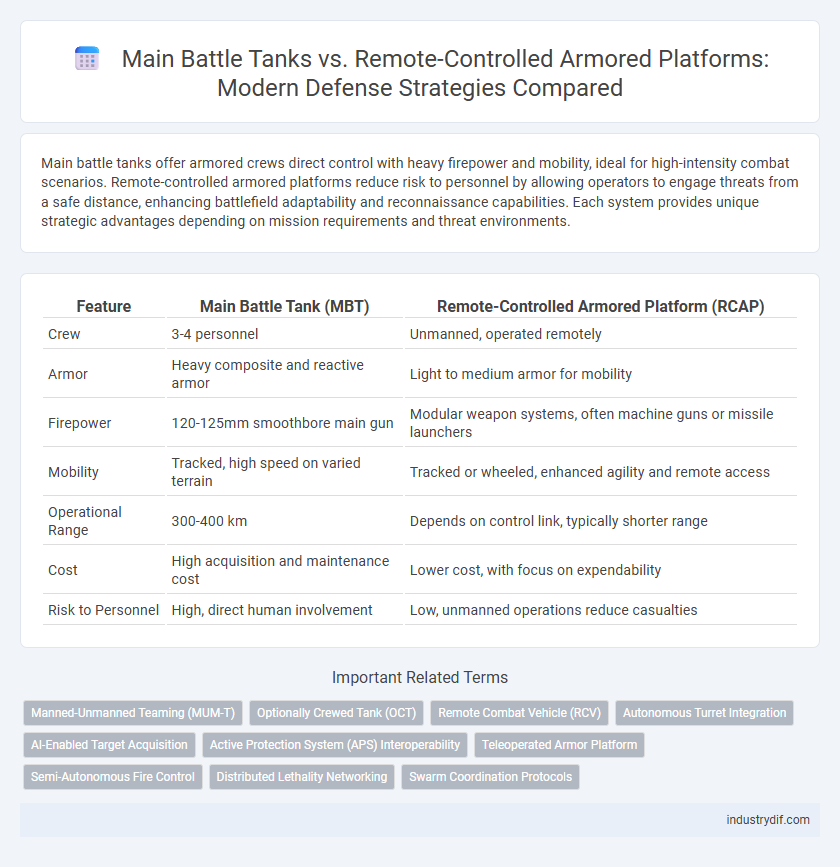
Main battle tanks offer armored crews direct control with heavy firepower and mobility, ideal for high-intensity combat scenarios. Remote-controlled armored platforms reduce risk to personnel by allowing operators to engage threats from a safe distance, enhancing battlefield adaptability and reconnaissance capabilities. Each system provides unique strategic advantages depending on mission requirements and threat environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Main Battle Tank (MBT) | Remote-Controlled Armored Platform (RCAP) |
|---|---|---|
| Crew | 3-4 personnel | Unmanned, operated remotely |
| Armor | Heavy composite and reactive armor | Light to medium armor for mobility |
| Firepower | 120-125mm smoothbore main gun | Modular weapon systems, often machine guns or missile launchers |
| Mobility | Tracked, high speed on varied terrain | Tracked or wheeled, enhanced agility and remote access |
| Operational Range | 300-400 km | Depends on control link, typically shorter range |
| Cost | High acquisition and maintenance cost | Lower cost, with focus on expendability |
| Risk to Personnel | High, direct human involvement | Low, unmanned operations reduce casualties |
Introduction to Modern Armored Warfare
Main battle tanks (MBTs) remain central in modern armored warfare due to their superior firepower, armor protection, and battlefield mobility. Remote-controlled armored platforms enhance situational awareness and reduce risk to personnel by enabling remote operations in high-threat environments. Integrating MBTs with unmanned systems creates a force multiplier effect, optimizing battlefield effectiveness and tactical flexibility.
Definition and Role of Main Battle Tanks (MBTs)
Main Battle Tanks (MBTs) are heavily armored combat vehicles equipped with powerful cannons and advanced targeting systems designed for frontline engagement and breakthrough operations. MBTs serve as the backbone of armored forces, providing a balance of firepower, mobility, and protection to dominate ground combat. In contrast, remote-controlled armored platforms offer tactical flexibility by enabling stand-off reconnaissance and precision strikes without risking crew lives.
