Classroom teaching relies on direct instruction where teachers deliver content during class time, allowing immediate interaction and clarification. Flipped classrooms invert this model by assigning lectures as homework, freeing class time for collaborative activities and deeper engagement with the material. This approach fosters active learning, critical thinking, and personalized support, enhancing overall student comprehension and retention.
Table of Comparison
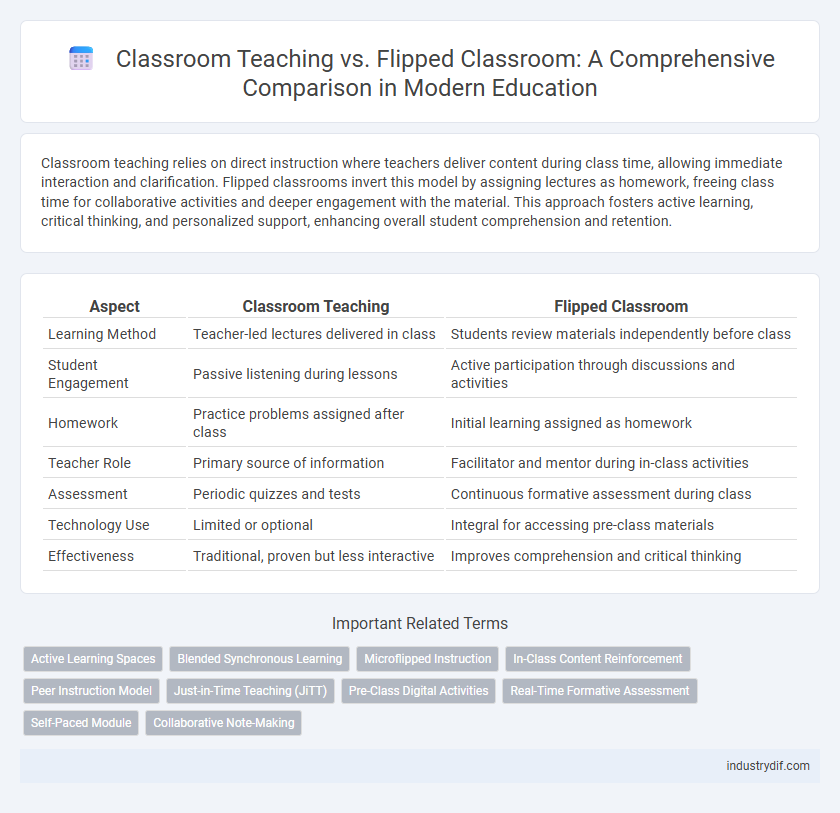
| Aspect | Classroom Teaching | Flipped Classroom |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Method | Teacher-led lectures delivered in class | Students review materials independently before class |
| Student Engagement | Passive listening during lessons | Active participation through discussions and activities |
| Homework | Practice problems assigned after class | Initial learning assigned as homework |
| Teacher Role | Primary source of information | Facilitator and mentor during in-class activities |
| Assessment | Periodic quizzes and tests | Continuous formative assessment during class |
| Technology Use | Limited or optional | Integral for accessing pre-class materials |
| Effectiveness | Traditional, proven but less interactive | Improves comprehension and critical thinking |
Definition of Classroom Teaching
Classroom teaching refers to the traditional instructional method where teachers deliver lessons directly to students in a physical classroom setting, facilitating real-time interaction and immediate feedback. This approach emphasizes structured schedules, curriculum adherence, and face-to-face communication to support learning objectives. It remains a foundational model in education, promoting a controlled environment for guided practice and collaborative activities.
Overview of the Flipped Classroom Model
The flipped classroom model in education reverses traditional teaching by delivering instructional content, often through video lectures, outside of class time, allowing in-class sessions to focus on interactive activities and personalized support. This approach enhances student engagement, promotes active learning, and improves comprehension by shifting passive listening to independent study. Research indicates that flipped classrooms can lead to higher academic performance and better retention compared to conventional lecture-based methods.
Key Differences Between Classroom and Flipped Approaches
Classroom teaching traditionally involves instructor-led lectures where students passively receive information, while flipped classrooms emphasize active learning by having students engage with instructional materials at home prior to class. In flipped approaches, classroom time is dedicated to interactive activities, problem-solving, and personalized guidance, enhancing student engagement and retention. Research shows flipped classrooms improve critical thinking skills and student performance by promoting collaboration and self-paced learning.
Student Engagement in Traditional vs Flipped Classrooms
Student engagement in traditional classrooms often wanes due to passive learning methods that rely heavily on lectures and note-taking. Flipped classrooms enhance student involvement by encouraging active participation through pre-class video materials and interactive in-class activities. Research shows that flipped learning environments increase motivation, critical thinking, and collaboration, leading to higher academic achievement and deeper understanding of the material.
Instructional Strategies and Methods
Classroom teaching typically relies on direct instruction where teachers deliver content through lectures and guided practice, emphasizing real-time interaction and immediate feedback. Flipped classroom methodology inverts this by assigning pre-class materials like videos or readings to build foundational knowledge, allowing in-class time to focus on collaborative activities, problem-solving, and personalized support. This approach enhances student engagement and deeper understanding by shifting the instructional strategies from passive reception to active learning.
