Defense pets offer unique tactical advantages by providing agile protection and immediate threat detection in combat zones. Tanks deliver heavy armor and firepower, capable of withstanding intense attacks and dominating the battlefield with robust fire support. Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) enhance defense strategies by performing reconnaissance, surveillance, and neutralizing threats remotely, minimizing risks to human personnel while increasing operational flexibility.
Table of Comparison
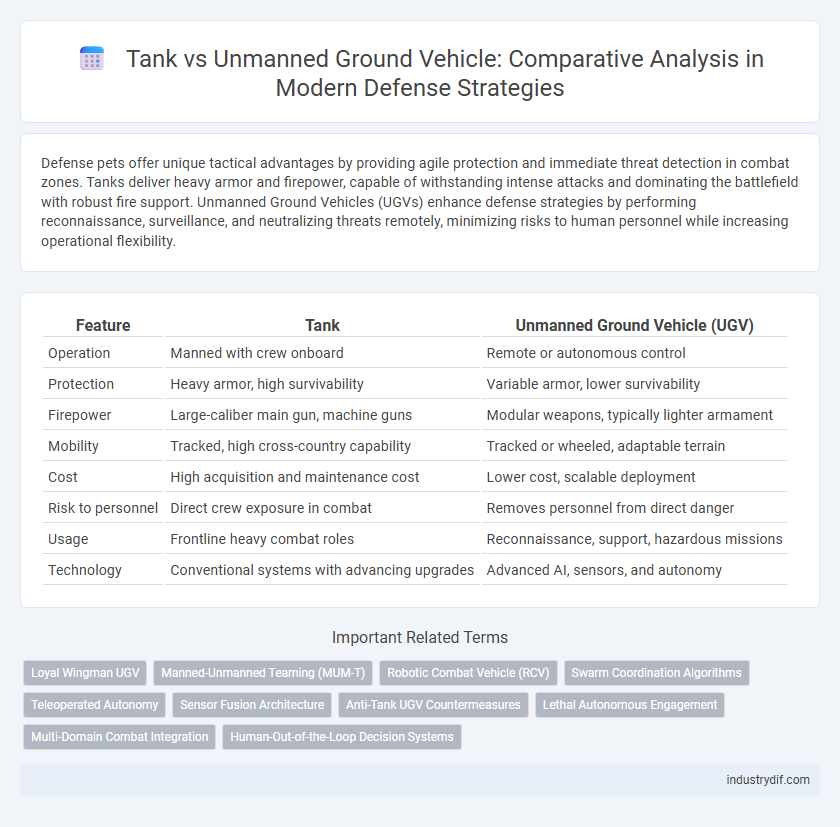
| Feature | Tank | Unmanned Ground Vehicle (UGV) |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Manned with crew onboard | Remote or autonomous control |
| Protection | Heavy armor, high survivability | Variable armor, lower survivability |
| Firepower | Large-caliber main gun, machine guns | Modular weapons, typically lighter armament |
| Mobility | Tracked, high cross-country capability | Tracked or wheeled, adaptable terrain |
| Cost | High acquisition and maintenance cost | Lower cost, scalable deployment |
| Risk to personnel | Direct crew exposure in combat | Removes personnel from direct danger |
| Usage | Frontline heavy combat roles | Reconnaissance, support, hazardous missions |
| Technology | Conventional systems with advancing upgrades | Advanced AI, sensors, and autonomy |
Introduction to Modern Armored Warfare
Modern armored warfare has evolved with the integration of unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) alongside traditional tanks, enhancing battlefield versatility and reducing human risk. Tanks remain dominant for their heavy armor and firepower, while UGVs contribute advanced surveillance, reconnaissance, and precision strike capabilities. The synergy between manned tanks and unmanned systems forms a comprehensive approach to contemporary ground combat operations.
