
Comparative Analysis: Passive Armor vs Active Defense
Passive armor relies on thick, reinforced materials like composite ceramics and steel to absorb and deflect kinetic and explosive threats, offering consistent physical protection but adding significant weight. Active Protection Systems (APS) use radar and sensors to detect incoming projectiles and intercept them with countermeasures, greatly enhancing survivability against modern anti-tank guided missiles and RPGs without substantially increasing vehicle weight. While passive armor provides a reliable baseline defense, APS offers a proactive, adaptive layer of protection that addresses evolving battlefield threats more efficiently.
Integration Challenges: APS on Legacy Armored Platforms
Integrating Active Protection Systems (APS) on legacy armored vehicles presents significant challenges due to limited onboard power supply, restricted space for sensor and interceptor installation, and compatibility issues with existing vehicle electronics and fire control systems. These constraints often necessitate extensive vehicle modifications, increasing costs and deployment timelines while potentially impacting vehicle mobility and armor integrity. Effective retrofitting demands tailored engineering solutions to balance APS efficacy with the operational parameters of older armored platforms.
Cost-Benefit Considerations in Defense Procurement
Armored vehicles offer robust passive protection with proven durability on the battlefield, but come with high production and maintenance costs that strain defense budgets. Active Protection Systems (APS) provide dynamic threat interception capabilities at a comparatively lower weight and can be integrated with existing platforms, potentially reducing long-term expenses. Evaluating cost-benefit in defense procurement requires analyzing lifecycle expenditures, operational effectiveness, and adaptability against evolving threats to optimize investment in armored protection solutions.
Recent Innovations in Vehicle Survivability
Recent innovations in vehicle survivability emphasize the integration of Active Protection Systems (APS) with advanced armored vehicles to counter emerging threats like anti-tank guided missiles and rocket-propelled grenades. Modern APS employ radar and infrared sensors to detect and intercept incoming projectiles milliseconds before impact, significantly enhancing the defensive capacity of armored platforms. These technological advancements reduce crew casualties and extend mission capabilities in contested environments, marking a pivotal evolution in armored vehicle defense strategies.
Future Trends in Armored Protection and APS Deployment
Future trends in armored protection emphasize the integration of advanced Active Protection Systems (APS) that combine radar, sensors, and countermeasures to intercept incoming threats in real time. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning enable APS to improve threat detection accuracy and response speed, significantly enhancing vehicle survivability on modern battlefields. The deployment of these systems will become more widespread across various armored platforms, shifting the focus from passive armor thickening to dynamic, multi-layered defense strategies.
Related Important Terms
Soft-Kill APS
Soft-Kill Active Protection Systems (APS) enhance armored vehicles' survivability by deploying electronic countermeasures such as infrared jammers and smoke screens to disrupt incoming anti-tank guided missiles (ATGMs) and rocket-propelled grenades (RPGs). Unlike Hard-Kill APS that physically intercept threats, Soft-Kill APS provide stealthy, non-destructive defense, minimizing collateral damage and maintenance while effectively reducing the hit probability on modern armored platforms.
Hard-Kill APS
Hard-Kill Active Protection Systems (APS) enhance armored vehicle survivability by detecting and intercepting incoming threats such as anti-tank guided missiles and rocket-propelled grenades before impact. These systems utilize radar or electro-optical sensors to trigger precise countermeasures, effectively neutralizing projectiles and minimizing vehicle damage in combat scenarios.
Modular Armor Kits
Modular armor kits enhance armored vehicles by providing scalable, mission-adaptable protection against kinetic and explosive threats, allowing rapid upgrades without compromising mobility. Integrating active protection systems with modular armor kits optimizes defense by intercepting projectiles while maintaining vehicle survivability and operational flexibility on the battlefield.
Explosive Reactive Armor (ERA)
Explosive Reactive Armor (ERA) enhances armored vehicle survivability by detonating upon impact, neutralizing the penetration capability of shaped charges and tandem warheads. Integrating ERA with Active Protection Systems (APS) creates a layered defense, combining passive explosive countermeasures with sensor-guided interception to effectively counter anti-tank munitions.
Trophy System
The Trophy Active Protection System enhances armored vehicle survivability by detecting, tracking, and neutralizing incoming anti-tank threats with precision interceptors, significantly reducing vulnerability against RPGs and ATGMs. Integrated on platforms like the Israeli Merkava tank and U.S. combat vehicles, Trophy provides real-time threat response, improving crew safety and battlefield effectiveness.
APS Integration Suite
The APS Integration Suite enhances armored vehicle survivability by seamlessly combining sensors, hard-kill interceptors, and electronic countermeasures into a cohesive defensive network. This integrated system enables real-time threat detection and rapid neutralization, significantly increasing operational effectiveness against modern anti-armor threats.
APS Countermeasure Launcher
Armored vehicles equipped with Active Protection Systems (APS) utilize Countermeasure Launchers to intercept and neutralize incoming threats such as anti-tank guided missiles and rocket-propelled grenades, enhancing survivability on the battlefield. These launchers deploy sensors and interceptors that detect, track, and destroy or deflect projectiles before impact, significantly reducing the effectiveness of enemy munitions against armored platforms.
Multi-Spectral Threat Detection
Armored vehicles integrated with Active Protection Systems (APS) utilize advanced multi-spectral threat detection technologies, combining infrared, ultraviolet, and radar sensors to identify and neutralize incoming projectiles such as RPGs, anti-tank guided missiles, and kinetic energy penetrators in real-time. This fusion of multi-spectral data enhances situational awareness and response accuracy, significantly improving survivability and operational effectiveness on the battlefield.
Hybrid Composite Armor
Hybrid Composite Armor significantly enhances armored vehicle survivability by integrating advanced materials such as ceramics, metal alloys, and polymer composites, providing superior resistance against kinetic energy penetrators and shaped charges. When combined with Active Protection Systems, this advanced armor creates a multi-layered defense, mitigating threats through both passive ballistic protection and real-time interception of incoming projectiles.
Sensor Fusion Node
The integration of a Sensor Fusion Node in armored vehicles significantly enhances threat detection by combining data from radar, infrared, and optical sensors to provide a comprehensive situational awareness picture. This fusion capability allows an Active Protection System to rapidly identify, track, and neutralize incoming projectiles, improving vehicle survivability against anti-tank guided missiles and rocket-propelled grenades.
Armored Vehicle vs Active Protection System Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com