Remote-Controlled Armored Platforms: An Overview
Remote-controlled armored platforms offer enhanced operational safety by enabling personnel to conduct high-risk missions without direct exposure to enemy fire. Equipped with advanced sensors, weapon systems, and AI-driven navigation, these platforms provide precision targeting and real-time battlefield data while maintaining a lower logistical footprint compared to main battle tanks. Their versatility in urban warfare and reconnaissance missions complements traditional armored forces, delivering strategic advantages in modern combat environments.
Key Differences in Design Philosophy
Main battle tanks prioritize heavy armor and powerful main guns for direct frontline engagement, emphasizing crew protection and firepower in conventional warfare. Remote-controlled armored platforms focus on modularity, reduced crew risk, and versatile mission profiles, leveraging advanced sensors and remote operation for reconnaissance or asymmetric combat roles. The key difference lies in manned survivability and sustained firepower versus unmanned adaptability and operational flexibility.
Mobility, Firepower, and Protection: Comparative Analysis
Main battle tanks offer superior firepower with high-caliber cannons and advanced targeting systems, while remote-controlled armored platforms rely on precision-guided munitions and modular weaponry for versatile engagement. In terms of mobility, remote-controlled platforms excel with lighter weight and agility, allowing rapid deployment in complex terrains compared to the heavier and slower main battle tanks. Protection-wise, main battle tanks provide robust armor designed to withstand direct hits, whereas remote-controlled platforms prioritize survivability through reduced crew risk and electronic countermeasures rather than heavy armor.
Human Crew vs Autonomous Operation
Main battle tanks rely on human crews providing real-time decision-making, situational awareness, and adaptive tactics critical in dynamic combat environments. Remote-controlled armored platforms leverage autonomous operation, integrating AI-driven sensors and decision algorithms to reduce human risk and enable persistent surveillance in high-threat zones. The balance between human intuition and machine precision defines evolving armored warfare strategies.
Battlefield Applications and Use Cases
Main battle tanks excel in frontline engagements with heavy armor, superior firepower, and crew-operated decision-making, enabling effective area denial and breakthrough maneuvers in conventional warfare. Remote-controlled armored platforms enhance battlefield versatility by providing reconnaissance, force multiplication, and risk mitigation in urban and asymmetric environments without endangering personnel. Integrating these systems improves operational capabilities by balancing direct combat strength with remote tactical flexibility across diverse mission scenarios.
Logistical and Maintenance Considerations
Main battle tanks require extensive logistical support due to their complex mechanical systems, heavy armor, and high fuel consumption, necessitating frequent maintenance and specialized repair crews. Remote-controlled armored platforms benefit from reduced crew-related logistical demands, but they face challenges in maintaining advanced sensor suites, communication links, and electronic warfare components. The trade-off between traditional durability and electronic complexity significantly impacts deployment strategies and sustainment planning in modern defense operations.
Future Trends in Armored Combat
Future trends in armored combat emphasize the integration of remote-controlled armored platforms alongside traditional main battle tanks to enhance battlefield versatility. Advances in autonomous navigation and AI-driven targeting systems enable unmanned platforms to perform high-risk reconnaissance and precision strikes, reducing soldier exposure. Collaborative operations between manned main battle tanks and unmanned vehicles will redefine armored warfare by increasing tactical flexibility and networked battlefield awareness.
Strategic Implications for Military Doctrine
Main battle tanks (MBTs) remain central to armored warfare due to their firepower, armor protection, and battlefield versatility, but the rise of remote-controlled armored platforms introduces new strategic dimensions by enabling risk reduction for personnel and increased operational persistence in high-threat environments. Remote-controlled platforms facilitate network-centric warfare, allowing integration with unmanned systems and real-time data sharing, which challenges traditional combined arms tactics and calls for doctrinal revisions emphasizing remote operations and cyber-physical resilience. Military doctrines must evolve to balance the enduring offensive and defensive roles of MBTs with the flexibility, scalability, and reduced vulnerability offered by remote-controlled armored vehicles.