Defining Tanks and Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs)
Tanks are heavily armored combat vehicles equipped with powerful main guns and tracks, designed for frontline ground warfare and capable of withstanding heavy fire. Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) are remotely operated or autonomous robotic systems used for various defense applications, including reconnaissance, logistics, and combat support, minimizing risk to personnel. Both tanks and UGVs play critical roles in modern military operations, with tanks emphasizing firepower and armor, while UGVs offer versatility and reduced human exposure in high-risk environments.
Technological Evolution: Tanks vs UGVs
Tanks have evolved with advancements in armor, firepower, and targeting systems, incorporating composite materials and active protection technologies to enhance battlefield survivability. Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) leverage cutting-edge AI, remote operation capabilities, and modular payloads, enabling versatile reconnaissance, logistics, and combat support roles. The integration of autonomous navigation and real-time data processing in UGVs represents a transformative shift in ground warfare technology, complementing traditional tank operations.
Firepower and Combat Effectiveness Comparison
Tanks possess superior firepower with heavy-caliber cannons capable of destroying fortified targets at long ranges, while unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) typically carry lighter, precision-guided weapons designed for specific tactical roles. The combat effectiveness of tanks is enhanced by their armor protection and crew decision-making, enabling sustained frontline engagement, whereas UGVs excel in high-risk, reconnaissance, and support missions with reduced personnel risk. Integration of advanced sensors and remote control systems in UGVs improves situational awareness, but tanks remain dominant in direct, high-intensity combat scenarios due to their robust offensive and defensive capabilities.
Mobility and Terrain Adaptability
Tanks exhibit superior mobility with heavy armor enabling them to traverse rugged and uneven terrains while maintaining combat effectiveness. Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) offer enhanced terrain adaptability through advanced sensors and autonomous navigation systems, allowing operations in hazardous or inaccessible environments. The integration of real-time data processing in UGVs optimizes route selection and obstacle avoidance, surpassing traditional tank maneuverability in complex settings.
Operational Roles and Mission Profiles
Tanks excel in heavy armor protection and direct firepower, making them ideal for frontline assault, urban combat, and breaching fortified positions. Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) enhance reconnaissance, logistics support, and risk reduction by operating in hazardous environments without endangering personnel. Their complementary deployment optimizes battlefield efficiency, with tanks dominating high-intensity engagements and UGVs performing surveillance, mine detection, and supply delivery in contested zones.
Survivability and Crew Protection
Tanks offer superior crew protection through heavily armored hulls and active defense systems, significantly enhancing survivability on the battlefield. Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) eliminate crew risk by operating remotely, allowing deployment in high-threat environments without endangering human life. Advances in autonomous threat detection and modular armor technology have improved UGV survivability, but tanks maintain an edge in sustained combat resilience and crew safety.
Autonomous Capabilities and AI Integration
Tanks equipped with advanced targeting systems still rely heavily on human operators, whereas Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) leverage AI-driven navigation and autonomous decision-making to perform reconnaissance, target acquisition, and threat elimination with minimal human intervention. AI integration enables UGVs to process real-time sensor data, adapt to dynamic battlefield environments, and execute complex missions independently, enhancing operational flexibility and survivability. These autonomous capabilities significantly reduce risks to personnel while increasing mission efficiency and responsiveness in modern defense scenarios.
Logistics, Maintenance, and Cost Analysis
Tanks require extensive logistics support including fuel, ammunition, and spare parts, resulting in high operational costs and complex maintenance schedules due to their mechanical and electronic components. Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) reduce personnel risks and are designed for modular maintenance, allowing for rapid replacement of parts and lower lifecycle expenses. Cost analysis reveals that while initial investment in UGV technology can be high, long-term savings emerge from reduced manpower needs, lower fuel consumption, and streamlined maintenance processes.
