Certificate programs provide comprehensive, structured learning paths with formal recognition valued by employers and institutions. Digital badges offer flexible, micro-credentialing that showcases specific skills or achievements through easily shareable, verifiable online formats. Both serve as impactful tools for skill validation, catering to different educational needs and professional goals.
Table of Comparison
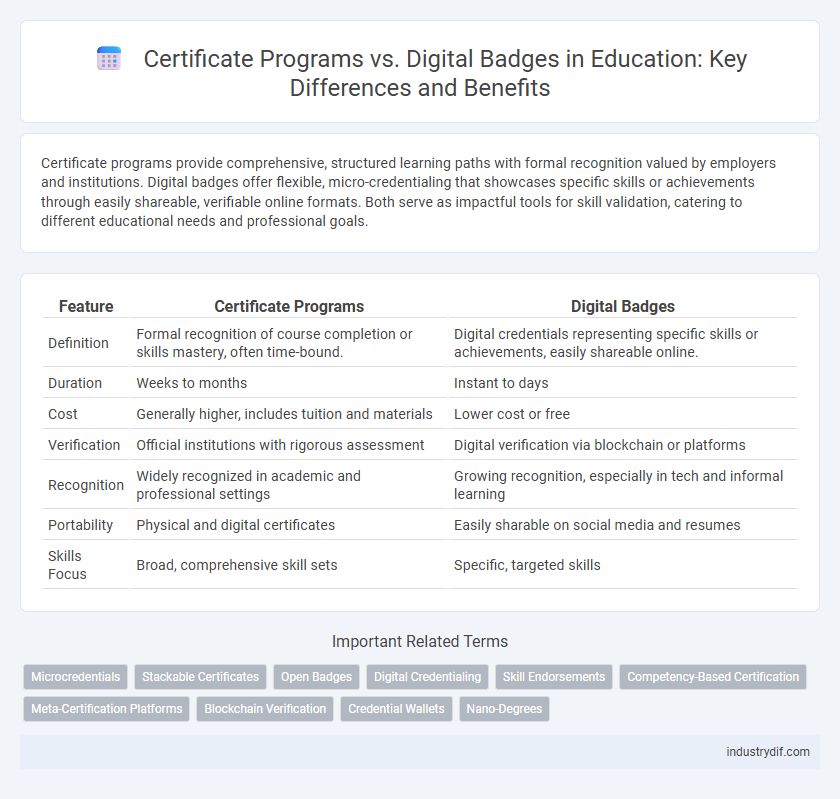
| Feature | Certificate Programs | Digital Badges |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal recognition of course completion or skills mastery, often time-bound. | Digital credentials representing specific skills or achievements, easily shareable online. |
| Duration | Weeks to months | Instant to days |
| Cost | Generally higher, includes tuition and materials | Lower cost or free |
| Verification | Official institutions with rigorous assessment | Digital verification via blockchain or platforms |
| Recognition | Widely recognized in academic and professional settings | Growing recognition, especially in tech and informal learning |
| Portability | Physical and digital certificates | Easily sharable on social media and resumes |
| Skills Focus | Broad, comprehensive skill sets | Specific, targeted skills |
Understanding Certificate Programs
Certificate programs provide structured, comprehensive learning experiences designed to impart specialized skills and knowledge in a specific field, often culminating in a formal document that validates achievement. These programs typically require a longer time commitment and include assessments to ensure competency, making them highly regarded by employers and educational institutions. Compared to digital badges, certificate programs offer deeper credibility and recognition due to their rigorous curriculum and accreditation standards.
What Are Digital Badges?
Digital badges are digital representations of skills, achievements, or competencies earned through specific learning activities or educational milestones. They encapsulate metadata that includes issuer information, criteria for earning, evidence of achievement, and expiration dates, making them verifiable and shareable across online platforms. These micro-credentials provide learners with flexible, personalized recognition that complements or enhances traditional certificate programs in education and professional development.
Key Differences Between Certificates and Badges
Certificate programs typically require completion of comprehensive coursework and assessments, providing formal recognition of mastery in a subject, often verified by educational institutions. Digital badges represent specific skills or achievements, are more granular, easily shareable online, and often issued through blockchain or digital platforms to ensure authenticity. The key difference lies in scope and formality: certificates cover broader learning outcomes with standardized formats, while badges highlight individual competencies and micro-credentials, appealing to continuous learning and professional development.
Industry Recognition and Credibility
Certificate programs often carry greater industry recognition and credibility due to their comprehensive curriculum, rigorous assessment, and endorsement by accredited institutions. Digital badges provide flexible, micro-credentialing that highlights specific skills but may lack the widespread acceptance of formal certificates. Employers typically value certificate programs higher for validating expertise, while digital badges are gaining traction for continuous professional development and skill verification.
Duration and Learning Commitment
Certificate programs typically require a longer duration, ranging from several weeks to months, demanding a substantial learning commitment and structured curriculum completion. Digital badges offer more flexibility with shorter learning cycles, often achievable in hours or days, allowing learners to acquire specific skills or competencies at their own pace. The duration and commitment levels directly influence the depth of knowledge and recognition associated with each credential in educational and professional contexts.
