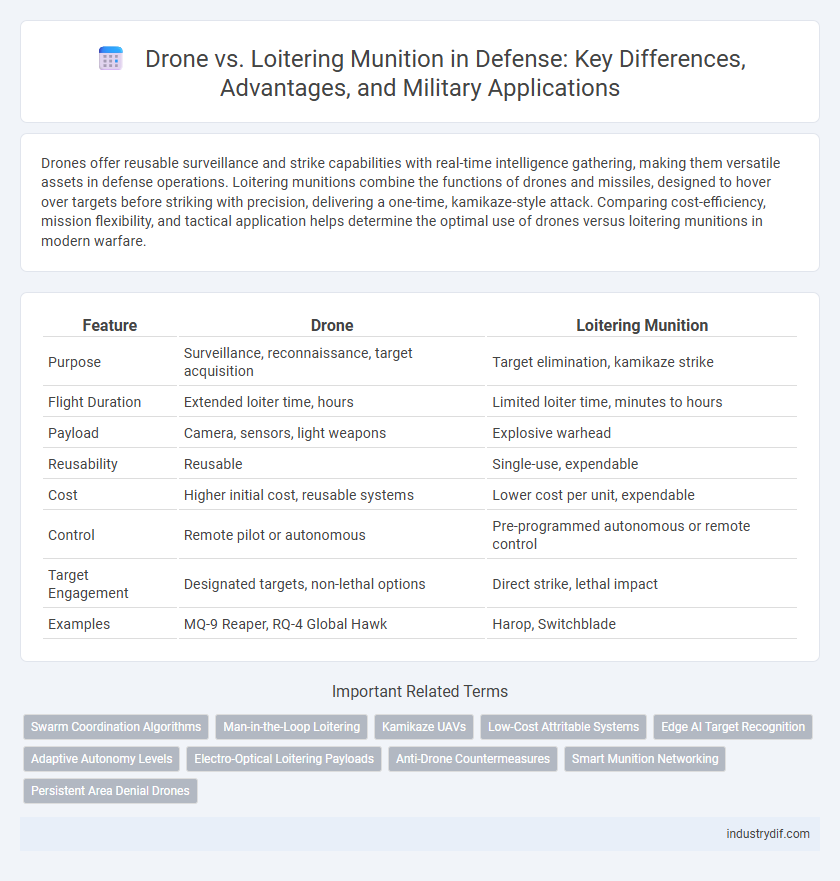
Drones offer reusable surveillance and strike capabilities with real-time intelligence gathering, making them versatile assets in defense operations. Loitering munitions combine the functions of drones and missiles, designed to hover over targets before striking with precision, delivering a one-time, kamikaze-style attack. Comparing cost-efficiency, mission flexibility, and tactical application helps determine the optimal use of drones versus loitering munitions in modern warfare.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Drone | Loitering Munition |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Surveillance, reconnaissance, target acquisition | Target elimination, kamikaze strike |
| Flight Duration | Extended loiter time, hours | Limited loiter time, minutes to hours |
| Payload | Camera, sensors, light weapons | Explosive warhead |
| Reusability | Reusable | Single-use, expendable |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, reusable systems | Lower cost per unit, expendable |
| Control | Remote pilot or autonomous | Pre-programmed autonomous or remote control |
| Target Engagement | Designated targets, non-lethal options | Direct strike, lethal impact |
| Examples | MQ-9 Reaper, RQ-4 Global Hawk | Harop, Switchblade |
Defining Drones and Loitering Munitions
Drones, also known as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), are remotely piloted or autonomous aircraft designed for reconnaissance, surveillance, and targeted strikes in defense operations. Loitering munitions, often called suicide drones, combine surveillance capabilities with explosive payloads, enabling them to hover over a target area before engaging in a precise attack. These systems differ from traditional drones by integrating loiter time with strike functionality, providing tactical flexibility in modern warfare.
Historical Evolution of Unmanned Systems
Unmanned systems evolved significantly since World War II with early radio-controlled drones like the German V-1 flying bomb, laying groundwork for modern loitering munitions and reconnaissance drones. Advances in GPS navigation, miniaturized sensors, and real-time data links in the 21st century accelerated the development of precision-guided loitering munitions capable of extended airborne endurance and target engagement. The convergence of drone technology and loitering munitions now drives asymmetric warfare strategies, with roots tracing back to Cold War reconnaissance UAVs and expendable missile systems.
Key Technological Differences
Drones feature reusable, multi-mission platforms equipped with advanced navigation systems, real-time data links, and versatile payload capacities, enabling surveillance, reconnaissance, and precision strikes. Loitering munitions combine drone-like flight with expendable, kamikaze-style strike capabilities, integrating autonomous target recognition and guided explosive delivery. Key technological distinctions include drones' emphasis on endurance and adaptability versus loitering munitions' focus on single-use, high-precision lethality through embedded warheads and terminal guidance systems.
Operational Roles in Modern Warfare
Drones serve critical roles in intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance (ISR), and precision strike missions, offering reusable platforms that provide persistent battlefield awareness and adaptable targeting. Loitering munitions combine the capabilities of drones and guided missiles, designed for one-time use to identify, track, and destroy high-value targets with minimal collateral damage. Both systems enhance operational flexibility but differ fundamentally in lifespan and mission execution, influencing their deployment in modern warfare strategies.
Payload Capabilities and Versatility
Drones offer greater payload capacity and versatile modular design, enabling them to carry various sensors, communication devices, and precision-guided munitions for multi-mission adaptability. Loitering munitions typically feature integrated warheads optimized for target destruction, prioritizing precision strike over payload variety. The payload adaptability of drones supports diverse operational requirements, whereas loitering munitions specialize in delivering focused explosive effects with high accuracy.
