Main battle tanks deliver unparalleled firepower, heavy armor, and crewed tactical decision-making, making them formidable in frontline combat against diverse threats. Uncrewed ground vehicles enhance battlefield versatility by performing reconnaissance, logistics, and targeted strikes without risking personnel. Combining main battle tanks with autonomous systems creates a balanced defense strategy leveraging the strengths of human operators and advanced robotics.
Table of Comparison
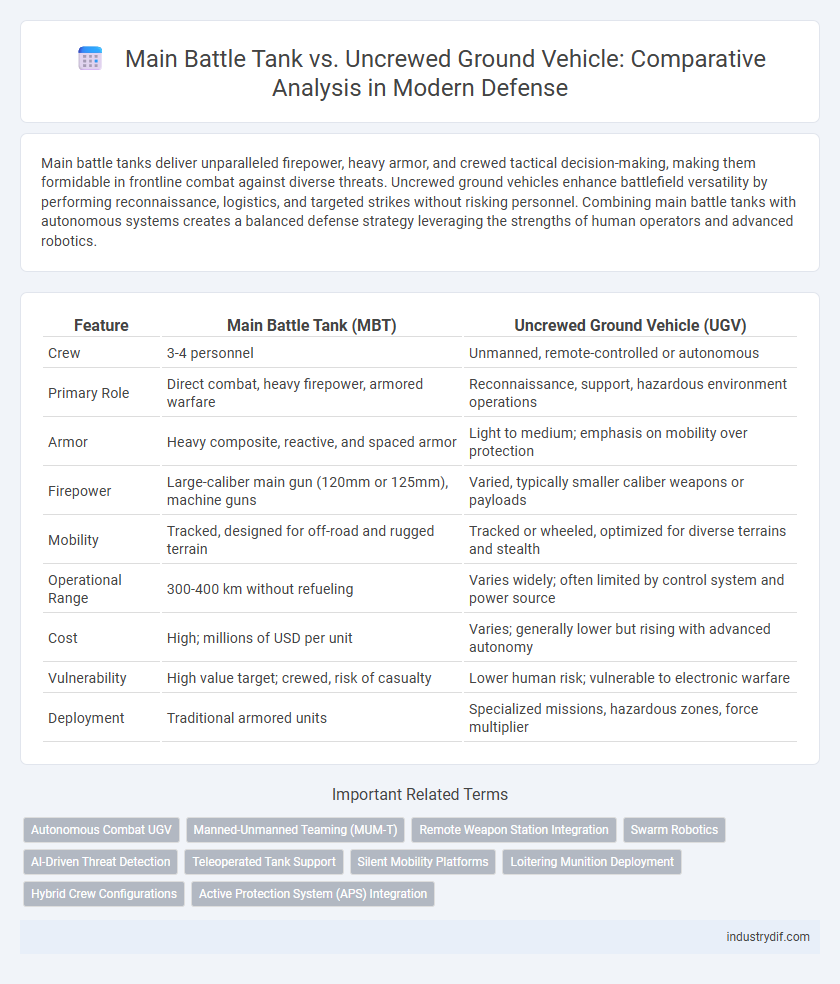
| Feature | Main Battle Tank (MBT) | Uncrewed Ground Vehicle (UGV) |
|---|---|---|
| Crew | 3-4 personnel | Unmanned, remote-controlled or autonomous |
| Primary Role | Direct combat, heavy firepower, armored warfare | Reconnaissance, support, hazardous environment operations |
| Armor | Heavy composite, reactive, and spaced armor | Light to medium; emphasis on mobility over protection |
| Firepower | Large-caliber main gun (120mm or 125mm), machine guns | Varied, typically smaller caliber weapons or payloads |
| Mobility | Tracked, designed for off-road and rugged terrain | Tracked or wheeled, optimized for diverse terrains and stealth |
| Operational Range | 300-400 km without refueling | Varies widely; often limited by control system and power source |
| Cost | High; millions of USD per unit | Varies; generally lower but rising with advanced autonomy |
| Vulnerability | High value target; crewed, risk of casualty | Lower human risk; vulnerable to electronic warfare |
| Deployment | Traditional armored units | Specialized missions, hazardous zones, force multiplier |
Main Battle Tank: Definition and Core Capabilities
A Main Battle Tank (MBT) is a heavily armored combat vehicle designed for frontline engagements, featuring powerful main guns, advanced fire control systems, and reinforced armor protection. MBTs excel in providing direct fire support, executing rapid maneuvers on varied terrains, and sustaining high survivability against anti-tank threats. Core capabilities include superior kinetic energy delivery, crew protection systems, and integration with combined arms operations for battlefield dominance.
