An aircraft carrier offers unparalleled air power projection, advanced defense systems, and rapid deployment capabilities crucial for modern naval warfare. In contrast, a mobile offshore base provides a flexible, modular platform for logistics support, enabling sustained operations far from home ports while enhancing fleet endurance. Both play complementary roles in maritime defense strategies by balancing combat readiness with operational support.
Table of Comparison
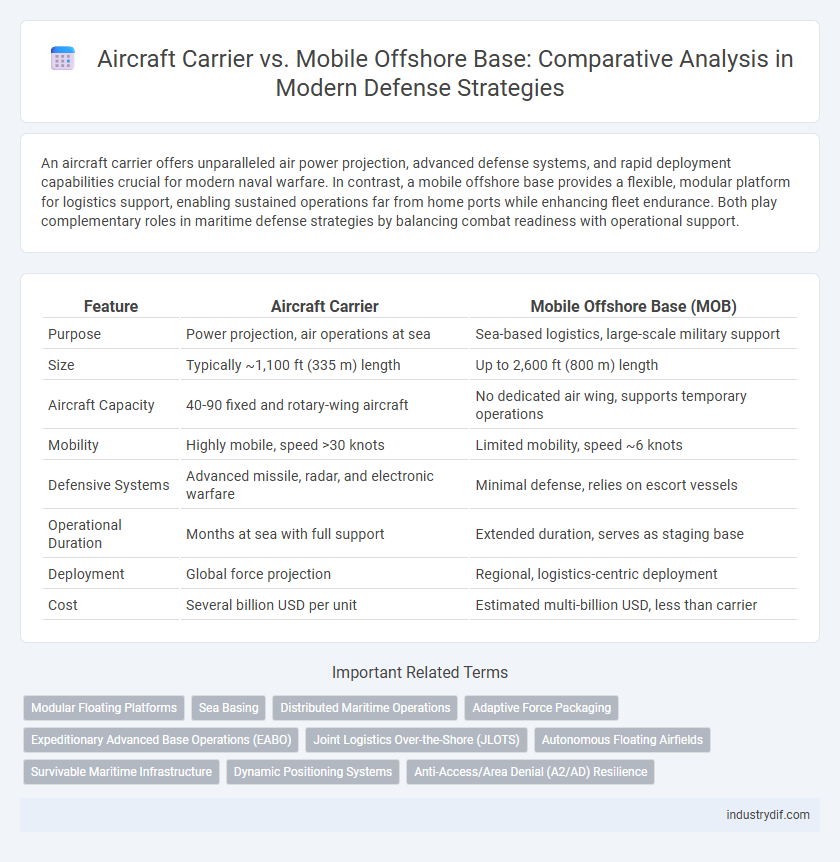
| Feature | Aircraft Carrier | Mobile Offshore Base (MOB) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Power projection, air operations at sea | Sea-based logistics, large-scale military support |
| Size | Typically ~1,100 ft (335 m) length | Up to 2,600 ft (800 m) length |
| Aircraft Capacity | 40-90 fixed and rotary-wing aircraft | No dedicated air wing, supports temporary operations |
| Mobility | Highly mobile, speed >30 knots | Limited mobility, speed ~6 knots |
| Defensive Systems | Advanced missile, radar, and electronic warfare | Minimal defense, relies on escort vessels |
| Operational Duration | Months at sea with full support | Extended duration, serves as staging base |
| Deployment | Global force projection | Regional, logistics-centric deployment |
| Cost | Several billion USD per unit | Estimated multi-billion USD, less than carrier |
Definition and Core Concepts: Aircraft Carrier vs Mobile Offshore Base
An aircraft carrier is a large naval vessel equipped with a full-length flight deck designed for launching and recovering military aircraft, serving as a mobile airbase at sea to project power and support naval operations. A mobile offshore base (MOB) is a modular, floating platform intended to provide logistical support and staging areas for military forces, enabling rapid deployment and sustainment far from traditional land bases. The core concept of an aircraft carrier revolves around air superiority and force projection, whereas a mobile offshore base emphasizes strategic flexibility and extended operational reach through its scalable and transportable infrastructure.