Future Trends in Armored Systems Integration
Future trends in armored systems integration emphasize the convergence of traditional tanks with unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) to enhance battlefield versatility and lethality. Advanced sensor fusion, AI-driven targeting, and autonomous operation capabilities allow UGVs to act as force multipliers alongside manned tanks, improving situational awareness and reducing crew risk. Expected developments include seamless communication networks and modular payload systems enabling dynamic mission reconfiguration and coordinated swarm tactics in diverse combat environments.
Related Important Terms
Loyal Wingman UGV
Loyal Wingman UGVs enhance modern armored warfare by providing autonomous reconnaissance and target acquisition, reducing risk to manned tanks during frontline operations. Equipped with advanced sensors and AI-driven decision-making, these unmanned vehicles extend situational awareness and firepower while coordinating seamlessly with tank units.
Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T)
Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T) enhances battlefield effectiveness by integrating tanks with Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) for reconnaissance, target acquisition, and force multiplication, leveraging the tank's firepower and the UGV's sensor and mobility capabilities. This synergy improves situational awareness, reduces crew risk, and enables real-time data sharing for rapid decision-making in complex combat scenarios.
Robotic Combat Vehicle (RCV)
Robotic Combat Vehicles (RCVs) offer enhanced battlefield adaptability with remote operation and autonomous targeting, reducing soldier risk compared to traditional tanks. Integrating advanced sensors, AI-driven navigation, and modular weapon systems, RCVs provide superior reconnaissance and precision strike capabilities in modern warfare.
Swarm Coordination Algorithms
Swarm coordination algorithms enable unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) to operate collaboratively, enhancing battlefield adaptability and reducing human risk compared to traditional tanks. These algorithms optimize real-time communication, autonomous decision-making, and dynamic formation control, providing UGV swarms with superior situational awareness and tactical versatility against armored threats.
Teleoperated Autonomy
Teleoperated autonomy in unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) combines remote human control with onboard AI processing to enhance situational awareness and decision-making on the battlefield, outperforming traditional manned tanks in reducing risk to personnel. These hybrid control systems enable tactical flexibility and rapid response in complex environments, providing a strategic advantage through real-time data integration and autonomous navigation capabilities.
Sensor Fusion Architecture
Tank sensor fusion architectures integrate data from radar, thermal imaging, LIDAR, and acoustic sensors to enhance target detection and situational awareness in complex combat environments. Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) utilize advanced sensor fusion frameworks combining multispectral cameras, inertial measurement units, and ultrasonic sensors to enable autonomous navigation and threat identification without human intervention.
Anti-Tank UGV Countermeasures
Anti-tank UGV countermeasures leverage advanced active protection systems, electronic warfare tactics, and autonomous threat detection algorithms to neutralize armored tank threats. Integration of sensor fusion, rapid-response kinetic interceptors, and directed energy weapons enhances UGV survivability against sophisticated tank armaments in modern battlefield environments.
Lethal Autonomous Engagement
Lethal autonomous engagement in tanks involves advanced targeting algorithms combined with heavy armor and firepower, enabling precision strikes against enemy units. Unmanned Ground Vehicles leverage AI-driven sensors and remote control capabilities to conduct high-risk missions without endangering personnel, providing tactical flexibility in complex combat scenarios.
Multi-Domain Combat Integration
Tanks provide heavy armor and firepower essential for direct combat, while unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) enhance operational flexibility through remote reconnaissance and precision targeting in multi-domain combat environments. Integrating tanks with UGVs enables synchronized ground, air, and cyber operations, improving battlefield situational awareness and force multiplier effects in complex threat scenarios.
Human-Out-of-the-Loop Decision Systems
Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) equipped with Human-Out-of-the-Loop (HOTL) decision systems enhance battlefield autonomy by executing complex maneuvers and target acquisition without direct human intervention, increasing operational efficiency and reducing soldier exposure to risk. Modern tanks integrated with HOTL systems leverage artificial intelligence and sensor fusion to improve threat detection and real-time response, offering a strategic advantage through faster decision-making compared to traditional manned platforms.
Tank vs Unmanned Ground Vehicle Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com