Uncrewed Ground Vehicle (UGV): Types and Functions
Uncrewed Ground Vehicles (UGVs) encompass a diverse range of types including reconnaissance drones, armed combat platforms, and logistics support units, each engineered to perform specific battlefield roles without risking human lives. Reconnaissance UGVs are equipped with advanced sensors and AI for real-time intelligence gathering, while armed UGVs deliver precision firepower alongside or in place of main battle tanks. Logistics UGVs enhance battlefield sustainability by autonomously transporting supplies and ammunition, thereby improving operational efficiency and force endurance.
Operational Doctrines: Crewed vs Uncrewed Platforms
Main battle tanks operate under doctrines emphasizing direct human control for adaptive decision-making in complex combat scenarios, leveraging crewed situational awareness and immediate tactical judgments. Uncrewed ground vehicles depend on autonomous systems and remote operation, optimized for high-risk missions where reducing personnel exposure is critical, yet limited by sensor fidelity and communication latency. The operational doctrine for crewed platforms prioritizes human intuition and rapid adaptability, while uncrewed vehicles focus on integration with networked warfare and persistence in hazardous environments.
Survivability and Protection Measures
Main battle tanks (MBTs) offer superior survivability through advanced composite armor, active protection systems (APS), and reinforced hull designs that withstand kinetic and explosive threats. Uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) enhance protection by minimizing crew risk, employing lightweight armor, and utilizing remote operation to avoid direct enemy engagement. Both platforms integrate electronic countermeasures and sensor fusion to detect and neutralize incoming threats, but MBTs prioritize physical resilience while UGVs emphasize tactical risk reduction through autonomy.
Firepower and Lethality Comparison
Main battle tanks (MBTs) typically feature high-caliber smoothbore cannons like the 120mm or 125mm guns, capable of firing a variety of armor-piercing and guided munitions that ensure superior firepower against armored targets. Uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) usually carry lighter weapons systems, such as automatic cannons or guided missile launchers, optimized for precision strikes and support roles rather than direct tank engagements. While MBTs deliver greater raw lethality through powerful main guns and robust ammunition, UGVs enhance battlefield effectiveness by leveraging advanced targeting systems, reduced crew risk, and flexible deployment in contested environments.
Mobility and Tactical Flexibility
Main battle tanks (MBTs) offer superior tactical flexibility through armored protection and heavy firepower, enabling aggressive frontline engagement and rapid response to evolving combat scenarios. Uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) excel in enhanced mobility by navigating hazardous or complex terrains without risking personnel, providing reconnaissance and flanking capabilities in dangerous zones. While MBTs dominate in shock action, UGVs complement missions with stealthy maneuverability and persistent operational presence in contested environments.
Sensor Suites and Battlefield Awareness
Main battle tanks rely on advanced multispectral sensor suites, including thermal imaging, radar, and laser rangefinders, to detect and engage targets in diverse combat environments. Uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) integrate sophisticated sensors such as LiDAR, high-resolution cameras, and AI-powered threat detection systems to provide enhanced situational awareness and real-time battlefield data without risking human life. The fusion of sensor inputs in UGVs enables rapid decision-making and autonomous navigation, offering a strategic advantage in reconnaissance and target acquisition compared to traditional manned vehicles.
Human-Machine Integration in Modern Warfare
Main battle tanks (MBTs) exemplify human-machine integration in modern warfare through direct crew control, leveraging advanced targeting systems and battlefield communication networks for coordinated operations. Uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) enhance combat capabilities by autonomously executing reconnaissance, logistics, and precision strikes with minimal human intervention, reducing personnel risk in high-threat environments. The synergy between MBTs and UGVs offers combined force effectiveness by merging human tactical decision-making with autonomous systems' operational endurance and adaptability.
Cost-Effectiveness and Lifecycle Logistics
Main battle tanks (MBTs) typically incur higher acquisition and maintenance costs due to complex armor systems and manned operations, contrasting with uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) which benefit from lower personnel risk and potentially reduced lifecycle expenses. UGVs offer enhanced cost-effectiveness in prolonged deployments through modular designs that streamline repairs and upgrades, minimizing logistics burdens. Lifecycle logistics for MBTs demand extensive supply chains for fuel, crew support, and parts, whereas UGVs leverage automation to simplify maintenance processes and optimize resource allocation.