Strategic Roles in Modern Defense Operations
Aircraft carriers serve as mobile airbases projecting naval air power globally, enabling rapid force deployment and air superiority in contested regions. Mobile Offshore Bases (MOBs) offer flexible, modular platforms for logistical support, command and control, and staging areas nearer conflict zones without the need for fixed bases. Both platforms enhance operational reach and sustainment, but carriers dominate in offensive strike capabilities while MOBs excel in strategic support and force multiplication.
Design and Structural Differences
Aircraft carriers feature a highly integrated design that combines a flight deck, hangars, and advanced propulsion systems within a heavily armored hull to support fixed-wing aircraft operations at sea. Mobile Offshore Bases (MOBs) consist of modular, semi-submersible platforms with a flat deck and adaptable structures designed primarily for logistical support, enabling deployment in deeper waters with focus on stability rather than speed. The structural differences are marked by aircraft carriers' emphasis on mobility and combat readiness, contrasted with MOBs prioritizing modularity, large cargo capacity, and long-term station-keeping capabilities.
Mobility and Deployment Capabilities
Aircraft carriers offer superior mobility and rapid deployment capabilities, able to project power across global maritime theaters with integrated air wings and advanced propulsion systems. Mobile offshore bases provide versatile modular platforms that can be positioned in strategic locations but typically require more time to establish operational readiness and lack the high-speed transit capabilities of carriers. The choice between these platforms hinges on mission requirements, with carriers excelling in force projection and mobility, while MOBs serve as flexible support hubs in contested environments.
Force Projection and Operational Reach
Aircraft carriers provide unparalleled force projection with their ability to launch and recover a wide variety of fixed-wing aircraft, enabling rapid air supremacy and strike capabilities across vast distances. Mobile offshore bases enhance operational reach by serving as flexible, sea-based staging platforms that support sustained logistics, maintenance, and deployment of forces closer to conflict zones without reliance on regional bases. Combining aircraft carriers' offensive air power with MOBs' extended support infrastructure significantly amplifies a navy's strategic reach and combat endurance.
Survivability and Defensive Systems
Aircraft carriers feature extensive layered defense systems including Aegis Combat System, missile interceptors, and electronic warfare suites, enhancing their survivability against air, surface, and subsurface threats. Mobile Offshore Bases (MOBs), designed for strategic logistics support, have limited self-defense capabilities, relying primarily on escort vessels and deployable sensors to detect and counter threats. The robust integrated defensive architecture of aircraft carriers significantly outmatches the comparatively vulnerable MOBs, ensuring sustained operational presence in high-threat environments.
Aircraft and Vessel Support Capacities
Aircraft carriers can support a larger air wing, typically 70 to 90 aircraft, offering diverse capabilities including strike, reconnaissance, and electronic warfare, while Mobile Offshore Bases (MOBs) provide limited, primarily rotary-wing and UAV support. MOBs excel in logistics and vehicle deployment with their modular platform design but lack the integrated aviation facilities and defensive systems of carriers. The carrier's advanced flight deck, maintenance facilities, and combat systems enable sustained air operations and rapid response, making it a superior platform for projecting air power compared to the MOB's auxiliary role.
Logistical and Sustainment Considerations
Aircraft carriers offer rapid deployment and sustained air operations with integrated maintenance facilities, enabling continuous force projection without reliance on external resupply. Mobile Offshore Bases provide modular logistics hubs capable of supporting prolonged field operations by facilitating storage, fuel, and equipment transfer in contested maritime environments. Both platforms present unique sustainment challenges, where aircraft carriers emphasize self-sufficiency and rapid sortie generation, while mobile offshore bases prioritize flexible, scalable logistics for extended operational endurance.
Cost-Efficiency and Resource Allocation
Aircraft carriers demand significant investment and long-term maintenance costs, often exceeding $10 billion per unit, whereas Mobile Offshore Bases (MOBs) offer a more flexible and cost-efficient alternative with lower initial expenditures and scalable deployment options. Resource allocation on MOBs optimizes operational versatility by supporting various military assets and reducing fuel consumption through modular infrastructure. The cost-efficiency of MOBs enhances strategic mobility while maintaining essential force projection capabilities without the extensive overhead associated with traditional aircraft carriers.
