Main Battle Tanks (MBTs) offer robust armor and superior firepower, making them highly effective in frontline engagements against various threats. Robotic Combat Vehicles (RCVs) provide enhanced agility and reduced risk to human operators, excelling in reconnaissance and rapid response scenarios. The integration of MBTs and RCVs in modern defense strategies combines heavy firepower with advanced technological versatility for improved battlefield dominance.
Table of Comparison
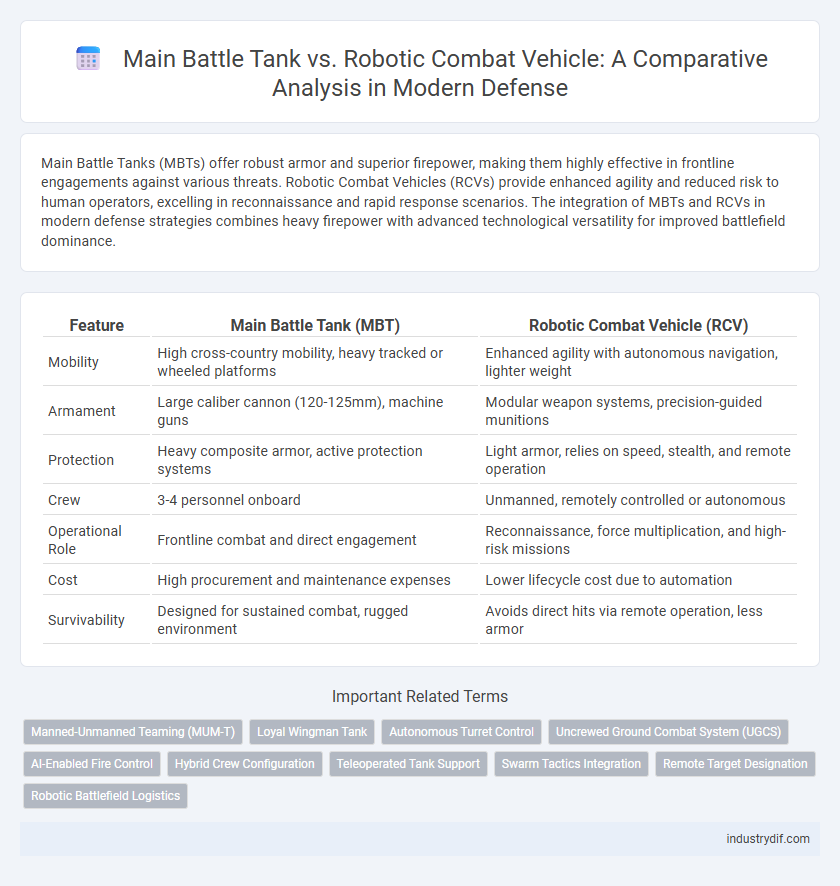
| Feature | Main Battle Tank (MBT) | Robotic Combat Vehicle (RCV) |
|---|---|---|
| Mobility | High cross-country mobility, heavy tracked or wheeled platforms | Enhanced agility with autonomous navigation, lighter weight |
| Armament | Large caliber cannon (120-125mm), machine guns | Modular weapon systems, precision-guided munitions |
| Protection | Heavy composite armor, active protection systems | Light armor, relies on speed, stealth, and remote operation |
| Crew | 3-4 personnel onboard | Unmanned, remotely controlled or autonomous |
| Operational Role | Frontline combat and direct engagement | Reconnaissance, force multiplication, and high-risk missions |
| Cost | High procurement and maintenance expenses | Lower lifecycle cost due to automation |
| Survivability | Designed for sustained combat, rugged environment | Avoids direct hits via remote operation, less armor |
Evolution of Main Battle Tanks and Robotic Combat Vehicles
Main Battle Tanks (MBTs) have evolved from heavily armored, crew-operated vehicles designed for direct firepower and battlefield dominance to incorporating advanced targeting systems, active protection, and hybrid powertrains for enhanced survivability and efficiency. Robotic Combat Vehicles (RCVs) represent the next evolution, combining unmanned operation with AI-driven situational awareness, enabling high-risk missions without endangering soldiers. The technological shift toward automation and network-centric warfare highlights a strategic transition, where RCVs complement or partially replace traditional MBTs to achieve greater operational flexibility and reduced human casualties.
