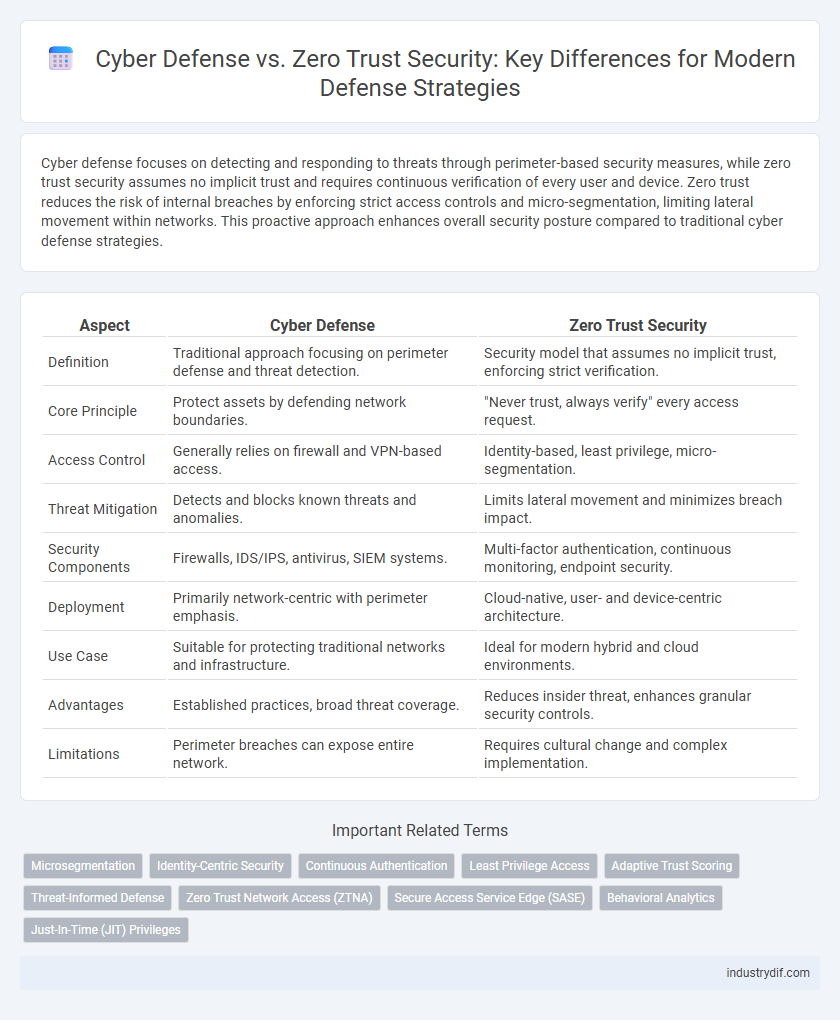
Cyber defense focuses on detecting and responding to threats through perimeter-based security measures, while zero trust security assumes no implicit trust and requires continuous verification of every user and device. Zero trust reduces the risk of internal breaches by enforcing strict access controls and micro-segmentation, limiting lateral movement within networks. This proactive approach enhances overall security posture compared to traditional cyber defense strategies.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cyber Defense | Zero Trust Security |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional approach focusing on perimeter defense and threat detection. | Security model that assumes no implicit trust, enforcing strict verification. |
| Core Principle | Protect assets by defending network boundaries. | "Never trust, always verify" every access request. |
| Access Control | Generally relies on firewall and VPN-based access. | Identity-based, least privilege, micro-segmentation. |
| Threat Mitigation | Detects and blocks known threats and anomalies. | Limits lateral movement and minimizes breach impact. |
| Security Components | Firewalls, IDS/IPS, antivirus, SIEM systems. | Multi-factor authentication, continuous monitoring, endpoint security. |
| Deployment | Primarily network-centric with perimeter emphasis. | Cloud-native, user- and device-centric architecture. |
| Use Case | Suitable for protecting traditional networks and infrastructure. | Ideal for modern hybrid and cloud environments. |
| Advantages | Established practices, broad threat coverage. | Reduces insider threat, enhances granular security controls. |
| Limitations | Perimeter breaches can expose entire network. | Requires cultural change and complex implementation. |
Understanding Cyber Defense: Core Principles and Strategies
Cyber defense centers on proactive measures including threat detection, incident response, and vulnerability management to safeguard digital assets from evolving cyber threats. Zero trust security enhances this framework by enforcing strict identity verification and access controls, assuming no inherent trust within the network perimeter. Implementing these core principles together creates a layered defense strategy that mitigates risks and strengthens overall organizational cybersecurity posture.