Future Trends in Maritime Defense Platforms
Aircraft carriers will continue to evolve with advancements in stealth technology, electromagnetic catapults, and unmanned air combat systems, enhancing their power projection and operational flexibility. Mobile Offshore Bases (MOBs) are emerging as modular, scalable platforms offering rapid deployment and persistent presence, particularly in contested or remote maritime regions. Future maritime defense strategies will likely integrate both platforms, leveraging the carrier's air superiority and MOB's logistical support to maintain strategic dominance across vast oceanic theaters.
Related Important Terms
Modular Floating Platforms
Modular floating platforms in mobile offshore bases offer scalable, reconfigurable solutions for forward deployment of military assets, enhancing operational flexibility compared to the fixed structure of traditional aircraft carriers. These platforms enable rapid assembly and customization for diverse mission requirements, including air support, logistics, and command, optimizing force projection in contested maritime environments.
Sea Basing
Aircraft carriers provide dynamic power projection with integrated air wings and rapid response capabilities, essential for sea basing in contested environments. Mobile Offshore Bases offer modular, scalable platforms for sustained logistics, repairs, and command operations, enhancing operational endurance without reliance on traditional port facilities.
Distributed Maritime Operations
Aircraft carriers serve as central power projection platforms with integrated air wings, enabling rapid strike capabilities and force multiplication. Mobile Offshore Bases provide flexible, scalable maritime infrastructure supporting distributed maritime operations by enhancing logistic sustainment and dispersing forces to reduce vulnerability.
Adaptive Force Packaging
Aircraft carriers leverage adaptive force packaging by integrating advanced air wings with modular mission packages to project power globally, ensuring rapid deployment and versatile strike capabilities. Mobile Offshore Bases complement this approach by providing flexible, scalable platforms for logistics, maintenance, and command support, enabling sustained operations in austere maritime environments.
Expeditionary Advanced Base Operations (EABO)
Aircraft carriers provide unparalleled power projection with integrated air wings and advanced command capabilities, essential for sustained naval dominance, while Mobile Offshore Bases (MOBs) offer flexible, scalable platforms designed to support Expeditionary Advanced Base Operations (EABO) by enabling rapid deployment and distributed maritime operations closer to contested shorelines. EABO emphasizes the use of MOBs to enhance force survivability and operational reach in anti-access/area denial (A2/AD) environments, complementing the traditional carrier strike group with dispersed, resilient staging points for amphibious forces and logistics.
Joint Logistics Over-the-Shore (JLOTS)
Aircraft carriers provide robust power projection with integrated air wings, but Mobile Offshore Bases (MOBs) offer versatile platforms for Joint Logistics Over-the-Shore (JLOTS) operations, enabling flexible, scalable resupply and equipment transfer directly from sea to shore without traditional port facilities. MOBs enhance sustainment of distributed forces by facilitating rapid offloading of cargo, fuel, and personnel in austere environments, complementing the operational reach of aircraft carriers in contested littoral zones.
Autonomous Floating Airfields
Autonomous floating airfields, including advanced Aircraft Carriers and Mobile Offshore Bases (MOBs), enhance naval power projection by providing flexible, relocatable platforms for fighter deployment and logistical support. Aircraft carriers offer integrated command systems and rapid strike capabilities, while MOBs prioritize modular scalability and sustained operational endurance in remote maritime zones.
Survivable Maritime Infrastructure
Aircraft carriers provide highly survivable maritime infrastructure with advanced defense systems and mobility, enabling power projection and sustained operations in contested environments. Mobile offshore bases offer scalable, adaptable platforms with lower radar signatures and modular capabilities, enhancing survivability through dispersion and operational flexibility in littoral zones.
Dynamic Positioning Systems
Dynamic Positioning Systems enable Aircraft Carriers to maintain precise station-keeping amid complex naval operations, leveraging advanced sensor arrays and thruster configurations for enhanced maneuverability. Mobile Offshore Bases rely on similar systems to stabilize platforms in open waters, yet their scaling and modularity demand adaptive control algorithms to counteract environmental forces effectively.
Anti-Access/Area Denial (A2/AD) Resilience
Aircraft carriers offer enhanced power projection with integrated air wings and advanced radar systems essential for A2/AD resilience, enabling strike capabilities beyond contested zones. Mobile Offshore Bases provide flexible, semi-permanent staging platforms capable of dispersing forces and supporting prolonged operations in denied environments but lack the rapid offensive reach and comprehensive air defense of carriers.
Aircraft Carrier vs Mobile Offshore Base Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com