Core Design Differences: Manned vs Unmanned Platforms
Main battle tanks (MBTs) feature heavily armored manned platforms with integrated crew stations, designed for direct human control and situational awareness. Robotic combat vehicles (RCVs) prioritize autonomous or remote operation, emphasizing modular payloads, advanced sensors, and communication networks over traditional armor protection. The core design difference lies in MBTs' reliance on onboard crew for real-time decision-making versus RCVs' reliance on AI and remote command systems for battlefield adaptability.
Battlefield Roles and Operational Capabilities
Main Battle Tanks (MBTs) deliver superior firepower, armor protection, and battlefield dominance with crewed operation for complex decision-making and sustained combat. Robotic Combat Vehicles (RCVs) offer enhanced reconnaissance, reduced crew risk, and increased deployment flexibility with autonomous or remote-controlled operations in high-threat environments. Integration of MBTs and RCVs enables force multiplication by combining heavy firepower and survivability with agility and advanced sensor capabilities.
Survivability, Armor, and Protection Technologies
Main Battle Tanks (MBTs) boast heavily armored composite and reactive armor systems designed to withstand kinetic energy penetrators and shaped charges, enhancing their survivability on the frontline. Robotic Combat Vehicles (RCVs) employ advanced sensor fusion, active protection systems (APS), and reduced thermal and radar signatures to evade detection and intercept incoming threats, compensating for generally lighter armor compared to MBTs. The integration of next-generation armor materials like nano-ceramics and electromagnetic armor in MBTs, alongside AI-driven threat response in RCVs, represents a paradigm shift in battlefield protection technologies.
Firepower: Weapon Systems and Targeting Integration
Main battle tanks feature advanced kinetic energy cannons capable of firing armor-piercing rounds with high accuracy, supported by sophisticated fire control systems integrating laser rangefinders and thermal imaging for precise targeting. Robotic combat vehicles leverage modular weapon systems, such as autocannons and guided missiles, enhanced by AI-driven targeting software that dynamically adjusts to real-time battlefield data. Targeting integration in robotic platforms enables networked sensors and data fusion, improving engagement speed and coordination beyond the capabilities of traditional main battle tank systems.
Mobility: Terrain Adaptability and Deployment
Main battle tanks (MBTs) boast superior terrain adaptability, equipped with advanced suspension systems and heavy armor allowing effective operation across rugged and uneven landscapes. Robotic combat vehicles (RCVs) leverage lightweight designs and autonomous navigation, enhancing rapid deployment and agility in diverse environments including urban and complex terrains. Integration of sensor fusion and AI in RCVs provides enhanced mobility control, ensuring precision movement in constrained or hazardous zones where traditional MBTs face operational limits.
Sensor Suites and Situational Awareness Enhancements
Main Battle Tanks (MBTs) integrate advanced sensor suites including thermal imaging, laser rangefinders, and radar systems to enhance target acquisition and battlefield awareness. Robotic Combat Vehicles (RCVs) leverage cutting-edge sensor fusion technologies, combining LIDAR, multispectral cameras, and AI-driven data analytics for real-time situational assessment and autonomous threat detection. The enhanced situational awareness in RCVs significantly improves operational responsiveness and reduces human risk in high-threat environments.
Autonomy, AI, and Remote Control Systems
Main Battle Tanks integrate advanced autonomous navigation and AI-driven targeting systems to enhance battlefield efficiency, while maintaining human oversight for complex decision-making. Robotic Combat Vehicles leverage fully autonomous operational capabilities combined with remote control systems, enabling rapid deployment in high-risk zones without endangering personnel. The interplay of AI algorithms in both platforms optimizes threat assessment, situational awareness, and coordinated maneuvers in modern combat environments.
Logistics, Maintenance, and Cost Efficiency
Main Battle Tanks require extensive logistical support and frequent maintenance due to their complex mechanical systems and heavy armor, leading to higher operational costs compared to Robotic Combat Vehicles. Robotic Combat Vehicles offer improved cost efficiency by reducing crew requirements and enabling remote operation, which lowers personnel risk and maintenance demands. The lighter weight and modular design of Robotic Combat Vehicles facilitate easier transport and faster deployment, streamlining logistics and reducing overall lifecycle expenses.
