Teacher-centered learning emphasizes direct instruction where the teacher controls the content and pace, often leading to passive student participation. Student-centered learning prioritizes active engagement, encouraging learners to take responsibility for their own education through collaboration and critical thinking. Shifting from teacher-centered to student-centered approaches enhances motivation, creativity, and deeper understanding in educational settings.
Table of Comparison
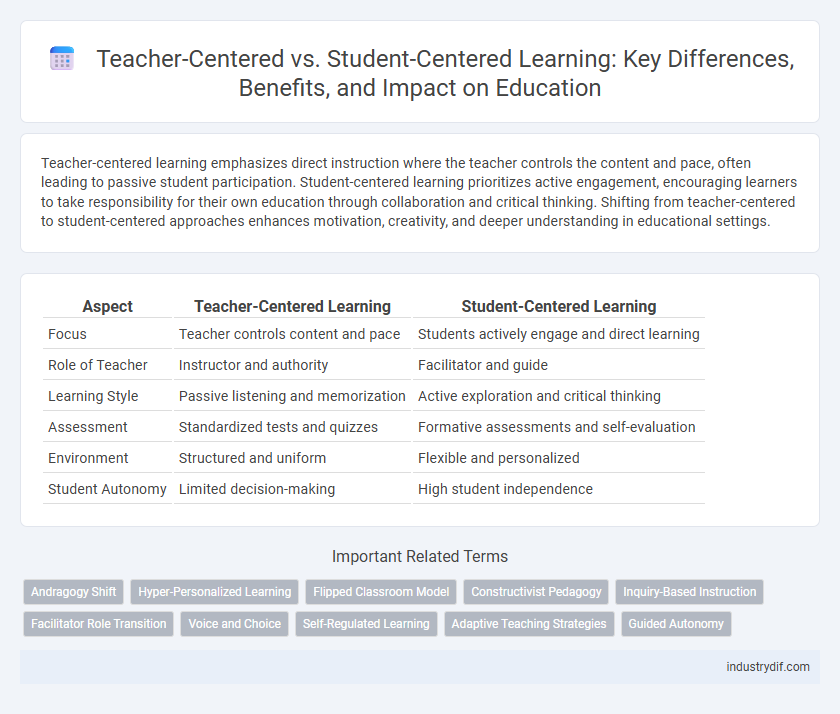
| Aspect | Teacher-Centered Learning | Student-Centered Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Teacher controls content and pace | Students actively engage and direct learning |
| Role of Teacher | Instructor and authority | Facilitator and guide |
| Learning Style | Passive listening and memorization | Active exploration and critical thinking |
| Assessment | Standardized tests and quizzes | Formative assessments and self-evaluation |
| Environment | Structured and uniform | Flexible and personalized |
| Student Autonomy | Limited decision-making | High student independence |
Defining Teacher-Centered Learning
Teacher-centered learning is an instructional approach where the teacher directs the lesson, controls the content, and makes key decisions regarding the learning process, focusing on knowledge transmission. In this model, students play a passive role, receiving information through lectures, demonstrations, and structured activities. The emphasis lies on standardized curricula, teacher authority, and assessment methods that prioritize memorization and factual recall.
Understanding Student-Centered Learning
Student-centered learning emphasizes active student participation, promoting critical thinking and problem-solving skills through collaborative and personalized educational experiences. This approach shifts the focus from teacher-led instruction to facilitating student autonomy, allowing learners to construct knowledge based on their interests and pace. Research indicates that student-centered methods improve motivation, engagement, and retention by aligning teaching strategies with diverse learning styles and needs.
Key Characteristics of Teacher-Centered Approaches
Teacher-centered learning emphasizes direct instruction where the teacher controls the content, pace, and assessment methods, ensuring a structured environment focused on knowledge transmission. This approach prioritizes lecture-based teaching, standardized testing, and clear expectations, often placing students in passive roles as information recipients. Classroom management centers on teacher authority, discipline, and uniformity, aiming to maintain order and deliver consistent educational outcomes.
Core Principles of Student-Centered Approaches
Student-centered learning prioritizes active engagement, personalized instruction, and the development of critical thinking skills, empowering learners to take ownership of their education. Core principles include collaboration, intrinsic motivation, and adaptability to diverse learning styles, fostering deeper understanding and retention. This approach contrasts with teacher-centered models by emphasizing facilitation over direct instruction and promoting learner autonomy.
Comparing Instructional Strategies
Teacher-centered learning emphasizes direct instruction where the teacher controls the content and pace, utilizing lectures and structured activities to deliver information efficiently. Student-centered learning promotes active engagement, encouraging collaboration, critical thinking, and personalized learning through discussions, projects, and inquiry-based tasks. Comparing instructional strategies reveals that teacher-centered methods prioritize knowledge transmission, while student-centered approaches foster deeper understanding and skill development by adapting to individual student needs.
Classroom Environment and Dynamics
Teacher-centered learning creates a structured classroom environment where the teacher directs all activities and controls the flow of information, emphasizing order and uniformity. Student-centered learning fosters an interactive and flexible classroom dynamic, encouraging collaboration, critical thinking, and active participation among students. This approach nurtures autonomy and adaptability, enhancing engagement and tailoring the learning experience to diverse student needs.
