Standard issue rifles provide reliable, straightforward functionality with proven durability and ease of use in diverse combat environments. Smart weapons incorporate advanced targeting systems, real-time data integration, and enhanced situational awareness, improving accuracy and tactical decision-making. The choice between the two depends on mission requirements, technological infrastructure, and the operator's training level.
Table of Comparison
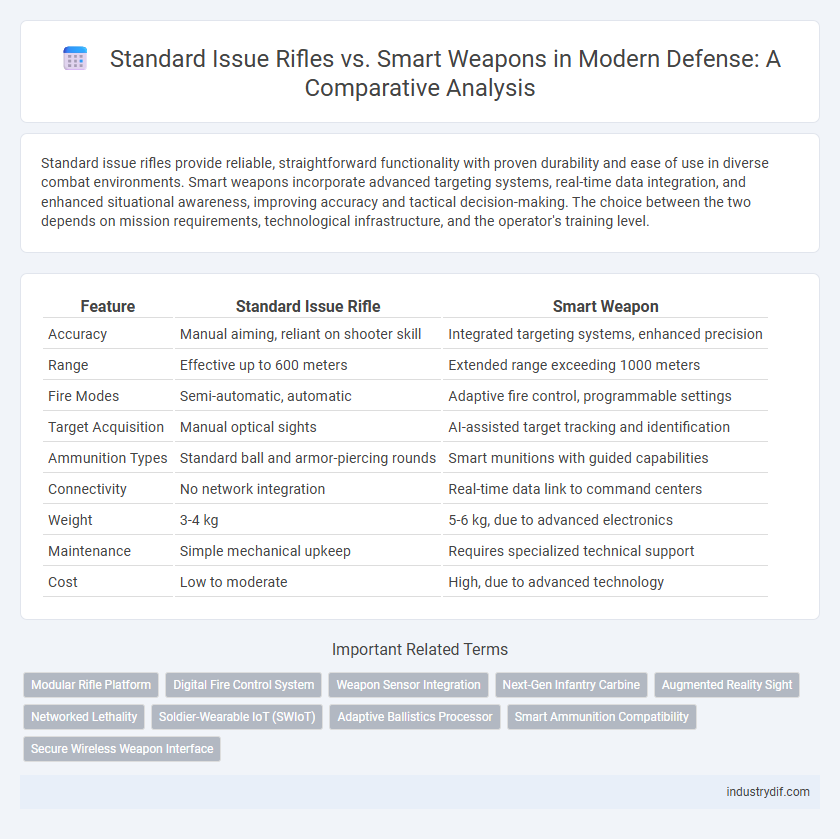
| Feature | Standard Issue Rifle | Smart Weapon |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Manual aiming, reliant on shooter skill | Integrated targeting systems, enhanced precision |
| Range | Effective up to 600 meters | Extended range exceeding 1000 meters |
| Fire Modes | Semi-automatic, automatic | Adaptive fire control, programmable settings |
| Target Acquisition | Manual optical sights | AI-assisted target tracking and identification |
| Ammunition Types | Standard ball and armor-piercing rounds | Smart munitions with guided capabilities |
| Connectivity | No network integration | Real-time data link to command centers |
| Weight | 3-4 kg | 5-6 kg, due to advanced electronics |
| Maintenance | Simple mechanical upkeep | Requires specialized technical support |
| Cost | Low to moderate | High, due to advanced technology |
Evolution of Infantry Firearms
Standard issue rifles represent the traditional backbone of infantry firearms, characterized by proven reliability, straightforward mechanics, and ease of mass production. Smart weapons incorporate advanced technologies such as integrated sensors, computerized targeting systems, and network connectivity, significantly enhancing accuracy and situational awareness on the battlefield. The evolution from standard rifles to smart weapons reflects a strategic shift towards increased lethality, precision, and interoperability in modern infantry combat scenarios.