Future Trends and Integration in Modern Armies
Future trends in defense emphasize the integration of Main Battle Tanks (MBTs) with Robotic Combat Vehicles (RCVs) to enhance battlefield effectiveness through collaborative operations. MBTs provide heavy armor and firepower, while RCVs offer reconnaissance, remote engagement, and force multiplication in high-risk environments, enabling modern armies to maintain superiority with lower personnel risk. Emerging technologies such as AI-driven autonomy, advanced sensor fusion, and network-centric warfare are driving the seamless coordination between manned and unmanned systems in next-generation armored formations.
Related Important Terms
Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T)
Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T) leverages the strengths of Main Battle Tanks (MBTs) and Robotic Combat Vehicles (RCVs) by integrating human decision-making with autonomous operational capabilities to enhance battlefield effectiveness. MBTs provide robust firepower and protection, while RCVs extend situational awareness and perform reconnaissance or high-risk tasks, enabling coordinated, flexible combat strategies.
Loyal Wingman Tank
The Loyal Wingman Tank integrates advanced AI and autonomous systems to support Main Battle Tanks by enhancing situational awareness and force multiplication on the battlefield. Combining heavy armor and firepower with robotic agility, it offers scalable combat solutions that reduce soldier risk while maintaining offensive and defensive capabilities.
Autonomous Turret Control
Main Battle Tanks equipped with advanced autonomous turret control systems utilize real-time target acquisition and decision-making algorithms to enhance precision and reduce operator workload. Robotic Combat Vehicles leverage AI-driven turret autonomy to perform rapid threat assessment and engagement in contested environments, increasing battlefield survivability and operational flexibility.
Uncrewed Ground Combat System (UGCS)
Uncrewed Ground Combat Systems (UGCS) like Robotic Combat Vehicles offer enhanced operational flexibility and reduced risk to personnel compared to traditional Main Battle Tanks by integrating AI-driven targeting and autonomous navigation. These systems provide scalable force projection and can operate in high-threat environments, complementing or potentially replacing crewed armored units in future defense strategies.
AI-Enabled Fire Control
AI-enabled fire control systems in main battle tanks enhance target acquisition accuracy and reduce engagement time through advanced sensor fusion and real-time data analytics, significantly improving battlefield lethality. Robotic combat vehicles leverage AI-driven fire control to operate autonomously in high-risk environments, allowing for precision strikes without endangering crew, thereby transforming modern combat tactics.
Hybrid Crew Configuration
Hybrid crew configurations in main battle tanks integrate human decision-making with autonomous robotic systems to enhance battlefield adaptability and operational efficiency. Robotic combat vehicles employ advanced AI and sensor fusion technologies to support remote or semi-autonomous operations, reducing crew risk while maintaining high mission effectiveness.
Teleoperated Tank Support
Teleoperated tank support enhances Main Battle Tank (MBT) operations by providing remote-controlled robotic combat vehicles (RCVs) that can perform reconnaissance, target acquisition, and suppress enemy fire without exposing crew members to direct danger. Integrating RCVs with MBTs improves battlefield situational awareness and force multiplication while reducing the risk of crew casualties in high-threat environments.
Swarm Tactics Integration
Main Battle Tanks (MBTs) equipped with advanced armor and firepower provide robust frontline dominance, while Robotic Combat Vehicles (RCVs) offer enhanced agility and remote operation capabilities critical for swarm tactics integration, enabling coordinated multi-unit assaults that overwhelm enemy defenses. Leveraging swarm intelligence algorithms, RCVs can execute synchronized maneuvers, target acquisition, and adaptive responses, complementing MBT firepower and survivability to transform modern battlefield dynamics.
Remote Target Designation
Main Battle Tanks rely on advanced fire control systems with integrated thermal imaging and laser rangefinders for precise remote target designation, enabling effective engagement at extended distances. Robotic Combat Vehicles enhance target acquisition accuracy through autonomous sensors and real-time data links, allowing remote operators to designate and prioritize targets efficiently without exposing personnel to direct combat risks.
Robotic Battlefield Logistics
Robotic Combat Vehicles enhance battlefield logistics by enabling autonomous resupply and equipment transport, reducing human risk and increasing operational tempo compared to traditional Main Battle Tanks. Their integration with AI-driven supply chains streamlines fuel, ammunition, and maintenance delivery, improving sustainment efficiency in dynamic combat environments.
Main Battle Tank vs Robotic Combat Vehicle Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com