Naval mines are traditional explosive devices anchored underwater to damage or sink enemy vessels upon contact, relying on passive mechanisms for detonation. Smart mines incorporate advanced sensors and technology to differentiate targets, enabling selective activation and improved strategic deployment. These intelligent systems reduce collateral damage and enhance maritime defense capabilities through real-time threat assessment.
Table of Comparison
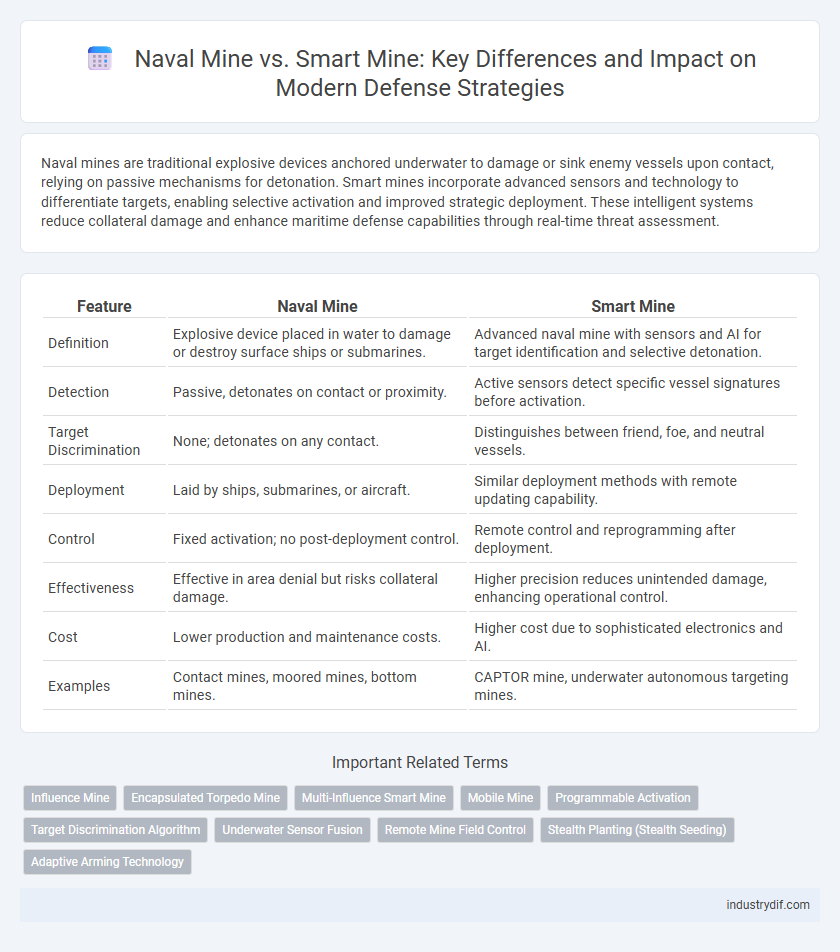
| Feature | Naval Mine | Smart Mine |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Explosive device placed in water to damage or destroy surface ships or submarines. | Advanced naval mine with sensors and AI for target identification and selective detonation. |
| Detection | Passive, detonates on contact or proximity. | Active sensors detect specific vessel signatures before activation. |
| Target Discrimination | None; detonates on any contact. | Distinguishes between friend, foe, and neutral vessels. |
| Deployment | Laid by ships, submarines, or aircraft. | Similar deployment methods with remote updating capability. |
| Control | Fixed activation; no post-deployment control. | Remote control and reprogramming after deployment. |
| Effectiveness | Effective in area denial but risks collateral damage. | Higher precision reduces unintended damage, enhancing operational control. |
| Cost | Lower production and maintenance costs. | Higher cost due to sophisticated electronics and AI. |
| Examples | Contact mines, moored mines, bottom mines. | CAPTOR mine, underwater autonomous targeting mines. |
Evolution of Naval Mines: Traditional to Smart Technology
Naval mines have evolved from traditional contact and magnetic-triggered devices to sophisticated smart mines equipped with advanced sensors and AI-driven targeting systems. These smart mines can distinguish between different ship classes, reducing collateral damage and increasing operational efficiency. Integration of remote activation and real-time data transmission further enhances their strategic value in modern naval warfare.