Zero Trust Security: A Paradigm Shift in Protection
Zero Trust Security represents a paradigm shift in cyber defense by eliminating implicit trust and continuously validating every user, device, and access request within a network. Unlike traditional perimeter-based security models, Zero Trust enforces strict identity verification and micro-segmentation to minimize attack surfaces and contain potential breaches. This approach enhances protection against advanced persistent threats, insider risks, and lateral movement within complex digital environments.
Key Differences Between Cyber Defense and Zero Trust Security
Cyber defense focuses on protecting networks and systems through broad strategies including firewalls, antivirus, and intrusion detection systems to prevent unauthorized access and attacks. Zero trust security operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify," enforcing strict identity verification for every user and device attempting to access resources, regardless of location inside or outside the network perimeter. Unlike traditional cyber defense, zero trust minimizes insider threats and lateral movement by segmenting network access and continuously monitoring user behavior.
Advantages and Limitations of Traditional Cyber Defense
Traditional cyber defense relies on perimeter-based security measures, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, which provide a strong first line of defense against external threats. However, this approach struggles to address insider threats and lateral movement within a network, creating vulnerabilities once an attacker breaches the perimeter. Its limitations include insufficient protection for cloud environments and an inability to adapt dynamically to evolving cyber threats, unlike zero trust security models that verify every access request continuously.
Zero Trust Architecture: Essential Components and Implementation
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is a cybersecurity framework that requires strict identity verification for every user and device attempting to access resources, regardless of their location within or outside the network perimeter. Essential components include continuous monitoring, micro-segmentation, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and least privilege access policies to minimize risk and contain potential breaches. Implementing ZTA involves integrating identity governance, endpoint security, encryption, and real-time analytics to enforce dynamic access controls and strengthen overall cyber defense.
Threat Detection and Response: Comparing Models
Cyber defense employs traditional perimeter-based threat detection tools that monitor network traffic and identify known attack patterns, while zero trust security adopts a continuous verification approach, assuming no implicit trust for any user or device. Zero trust frameworks enhance response capabilities by enforcing strict access controls and real-time anomaly detection across all access points, reducing the attack surface significantly. The integration of machine learning in zero trust models allows for adaptive threat detection and faster incident response compared to conventional cyber defense systems.
Access Management: Perimeter-Based vs Identity-Centric Security
Cyber defense traditionally relies on perimeter-based access management, which establishes security barriers around a network to monitor and control incoming and outgoing traffic. Zero trust security shifts this model to an identity-centric approach, enforcing strict access controls based on user identity, device health, and continuous verification regardless of network location. Implementing zero trust minimizes risks by ensuring that every access request is authenticated and authorized, reducing vulnerabilities inherent in perimeter-based defenses.
Industry Adoption: Trends in Cyber Defense and Zero Trust
Industry adoption of cyber defense and zero trust security has surged as organizations prioritize safeguarding digital assets against advanced threats. Enterprises across sectors are increasingly implementing zero trust frameworks, emphasizing continuous verification and least privilege access to enhance cyber resilience. Market analysis reveals rapid growth in zero trust deployments fueled by regulatory pressures and rising incidents of sophisticated cyberattacks targeting supply chains and critical infrastructure.