Defining Standard Issue Rifles
Standard issue rifles serve as the primary firearm distributed to soldiers, designed for reliability, ease of use, and mass production to meet diverse combat scenarios. These rifles typically feature conventional ballistics, manual aiming systems, and mechanical operation suitable for various terrains and conditions. Their standardized design ensures compatibility with existing ammunition, accessories, and maintenance protocols essential for coordinated defense strategies.
What Constitutes a Smart Weapon?
A smart weapon integrates advanced technologies such as sensors, GPS, and digital targeting systems to enhance accuracy and situational awareness beyond standard issue rifles. These weapons utilize real-time data processing to make autonomous or semi-autonomous targeting decisions, reducing human error on the battlefield. Enhanced connectivity with command systems allows smart weapons to adapt dynamically to changing combat conditions, offering a significant tactical advantage over traditional firearms.
Key Technological Differences
Standard issue rifles utilize traditional ballistic ammunition with mechanical firing systems, emphasizing reliability and ease of maintenance under diverse combat conditions. Smart weapons integrate advanced electronics, incorporating sensors, computerized targeting systems, and network connectivity to enhance accuracy and real-time situational awareness. Key technological differences include the presence of embedded microprocessors, laser rangefinders, and guided munitions capabilities in smart weapons, contrasting with the manual targeting and fixed ballistics performance of standard rifles.
Accuracy and Target Acquisition
Standard issue rifles offer reliable accuracy with consistent performance across various environmental conditions, utilizing iron sights or basic optical scopes. Smart weapons enhance target acquisition through integrated advanced sensors, real-time data processing, and automated tracking systems, significantly improving hit probability in dynamic combat scenarios. The fusion of digital targeting technologies in smart weapons reduces human error and accelerates engagement time, outperforming traditional rifles in precision and efficiency.
Maintenance and Reliability
Standard issue rifles are known for their simplicity, ease of maintenance, and proven reliability under various combat conditions, often requiring minimal specialized tools or training for upkeep. Smart weapons incorporate advanced electronics and software systems, which can enhance targeting and adaptability but introduce complexities in maintenance, demanding regular diagnostics and expert technical support. Reliability of smart weapons can be affected by environmental factors impacting their electronic components, whereas standard rifles generally offer consistent performance with fewer failure points in harsh field environments.
Training and Soldier Adaptation
Standard issue rifles require extensive training focused on marksmanship, weapon maintenance, and manual operation, enabling soldiers to develop muscle memory and tactical discipline. Smart weapons integrate advanced targeting systems, reducing the learning curve for accuracy and situational awareness but demand additional training in digital interfaces and software troubleshooting. Soldiers adapting to smart weapons benefit from enhanced precision and real-time data feedback, yet they must balance technological reliance with traditional combat skills to maintain operational readiness.
Cost and Procurement Considerations
Standard issue rifles have lower upfront costs and simpler procurement processes due to widespread production and established supply chains, making them more accessible for large-scale military deployment. Smart weapons require higher initial investments in advanced technology integration, training, and maintenance infrastructure, often resulting in increased lifecycle costs. Procurement decisions must balance budget constraints with strategic capabilities, considering the potential long-term savings from enhanced accuracy and reduced ammunition waste offered by smart weapons.
Battlefield Applications and Limitations
Standard issue rifles offer reliability and straightforward maintenance, making them effective for consistent combat performance across varied battlefield conditions. Smart weapons incorporate advanced targeting systems, sensors, and connectivity, enhancing precision and situational awareness but often require more power and technical support. Limitations of smart weapons include higher costs, potential electronic failures in harsh environments, and increased training demands compared to conventional rifles.
Future Trends in Military Firearms
Future military firearms emphasize integrating smart technology with standard issue rifles to enhance battlefield efficiency and soldier survivability. Emerging smart weapons feature advanced targeting systems, real-time data connectivity, and adaptive ammunition capabilities, enabling precision engagement and reduced collateral damage. The evolution toward networked firearms reflects a strategic shift prioritizing interoperability, situational awareness, and automated threat assessment in modern combat operations.