Skills Representation and Validation
Certificate programs offer comprehensive skill validation through structured coursework and assessments, providing formal recognition often recognized by employers and educational institutions. Digital badges represent specific skills or achievements using metadata that verifies the holder's competency in real-time, enabling instant and verifiable skill credentials across digital platforms. Both forms enhance skills representation, but certificates emphasize formal education pathways while digital badges prioritize flexible, micro-credentialing within skill ecosystems.
Cost Comparison: Certificates vs Badges
Certificate programs typically involve higher costs due to course fees, materials, and exam charges, often ranging from several hundred to thousands of dollars. Digital badges offer a cost-effective alternative, with many available for free or at a fraction of the price, leveraging online platforms and micro-credentialing systems. The affordability of digital badges makes them accessible for continuous skill development and professional recognition without the financial burden associated with traditional certificates.
Employment Value and Career Impact
Certificate programs provide comprehensive skill validation that employers often recognize as evidence of formal training, enhancing candidates' credibility in competitive job markets. Digital badges offer micro-credentialing that highlights specific competencies and achievements, allowing professionals to showcase targeted skills quickly and boost career opportunities in evolving industries. Both credentials support career advancement, but certificates tend to carry greater weight for roles requiring in-depth expertise, while digital badges excel in demonstrating ongoing learning and adaptability.
Technology and Accessibility
Certificate programs offer comprehensive technology-focused curricula that provide in-depth knowledge and skills, often recognized by academic institutions and employers. Digital badges emphasize accessibility by enabling learners to earn and share micro-credentials online, facilitating immediate validation of specific competencies. Both forms leverage e-learning platforms to enhance flexibility, but digital badges excel in quick, stackable recognition ideal for evolving tech skills.
Choosing the Right Path for Professional Growth
Certificate programs offer comprehensive, structured learning and recognized credentials that enhance career advancement opportunities, while digital badges provide flexible, skill-specific recognition suited for showcasing targeted competencies. Evaluating industry relevance, time commitment, and long-term career goals is essential to select the credential that aligns with professional growth objectives. Employers increasingly value micro-credentials like digital badges for up-to-date skills, but certificates often carry stronger weight in formal education and certification requirements.
Related Important Terms
Microcredentials
Microcredentials such as certificate programs and digital badges offer flexible, skill-specific recognition to enhance employability and lifelong learning. Certificate programs typically provide comprehensive, formal instruction with in-depth assessment, whereas digital badges represent verified competencies or micro-skills recognized by industry and educational institutions.
Stackable Certificates
Stackable certificates offer a flexible, modular approach to education by allowing learners to accumulate credentials that build toward a comprehensive qualification, contrasting with digital badges which primarily signify specific skills or achievements. This structure enhances career advancement by providing clear, progressive milestones within certificate programs, supporting lifelong learning and workforce adaptability.
Open Badges
Open Badges, a type of digital badge, offer verifiable and shareable recognition for specific skills and achievements, providing a flexible alternative to traditional certificate programs that often require longer time commitments and broader coursework. These open standards enhance learner portability by enabling easy integration with resumes and online profiles, fostering micro-credentialing in education and workforce development.
Digital Credentialing
Digital credentialing through digital badges offers verifiable, shareable achievements that are earned for specific skills or competencies, providing flexibility and micro-learning recognition in education. Certificate programs typically represent broader course completion, while digital badges enable granular tracking of learner progress across diverse educational platforms.
Skill Endorsements
Certificate programs offer comprehensive validation of skill mastery through formal coursework and assessments, while digital badges provide micro-credentials highlighting specific skill endorsements that can be easily shared across professional platforms. Employers increasingly recognize digital badges for their ability to verify targeted competencies and continuous learning in real-time.
Competency-Based Certification
Competency-based certification emphasizes mastery of specific skills and knowledge, with certificate programs offering structured, comprehensive learning paths while digital badges provide micro-credentials that validate discrete competencies in real-time. Both formats enhance professional development but differ in scope and flexibility, catering to diverse learner needs and industry demands.
Meta-Certification Platforms
Meta-certification platforms enhance credential transparency by integrating certificate programs and digital badges into unified, verifiable profiles, enabling employers and educators to assess skills and learning outcomes more effectively. These platforms leverage blockchain and digital identity technologies to securely validate and share achievements across diverse education and professional ecosystems.
Blockchain Verification
Certificate programs offer formal recognition of skills through comprehensive coursework, while digital badges provide micro-credentials verified via blockchain technology, ensuring tamper-proof authentication and instant sharing capabilities. Blockchain verification strengthens trust in digital badges by maintaining transparent, immutable records of achievements, enabling educators and employers to efficiently validate credentials.
Credential Wallets
Certificate programs offer formal recognition of skills and often integrate seamlessly into credential wallets, providing verifiable proof of achievement for employers and institutions. Digital badges complement this by enabling micro-credentialing that can be stored and shared within these wallets for a flexible, skills-based validation system.
Nano-Degrees
Nano-degrees offer a comprehensive and industry-recognized learning experience that surpasses traditional certificate programs by providing specialized skills in emerging fields such as AI, data science, and digital marketing. Digital badges complement nano-degrees by visually representing specific competencies and micro-credentials earned, enhancing employability through verifiable skill endorsements across professional networks.
Certificate Programs vs Digital Badges Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com