Future Trends: Synergy or Competition?
Main battle tanks (MBTs) continue to dominate armored warfare with heavy firepower and armor protection, while uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) offer enhanced reconnaissance, reduced human risk, and networked battlefield integration. Future trends indicate increasing synergy as MBTs integrate UGV support for target acquisition, electronic warfare, and logistics, enhancing overall combat effectiveness. Advances in AI, autonomous navigation, and sensor fusion will drive collaborative operations rather than direct competition between MBTs and UGVs.
Related Important Terms
Autonomous Combat UGV
Autonomous combat uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) are transforming modern warfare by offering enhanced operational flexibility, reducing risk to personnel, and enabling persistent surveillance and target engagement in complex environments. Unlike traditional main battle tanks, these UGVs leverage advanced AI, sensor fusion, and remote control capabilities to execute precise missions with reduced logistic footprints and increased adaptability on dynamic battlefields.
Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T)
Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T) leverages the strategic strengths of main battle tanks and uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) by integrating human decision-making with autonomous systems to enhance battlefield situational awareness and operational efficiency. This collaboration allows main battle tanks to extend their reach and survivability through remote UGV reconnaissance, target acquisition, and threat neutralization, thereby transforming traditional armored warfare dynamics.
Remote Weapon Station Integration
Main battle tanks benefit from Remote Weapon Station (RWS) integration by enhancing crew survivability and situational awareness through stabilized, remotely operated weapon systems with advanced targeting sensors. Uncrewed ground vehicles equipped with RWS offer autonomous or remote offensive capabilities, enabling precision engagement in high-risk environments without endangering personnel.
Swarm Robotics
Main battle tanks (MBTs) exhibit unmatched firepower and armor protection, but uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) leveraging swarm robotics enable distributed, adaptive combat strategies with enhanced situational awareness and reduced human risk. Swarm robotics in UGVs enhances operational flexibility by allowing coordinated maneuvers, target acquisition, and damage mitigation, challenging the traditional dominance of MBTs on modern battlefields.
AI-Driven Threat Detection
Main battle tanks equipped with advanced AI-driven threat detection systems can identify and engage targets with high precision, enhancing battlefield survivability and lethality. Uncrewed ground vehicles leverage AI for autonomous threat recognition and rapid response, enabling remote operations that minimize human risk while maintaining situational awareness.
Teleoperated Tank Support
Teleoperated tank support enhances main battle tank operations by providing remote firepower and reconnaissance capabilities without risking crew safety, significantly improving battlefield adaptability and survivability. Integrating uncrewed ground vehicles with manned tanks leverages advanced sensor networks and autonomous navigation to execute high-risk missions and counter threats more efficiently.
Silent Mobility Platforms
Silent mobility platforms in main battle tanks leverage advanced thermal insulation and noise reduction technologies to minimize acoustic and infrared signatures, enhancing survivability in contested environments. Uncrewed ground vehicles prioritize stealth through electric propulsion and lightweight composite materials, enabling discreet reconnaissance and precision strikes without exposing operators to direct threats.
Loitering Munition Deployment
Main battle tanks provide armored firepower and crewed decision-making on the battlefield, but uncrewed ground vehicles equipped with loitering munitions offer increased operational flexibility and reduced crew risk by autonomously surveilling and engaging targets. Loitering munitions deployed from uncrewed platforms enhance precision strike capabilities against enemy armor and fortifications, complementing traditional tank units in contested environments.
Hybrid Crew Configurations
Hybrid crew configurations in main battle tanks integrate human operators with autonomous uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) to enhance battlefield adaptation and operational resilience. This synergy leverages human decision-making alongside UGVs' remote sensing and precision targeting, optimizing force projection in complex combat scenarios.
Active Protection System (APS) Integration
Main battle tanks equipped with advanced Active Protection Systems (APS) provide enhanced survivability against anti-tank guided missiles and RPGs, whereas uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) integrate APS for threat detection and interception while maintaining autonomous operation capabilities. APS integration in both platforms employs radar and sensor fusion technology, but UGVs benefit from real-time data processing and remote control adaptability, optimizing battlefield threat neutralization.
Main battle tank vs Uncrewed ground vehicle Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com