Assessment Methods: Traditional vs Progressive
Teacher-centered learning typically relies on traditional assessment methods such as standardized tests, quizzes, and exams that emphasize memorization and recall of factual knowledge. Student-centered learning incorporates progressive assessment methods including portfolios, peer assessments, and project-based evaluations that prioritize critical thinking, creativity, and practical application of skills. Progressive assessments provide ongoing feedback and foster deeper understanding by aligning evaluation with individual student growth and diverse learning styles.
Student Engagement and Motivation
Student-centered learning significantly enhances student engagement and motivation by actively involving learners in the educational process, fostering critical thinking, collaboration, and personalized feedback. Unlike teacher-centered learning, which often leads to passive absorption of information, student-centered approaches encourage ownership of learning and intrinsic motivation. Research shows that environments promoting autonomy and interactive participation increase not only academic achievement but also long-term enthusiasm for learning.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Teacher-centered learning often faces challenges such as limited student engagement and passive knowledge absorption, which can hinder critical thinking development and creativity. Student-centered learning may encounter difficulties in maintaining classroom management and requires significant teacher adaptability and resource availability, potentially leading to inconsistent learning outcomes. Both approaches need balanced integration to effectively address diverse learner needs and optimize educational success.
Future Trends in Instructional Paradigms
Future trends in instructional paradigms emphasize a shift from teacher-centered learning, which prioritizes direct instruction and content delivery, toward student-centered learning that fosters critical thinking, collaboration, and personalized experiences. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and adaptive learning platforms enable customizable educational pathways, enhancing student engagement and autonomy. Educational frameworks increasingly support competency-based assessments and experiential learning, preparing students for dynamic, real-world challenges.
Related Important Terms
Andragogy Shift
The andragogy shift emphasizes student-centered learning, prioritizing adult learners' autonomy, experience, and intrinsic motivation over traditional teacher-centered instruction that relies on direct transmission of knowledge. This approach fosters critical thinking, collaborative problem-solving, and practical application, aligning education with adult learners' needs and real-world contexts.
Hyper-Personalized Learning
Hyper-personalized learning in student-centered education leverages adaptive technologies and real-time data analytics to tailor instruction to individual learners' needs, preferences, and pace, significantly enhancing engagement and outcomes. In contrast, teacher-centered learning often follows a fixed curriculum and uniform pacing, limiting opportunities for personalized feedback and customized learning paths.
Flipped Classroom Model
The flipped classroom model shifts instructional delivery from teacher-centered lectures to student-centered active learning, promoting engagement through pre-class video lectures and in-class collaborative activities. This approach enhances critical thinking, facilitates personalized feedback, and fosters deeper understanding by allowing students to apply concepts in a supportive environment.
Constructivist Pedagogy
Teacher-centered learning prioritizes direct instruction and content delivery, positioning the teacher as the primary authority, whereas student-centered learning, rooted in constructivist pedagogy, emphasizes active learner engagement, collaboration, and knowledge construction through exploration and critical thinking. Constructivist classrooms facilitate personalized learning experiences that adapt to students' prior knowledge and promote deeper understanding by encouraging inquiry, reflection, and problem-solving.
Inquiry-Based Instruction
Inquiry-based instruction in student-centered learning promotes active exploration and critical thinking by encouraging students to ask questions, investigate, and construct knowledge, contrasting with teacher-centered learning that relies on direct instruction and passive reception. Research shows inquiry-based models improve engagement, problem-solving skills, and long-term retention by fostering autonomy and deeper understanding.
Facilitator Role Transition
The facilitator role transition in education shifts from teacher-centered learning, where instructors direct knowledge transfer, to student-centered learning, emphasizing guides who support active learner engagement and critical thinking. This evolution fosters autonomy, collaboration, and personalized learning experiences by prioritizing student agency over traditional authoritative teaching methods.
Voice and Choice
Teacher-centered learning limits student voice and choice by prioritizing instructor-led instruction and standardized content delivery, often resulting in passive learning experiences. In contrast, student-centered learning enhances engagement and motivation by empowering learners with greater autonomy to influence their educational paths and actively participate in decision-making processes.
Self-Regulated Learning
Teacher-centered learning often limits opportunities for self-regulated learning by emphasizing direct instruction and passive student roles, while student-centered learning promotes autonomy, critical thinking, and metacognitive skills essential for effective self-regulation. Research highlights that environments fostering student engagement and responsibility significantly enhance learners' ability to set goals, monitor progress, and adjust strategies independently.
Adaptive Teaching Strategies
Teacher-centered learning often employs adaptive teaching strategies that tailor content delivery to group pacing and curriculum standards, ensuring consistent knowledge acquisition; student-centered learning adapts by personalizing instructional methods to individual learning styles and interests, promoting active engagement and critical thinking development. Adaptive teaching in teacher-centered models emphasizes structured guidance, while in student-centered environments, it prioritizes flexibility to meet diverse learner needs and foster autonomous skill-building.
Guided Autonomy
Guided autonomy in student-centered learning empowers learners to take initiative while benefiting from structured teacher support, enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving skills. In contrast, teacher-centered learning limits autonomy by prioritizing direct instruction and control, potentially restricting student engagement and creativity.
Teacher-centered Learning vs Student-centered Learning Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com