Key Differences Between Naval and Smart Mines
Naval mines are traditional explosive devices deployed in maritime environments to obstruct enemy vessels, activated by contact, magnetic, or acoustic triggers. Smart mines incorporate advanced sensors, programmable logic, and communication systems to distinguish between different ship types, enhancing target discrimination and reducing collateral damage. Unlike naval mines, smart mines can be remotely controlled, reprogrammed, and integrated into wider network-centric warfare systems for improved operational flexibility.
Strategic Roles of Naval Mines in Modern Warfare
Naval mines serve as cost-effective area denial weapons, creating strategic barriers to restrict enemy naval movement and protect critical sea lanes. Smart mines enhance this role by incorporating sensors and programmable targeting algorithms, enabling selective activation against specific vessel types and minimizing unintended damage. Their deployment shapes maritime tactics by controlling strategic chokepoints and forcing adversaries into predictable, vulnerable routes.
Innovations Powering Smart Mine Capabilities
Smart mines incorporate advanced sensors, AI algorithms, and remote communication systems to enhance detection accuracy and threat assessment in maritime defense. These innovations enable real-time data transmission and adaptive targeting, significantly improving operational efficiency compared to traditional naval mines. Integration with network-centric warfare platforms allows smart mines to respond dynamically to environmental changes and enemy maneuvers.
Detection and Countermeasure Techniques
Naval mines rely on traditional detection methods such as sonar, magnetic anomaly detectors, and underwater drones, yet they are often countered by sweeping techniques and explosive ordnance disposal teams. Smart mines incorporate advanced sensors, AI-based target recognition, and communication capabilities, complicating detection through adaptive signatures and remote activation, requiring integrated electronic warfare and machine learning-enabled countermeasures. Effective defense against smart mines leverages multi-sensor fusion, autonomous underwater vehicles equipped with neural networks, and real-time data analytics to neutralize threats before activation.
Deployment Methods: Conventional vs. Intelligent Systems
Naval mines are traditionally deployed using ships, aircraft, or submarines, relying on pre-set patterns and manual placement for area denial or channel blocking. Smart mines utilize intelligent systems that enable autonomous deployment, adapting to environmental conditions and threat detection to optimize coverage and target engagement. Advanced sensors and communication networks allow smart mines to be remotely controlled or self-activated, enhancing strategic flexibility and minimizing collateral damage.
Operational Advantages of Smart Mines
Smart mines provide enhanced operational advantages over traditional naval mines through advanced sensor integration and programmable targeting capabilities. These mines can differentiate between friendly, neutral, and enemy vessels, thereby reducing the risk of unintended detonations and improving strategic deployment flexibility. Their ability to communicate with command centers allows real-time adjustments in minefield configurations, maximizing defensive efficiency and adaptability in dynamic maritime environments.
Risk Factors and Safety Considerations
Naval mines pose significant risk factors due to their unpredictable detonation triggered by contact or proximity, often causing collateral damage to both military and civilian vessels. Smart mines incorporate advanced sensors and programmable logic to differentiate targets, reducing unintended activations and enhancing safety for non-combatants. Despite improved discrimination, smart mines still require stringent safety protocols to prevent accidental deployment and ensure deactivation after conflict to minimize long-term maritime hazards.
Legal and Ethical Implications in Maritime Defense
Naval mines and smart mines carry distinct legal and ethical considerations in maritime defense, with international maritime law rigorously regulating their deployment to prevent indiscriminate harm to civilian vessels. Smart mines, equipped with advanced sensors and target discrimination technology, offer improved compliance with the principles of distinction and proportionality under the Law of Armed Conflict by reducing unintended casualties and environmental impact. However, both types demand strict adherence to legal frameworks such as the Hague and Geneva Conventions to ensure accountability and mitigate risks to neutral shipping and non-combatants.