Related Important Terms
Modular Rifle Platform
Standard issue rifles offer reliability and ease of maintenance through a modular rifle platform that allows quick customization of components such as barrels, stocks, and optics to suit diverse combat scenarios. Smart weapons enhance this flexibility by integrating advanced targeting systems, sensors, and connectivity features that improve accuracy, situational awareness, and networked battlefield communication.
Digital Fire Control System
Standard issue rifles rely on mechanical sights and operator skill, whereas smart weapons integrate advanced Digital Fire Control Systems to enhance targeting accuracy through real-time data analysis and automatic ballistic adjustments. This technology leverages sensors, GPS, and computerized algorithms to increase hit probability, reduce collateral damage, and improve soldier performance in diverse combat environments.
Weapon Sensor Integration
Standard issue rifles rely on manual targeting and basic iron sights, limiting situational awareness and engagement efficiency. Smart weapons incorporate advanced sensor integration such as infrared, laser rangefinders, and ballistic calculators, enhancing real-time target acquisition and improving combat accuracy and responsiveness.
Next-Gen Infantry Carbine
Next-Gen Infantry Carbines integrate advanced targeting systems, biometric sensors, and adaptive fire modes, surpassing standard issue rifles in precision and battlefield adaptability. These smart weapons enhance soldier lethality through real-time data sharing and automated threat recognition, redefining infantry combat effectiveness.
Augmented Reality Sight
Standard issue rifles typically feature fixed optical sights that offer reliable targeting but limited situational awareness, whereas smart weapons equipped with augmented reality (AR) sights enhance soldier performance by integrating real-time data overlays such as range, enemy location, and environmental conditions directly into the shooter's field of view. AR sights improve accuracy and decision-making speed by providing dynamic targeting information, reducing cognitive load and enabling quicker engagement in complex combat environments.
Networked Lethality
Standard issue rifles offer reliability and ease of maintenance, but smart weapons enhance networked lethality by integrating advanced sensors, real-time data sharing, and target tracking capabilities to increase accuracy and situational awareness on the battlefield. The ability to connect with command systems and other units enables coordinated strikes and rapid decision-making, significantly improving force effectiveness in modern combat environments.
Soldier-Wearable IoT (SWIoT)
Standard issue rifles provide reliable firepower and durability but lack integrated connectivity and real-time data sharing capabilities, limiting battlefield situational awareness. Smart weapons equipped with Soldier-Wearable IoT (SWIoT) technology enhance combat effectiveness by enabling seamless communication, target tracking, and performance monitoring through interconnected sensors and data analytics.
Adaptive Ballistics Processor
Standard issue rifles offer reliable performance with fixed ballistics parameters, whereas smart weapons equipped with Adaptive Ballistics Processors dynamically adjust trajectory calculations in real-time for enhanced targeting accuracy under varying environmental conditions. The Adaptive Ballistics Processor integrates sensor data such as wind speed, temperature, and range to optimize bullet path, significantly improving hit probability over traditional fixed-caliber rifles.
Smart Ammunition Compatibility
Smart weapons offer enhanced operational capabilities through smart ammunition compatibility, allowing integrated sensors and communication systems to optimize target engagement and improve hit probability. Standard issue rifles lack this advanced interoperability, relying on traditional ammunition without real-time data integration or adaptive targeting features.
Secure Wireless Weapon Interface
Standard issue rifles typically rely on mechanical and analog systems with limited connectivity, whereas smart weapons integrate Secure Wireless Weapon Interfaces (SWWI) that enable encrypted data transmission for real-time situational awareness and remote control. The SWWI enhances operational security by preventing unauthorized access and ensuring seamless communication between weapon systems and command networks in modern defense environments.
Standard issue rifle vs Smart weapon Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com