Guidance Systems and Autonomy
Loitering munitions integrate advanced autonomous guidance systems, combining real-time target acquisition with precision strike capabilities, surpassing traditional drone reliance on remote pilot control. These systems utilize GPS, inertial navigation, and AI-driven image recognition to enhance mission adaptability and reduce operator intervention. Enhanced autonomy in loitering munitions enables dynamic decision-making in contested environments, optimizing target engagement and survivability compared to conventional drones.
Cost Analysis and Resource Allocation
Loitering munitions generally offer higher precision at a lower operational cost compared to traditional drones, making them cost-effective for targeted strikes in defense scenarios. Resource allocation favors loitering munitions when minimizing collateral damage and maximizing strike efficiency are critical, optimizing both manpower and budget. Conversely, drones provide broader reconnaissance capabilities but incur higher maintenance and training costs, impacting long-term defense expenditure.
Effectiveness in Contested Environments
Loitering munitions offer persistent surveillance and precision strikes in contested environments, reducing risk to personnel by combining reconnaissance and attack capabilities in a single platform. Drones provide longer endurance and flexibility for intelligence gathering but often require separate munition deployment, which may increase exposure to enemy defenses. Effectiveness hinges on mission parameters, with loitering munitions excelling in rapid target engagement and drones favored for sustained situational awareness.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
Regulatory frameworks governing drones and loitering munitions differ significantly due to their distinct operational roles and potential for lethality, with most countries imposing stricter controls on loitering munitions under international arms treaties. Legal considerations emphasize compliance with the laws of armed conflict and rules of engagement, mandating rigorous identification and targeting protocols to minimize civilian harm. Emerging policies also address challenges related to autonomous decision-making, accountability, and cross-border use, highlighting the need for clear regulations on export controls and permissible deployment zones.
Future Trends in Unmanned Defense Systems
Future trends in unmanned defense systems emphasize increasing integration of artificial intelligence in drones and loitering munitions to enhance autonomous target recognition and decision-making capabilities. Advances in sensor fusion and swarm technology are enabling coordinated operations between multiple unmanned platforms, improving battlefield situational awareness and strike precision. The development of stealthier, longer-endurance drones and loitering munitions is set to revolutionize reconnaissance and precision strike missions in contested environments.
Related Important Terms
Swarm Coordination Algorithms
Swarm coordination algorithms in drones enable autonomous, real-time decision-making and dynamic target allocation, enhancing mission adaptability and resilience against electronic countermeasures. Loitering munitions rely on similar algorithms but prioritize precision strike coordination and synchronized attack vectors, optimizing lethality in contested environments.
Man-in-the-Loop Loitering
Man-in-the-Loop loitering munitions integrate real-time operator control, allowing precise target identification and engagement while minimizing collateral damage, unlike autonomous drones that may operate with limited human oversight. These systems enhance battlefield adaptability by combining the extended surveillance capabilities of drones with the selective strike precision of human-controlled loitering munitions.
Kamikaze UAVs
Kamikaze UAVs, a type of loitering munition, combine reconnaissance capabilities with precision strike functionality, enabling targeted, real-time engagement of enemy assets with minimal collateral damage. Unlike traditional drones focused on surveillance, these loitering munitions autonomously search, identify, and destroy high-value targets, enhancing battlefield efficiency and reducing operator risk.
Low-Cost Attritable Systems
Low-cost attritable systems like loitering munitions offer a cost-effective alternative to traditional drones by enabling strike capabilities with expendable platforms designed for one-way missions. These systems reduce risks to high-value assets and personnel while providing flexible, persistent surveillance and targeted engagement in contested environments.
Edge AI Target Recognition
Edge AI target recognition enhances both drones and loitering munitions by enabling real-time, on-device processing of sensor data to accurately identify threats with minimal latency and reduced communication dependency. This capability significantly improves mission effectiveness in contested environments by allowing autonomous decision-making and faster target engagement while minimizing electronic warfare vulnerabilities.
Adaptive Autonomy Levels
Adaptive autonomy levels in drones enable real-time mission adjustments, enhancing operational flexibility and endurance, while loitering munitions leverage preset autonomy to prioritize target acquisition and strike effectiveness. Optimizing these autonomy frameworks improves threat response, reduces operator burden, and maximizes tactical advantage in contested environments.
Electro-Optical Loitering Payloads
Electro-optical loitering payloads in drones and loitering munitions provide real-time intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities with high-resolution imaging and extended target tracking, enhancing battlefield situational awareness. These payloads enable precision targeting by integrating advanced sensors such as infrared and thermal cameras, improving threat identification and reducing collateral damage in defense operations.
Anti-Drone Countermeasures
Loitering munitions are designed for precision strikes by lingering over targets, while drones primarily serve reconnaissance or multi-mission roles, influencing distinct anti-drone countermeasures strategies. Effective defense against these threats requires radar and RF signal jamming to disrupt drone control, alongside directed-energy weapons and kinetic interceptors optimized for neutralizing both loitering munitions and surveillance drones.
Smart Munition Networking
Smart munition networking enhances the capabilities of both drones and loitering munitions by enabling real-time data sharing, coordinated target acquisition, and dynamic mission adjustments, significantly improving battlefield efficiency and precision strikes. Advanced communication protocols and AI-driven algorithms facilitate seamless integration within defense networks, allowing drones to act as forward scouts while loitering munitions execute precision attacks based on shared intelligence.
Persistent Area Denial Drones
Persistent area denial drones provide continuous surveillance and rapid response capabilities, outperforming loitering munitions in sustained operational endurance and real-time target engagement. Equipped with advanced sensor fusion and autonomous target recognition, these drones enhance battlefield control by maintaining prolonged presence over strategic zones without immediate detonation constraints.
Drone vs Loitering munition Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com