Future Trends in Mine Warfare Technology
Future trends in mine warfare technology emphasize increased automation and network-centric capabilities, with smart mines integrating AI for target recognition and selective engagement. Naval mines are evolving from traditional passive devices to adaptive systems capable of autonomous decision-making and communication within underwater sensor networks. Enhanced stealth, reusability, and multi-effect warheads are driving the development of next-generation mines to counter advanced naval threats effectively.
Related Important Terms
Influence Mine
Influence mines, a subtype of smart naval mines, detect specific signatures such as magnetic, acoustic, or pressure changes from ships rather than relying on direct contact, enhancing target discrimination and detonation accuracy. Compared to traditional contact naval mines, influence mines increase strategic effectiveness by minimizing false triggers and adapting to modern naval countermeasures through programmable fuzing systems.
Encapsulated Torpedo Mine
The encapsulated torpedo mine represents a significant advancement over traditional naval mines by integrating a self-propelled torpedo within a protective casing, enhancing stealth and precision targeting underwater threats. Unlike conventional contact or influence mines, this smart mine utilizes advanced sensors and guidance systems to detect, track, and engage enemy vessels autonomously, increasing operational effectiveness in naval defense scenarios.
Multi-Influence Smart Mine
Multi-Influence Smart Mines represent a significant advancement over traditional Naval Mines by integrating acoustic, magnetic, and pressure sensors to enhance detection accuracy and target discrimination. These smart mines reduce false activations and increase lethality against modern naval vessels through adaptive threat assessment and selective engagement capabilities.
Mobile Mine
Naval mines are traditional unmoving explosive devices deployed to deter or damage enemy vessels, while smart mines incorporate sensors and autonomous targeting systems to selectively engage threats. Mobile mines, a subset of smart mines, enhance strategic flexibility by using propulsion mechanisms to reposition themselves underwater, increasing the effectiveness and adaptability of minefields in dynamic maritime combat environments.
Programmable Activation
Naval mines rely on preset activation mechanisms triggered by contact or basic sensors, whereas smart mines utilize programmable activation systems that enable selective deployment based on specific target signatures, environmental conditions, and real-time threat assessments. This programmable flexibility enhances strategic control and reduces collateral damage by allowing adaptive activation protocols in complex maritime defense scenarios.
Target Discrimination Algorithm
Naval mines utilize basic target activation mechanisms often relying on simple acoustic or magnetic triggers, whereas smart mines incorporate advanced target discrimination algorithms that analyze multiple sensor inputs such as acoustic, magnetic, pressure, and seismic signatures to accurately differentiate between military vessels and civilian ships. These sophisticated algorithms significantly reduce false activations and enhance threat effectiveness by identifying specific vessel classes, sizes, and movement patterns within contested maritime environments.
Underwater Sensor Fusion
Naval mines rely on basic acoustic or magnetic triggers to detect targets, whereas smart mines utilize advanced underwater sensor fusion techniques, integrating sonar, pressure, and electric field sensors for precise threat identification and reduced false alarms. This multi-sensor fusion enhances target discrimination and situational awareness, enabling smart mines to adapt to dynamic underwater environments and selectively engage high-value naval assets.
Remote Mine Field Control
Naval mines deployed for maritime defense typically lack real-time adaptability, while smart mines integrate advanced sensors and communication capabilities enabling remote minefield control for dynamic threat response. Remote minefield control allows for selective activation or deactivation of smart mines, minimizing risks to friendly vessels and enhancing strategic maritime security management.
Stealth Planting (Stealth Seeding)
Naval mines are traditionally deployed through predictable patterns that risk early detection, whereas smart mines utilize stealth planting techniques incorporating low-noise propulsion and adaptive deployment algorithms to minimize acoustic and magnetic signatures. This advanced stealth seeding enables smart mines to remain undetected in contested waters, enhancing strategic area denial while reducing vulnerability to countermeasure systems.
Adaptive Arming Technology
Naval mines equipped with Adaptive Arming Technology adjust detonation parameters based on real-time environmental data and vessel characteristics, enhancing threat discrimination and operational safety. Smart mines leverage sensors and algorithms to dynamically adapt arming states, minimizing collateral damage while maximizing strategic effectiveness in diverse maritime conditions.
Naval Mine vs Smart Mine Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com