Compliance and Regulatory Implications
Cyber defense frameworks must align with compliance mandates such as NIST SP 800-53 and ISO/IEC 27001 to ensure robust regulatory adherence, while zero trust security models enhance this compliance by enforcing strict identity verification and minimizing insider threats. Implementing zero trust architecture supports meeting requirements from regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) by continuously validating trust and segmenting networks. Organizations adopting these models achieve stronger defense postures and reduce legal risks through comprehensive audit trails and real-time access control policies.
Building a Future-Ready Security Framework
Cyber defense integrates threat detection and response mechanisms to safeguard digital assets, while zero trust security enforces strict identity verification and access control regardless of network location. Building a future-ready security framework requires combining these strategies to ensure continuous monitoring, adaptive risk management, and granular access policies. Emphasizing zero trust principles within a comprehensive cyber defense model enhances resilience against evolving cyber threats and insider attacks.
Related Important Terms
Microsegmentation
Cyber defense strategies leverage microsegmentation within Zero Trust Security to isolate network segments, minimizing attack surfaces and containing breaches effectively. This approach enforces strict access controls based on identity and device posture, preventing lateral movement across critical defense networks.
Identity-Centric Security
Cyber defense prioritizes safeguarding digital assets through advanced threat detection and response mechanisms, whereas Zero Trust security emphasizes continuous verification of identity and strict access controls to prevent unauthorized access. Identity-centric security integrates Zero Trust principles by ensuring every user and device is authenticated and authorized, minimizing risks associated with compromised credentials and insider threats.
Continuous Authentication
Continuous authentication strengthens cyber defense frameworks by constantly verifying user identities through behavioral biometrics and contextual data, reducing reliance on initial access checkpoints. Zero trust security's core principle of never trusting implicitly aligns with continuous authentication, ensuring persistent validation to prevent unauthorized access and insider threats.
Least Privilege Access
Cyber defense strategies leveraging Zero Trust Security prioritize Least Privilege Access by ensuring users and devices operate with the minimum necessary permissions, significantly reducing attack surfaces. Implementing strict access controls limits lateral movement within networks, enhancing protection against advanced persistent threats and insider attacks.
Adaptive Trust Scoring
Cyber defense increasingly integrates Adaptive Trust Scoring within Zero Trust Security models to dynamically assess user behavior and device posture, enabling precise access control and minimizing insider threats. This approach enhances threat detection accuracy by continuously updating trust levels based on real-time analytics and contextual data, ensuring robust protection against evolving cyberattacks.
Threat-Informed Defense
Threat-informed defense in cyber security integrates intelligence on adversary tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to enhance zero trust security models, ensuring continuous verification and minimizing attack surfaces. By leveraging real-time threat data, organizations can implement adaptive access controls and network segmentation, aligning with zero trust principles to proactively detect and mitigate sophisticated cyber threats.
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) provides a dynamic, identity-based approach to cyber defense by strictly enforcing access controls and continuously verifying user and device legitimacy, reducing attack surfaces compared to traditional perimeter-based defenses. By segmenting networks and granting least-privilege access, ZTNA minimizes lateral movement risks and enhances protection against advanced persistent threats in defense environments.
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
Cyber defense strategies increasingly integrate Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) frameworks, which combine network security functions with wide-area networking to enforce zero trust principles effectively. SASE enables granular access control and continuous verification, ensuring resilient protection against evolving cyber threats through converged security and network management.
Behavioral Analytics
Cyber defense leverages behavioral analytics to detect anomalies and insider threats by continuously monitoring user activities and network patterns, enhancing threat identification beyond traditional signature-based methods. Zero trust security integrates behavioral analytics as a core component to enforce strict access controls and verify user behavior in real-time, minimizing attack surfaces and preventing lateral movement within the network.
Just-In-Time (JIT) Privileges
Cyber defense strategies increasingly integrate Just-In-Time (JIT) Privileges to minimize exposure by granting users temporary, need-based access, effectively reducing attack surfaces compared to traditional always-on permissions. Zero trust security frameworks leverage JIT Privileges to enforce strict identity verification and contextual access policies, ensuring minimal privilege duration aligns with real-time risk assessments for enhanced protection against insider threats and lateral movement.
Cyber defense vs Zero trust security Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com