Related Important Terms
Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T)
Main battle tanks equipped with advanced firepower and armor remain crucial on the battlefield but increasingly operate in tandem with remote-controlled armored platforms to enhance situational awareness and operational reach. Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T) leverages the strengths of human decision-making and autonomous systems, enabling coordinated missions that improve force protection, reduce risk to personnel, and optimize target engagement efficiency.
Optionally Crewed Tank (OCT)
Optionally Crewed Tanks (OCTs) integrate advanced autonomous systems with traditional manned capabilities, enhancing battlefield flexibility and crew survivability compared to fully remote-controlled armored platforms. These hybrid solutions leverage real-time sensor fusion and AI-driven targeting to maintain operational control in contested environments while reducing human risk and sustaining lethality.
Remote Combat Vehicle (RCV)
Remote Combat Vehicles (RCVs) enhance battlefield versatility by providing advanced surveillance, remote targeting, and reduced crew risk compared to traditional Main Battle Tanks (MBTs), leveraging autonomous navigation and network-centric warfare capabilities. Equipped with modular weapon systems and real-time data links, RCVs optimize force projection while minimizing personnel exposure in high-threat environments.
Autonomous Turret Integration
Main battle tanks are increasingly incorporating autonomous turret integration to enhance targeting precision and reduce crew vulnerability, leveraging advanced AI algorithms and sensor fusion. Remote-controlled armored platforms utilize autonomous turrets to provide flexible, unmanned firepower support in high-risk environments, improving operational safety and tactical responsiveness.
AI-Enabled Target Acquisition
AI-enabled target acquisition in main battle tanks enhances real-time threat detection through advanced sensor fusion and machine learning algorithms, improving precision and battlefield survivability. Remote-controlled armored platforms leverage AI for autonomous target recognition and rapid decision-making, enabling effective engagement with reduced risk to human operators in high-threat environments.
Active Protection System (APS) Interoperability
Active Protection System (APS) interoperability on main battle tanks enhances threat detection and neutralization by integrating multiple sensor arrays and countermeasures, while remote-controlled armored platforms leverage modular APS units for flexible deployment in diverse combat scenarios. Seamless APS communication protocols between manned tanks and unmanned platforms enable coordinated defense strategies, significantly improving survivability against advanced anti-tank guided missiles and kinetic threats.
Teleoperated Armor Platform
Teleoperated Armor Platforms offer enhanced battlefield flexibility and reduced risk to personnel by enabling remote control of armored vehicles through secure communication networks, leveraging advanced sensors and AI for real-time threat assessment and target engagement. Unlike traditional Main Battle Tanks, these systems provide modular payloads and rapid adaptability to complex environments, facilitating precision strikes and reconnaissance without exposing operators to direct combat hazards.
Semi-Autonomous Fire Control
Semi-autonomous fire control systems in main battle tanks enhance target acquisition speed and precision by integrating advanced sensors, AI algorithms, and real-time data processing to optimize engagement decisions. Remote-controlled armored platforms leverage similar semi-autonomous fire control technologies to reduce crew risk while maintaining effective lethality and operational flexibility in high-threat environments.
Distributed Lethality Networking
Main battle tanks equipped with advanced armor and firepower remain pivotal in frontline engagements, while remote-controlled armored platforms enhance distributed lethality networking by providing scalable, networked precision strikes with reduced risk to personnel. Integrating these systems enables synergistic battlefield dominance through real-time data sharing, force multiplication, and adaptive targeting across multidomain operational environments.
Swarm Coordination Protocols
Main battle tanks rely on heavily armored firepower and crew expertise, while remote-controlled armored platforms utilize advanced swarm coordination protocols enabling synchronized maneuvers, target prioritization, and real-time data sharing among multiple units to overwhelm enemy defenses. Swarm protocols enhance operational efficiency by distributing battlefield roles dynamically, increasing battlefield situational awareness and reducing vulnerability compared to single-crew systems.
Main battle tank vs remote-controlled armored platform Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com