Impact on Learning Outcomes
Classroom teaching traditionally relies on direct instruction, which often limits student engagement and active learning, potentially impacting knowledge retention and understanding. Flipped classroom models, by shifting lecture content outside class and dedicating in-person time to interactive activities, enhance critical thinking skills, collaboration, and personalized feedback. Studies indicate flipped classrooms improve academic performance and foster deeper comprehension compared to conventional methods.
Technology Integration in Classroom vs Flipped Models
Technology integration in traditional classroom teaching often involves occasional use of digital tools like projectors and interactive whiteboards, whereas flipped classroom models rely heavily on technology for delivering lectures via videos and online platforms. The flipped model promotes active learning by enabling students to engage with content outside class through multimedia resources, freeing face-to-face time for collaborative activities. This approach harnesses educational technologies such as Learning Management Systems (LMS), video conferencing, and interactive assessments to enhance personalized learning and real-time feedback.
Teacher Roles and Responsibilities
In traditional classroom teaching, the teacher primarily delivers content through lectures and manages student behavior, ensuring comprehension during class time. In contrast, the flipped classroom shifts the teacher's role to a facilitator who guides interactive activities, fosters critical thinking, and provides personalized support as students engage with lecture materials independently. This shift requires teachers to design engaging pre-class content and prepare dynamic in-class exercises that promote active learning and deeper understanding.
Assessment Techniques in Both Approaches
Assessment techniques in traditional classroom teaching primarily involve standardized tests, quizzes, and in-class participation to gauge student understanding. In a flipped classroom, formative assessments such as online quizzes, video reflections, and peer evaluations play a crucial role in monitoring ongoing learning outside of class. Both approaches utilize summative assessments, but flipped classrooms emphasize continuous feedback and active learning metrics to enhance student performance.
Challenges and Best Practices for Implementation
Classroom teaching faces challenges such as limited student engagement and fixed pacing, while flipped classrooms demand reliable technology and student self-discipline for effective learning. Best practices for implementing flipped classrooms include creating clear instructional videos, fostering active in-class discussions, and providing continuous feedback to monitor student progress. Successful adoption requires professional development for educators and structured time management to balance pre-class preparation with interactive classroom activities.
Related Important Terms
Active Learning Spaces
Active learning spaces in flipped classrooms foster student engagement by facilitating collaboration, discussion, and hands-on activities, contrasting with traditional classroom teaching that often centers on passive lecture-based instruction. These dynamic environments leverage technology and flexible seating arrangements to promote critical thinking and personalized learning experiences.
Blended Synchronous Learning
Blended synchronous learning integrates traditional classroom teaching with flipped classroom strategies, allowing real-time interaction between in-person and remote students to enhance engagement and comprehension. This model leverages digital tools for pre-class content delivery and uses synchronous sessions for active discussions, promoting deeper learning through collaboration.
Microflipped Instruction
Microflipped instruction enhances traditional classroom teaching by delivering concise, targeted video lessons outside of class, allowing in-person sessions to focus on active learning and personalized support. This approach increases student engagement and comprehension by combining the benefits of flipped classrooms with microlearning principles, fostering deeper understanding in less time.
In-Class Content Reinforcement
In-class content reinforcement in traditional classroom teaching relies on direct instruction followed by immediate practice and teacher-led clarification, enhancing instant feedback and skill mastery. Flipped classrooms shift initial content delivery outside class, using in-class time for collaborative problem-solving and deeper application, fostering active learning and improved concept retention.
Peer Instruction Model
The Peer Instruction model enhances student engagement and comprehension by encouraging collaborative problem-solving and discussion during class, contrasting with traditional classroom teaching where lectures dominate. This approach leverages peer-to-peer interaction to deepen understanding and improve retention, making it a pivotal strategy in flipped classrooms.
Just-in-Time Teaching (JiTT)
Just-in-Time Teaching (JiTT) integrates pre-class assignments with classroom activities, enhancing student engagement and enabling instructors to tailor lessons based on real-time feedback. This approach contrasts with traditional classroom teaching by shifting content delivery outside class, fostering active learning and deeper comprehension during face-to-face sessions.
Pre-Class Digital Activities
Pre-class digital activities in flipped classrooms, such as video lectures and interactive quizzes, enhance student engagement and knowledge retention compared to traditional classroom teaching where instruction primarily occurs in class. These activities allow students to learn at their own pace, promoting deeper understanding and better preparation for in-class discussions and collaborative problem-solving.
Real-Time Formative Assessment
Real-time formative assessment in traditional classroom teaching often relies on direct teacher observation and immediate feedback during lessons, allowing for timely adjustments to instruction. In a flipped classroom, digital tools enable continuous, data-driven assessment outside of class, empowering educators to tailor in-person sessions based on students' pre-class performance analytics.
Self-Paced Module
Self-paced modules in flipped classrooms enhance personalized learning by allowing students to review instructional content at their own pace, leading to improved comprehension and retention compared to traditional classroom teaching. This flexibility promotes active engagement and enables educators to allocate classroom time for collaborative activities and individualized support.
Collaborative Note-Making
Collaborative note-making in flipped classrooms enhances student engagement and knowledge retention by encouraging active participation and peer-to-peer learning outside traditional lecture times. This method contrasts with classroom teaching, where notes are often individually taken during passive listening, limiting opportunities for immediate clarification and collective knowledge construction.
Classroom Teaching vs Flipped Classroom Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com